Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
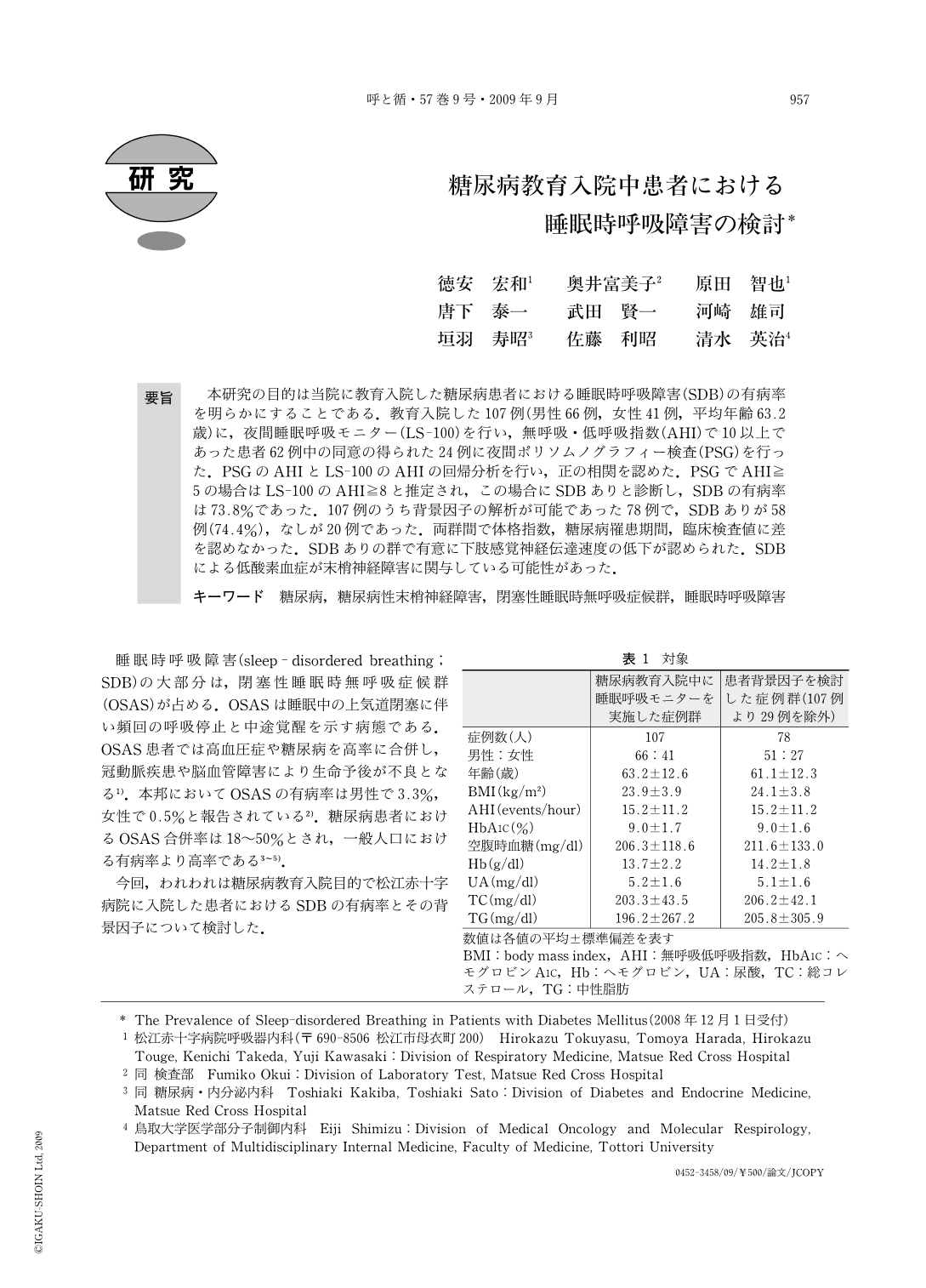
要旨 本研究の目的は当院に教育入院した糖尿病患者における睡眠時呼吸障害(SDB)の有病率を明らかにすることである.教育入院した107例(男性66例,女性41例,平均年齢63.2歳)に,夜間睡眠呼吸モニター(LS-100)を行い,無呼吸・低呼吸指数(AHI)で10以上であった患者62例中の同意の得られた24例に夜間ポリソムノグラフィー検査(PSG)を行った.PSGのAHIとLS-100のAHIの回帰分析を行い,正の相関を認めた.PSGでAHI≧5の場合はLS-100のAHI≧8と推定され,この場合にSDBありと診断し,SDBの有病率は73.8%であった.107例のうち背景因子の解析が可能であった78例で,SDBありが58例(74.4%),なしが20例であった.両群間で体格指数,糖尿病罹患期間,臨床検査値に差を認めなかった.SDBありの群で有意に下肢感覚神経伝達速度の低下が認められた.SDBによる低酸素血症が末梢神経障害に関与している可能性があった.
The purpose of this study was to determine the prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) in 107 diabetic patients, including 66 males and 41 females (mean age, 63.2 years), hospitalized for therapeutic education on diabetes mellitus(DM). Portable polysomnography(PSG)(Pulsleep LS-100; Fukuda Densi Co. Ltd. Japan) was performed on all patients. Next, 24 patients who had an apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of≧10 were subjected to an overnight PSG. Because we observed a positive correlation between the AHI values determined using the LS-100 unit and overnight PSG, it was estimated that AHI of≧5 obtained by overnight PSG, diagnostic criterion for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, was equivalent to AHI of≧8 obtained by LS-100. The prevalence ratio of SDB was 73.8%. Among 107 patinets, 78 patients that we could analyze were then divided into 2 groups depending on whether the AHI values obtained by LS-100 were ≧8 (SDB group; 58 patients) or <8 (non-SDB group; 20 patients). There were no significant differences between the 2 groups with regard to body mass index, the duration of DM, and other laboratory data. The sensory nerve conduction velocity of the sural nerve was significantly lower in the SDB group than that in the non-SDB group. Hypoxemia caused by SDB might have played a role in diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Copyright © 2009, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


