Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
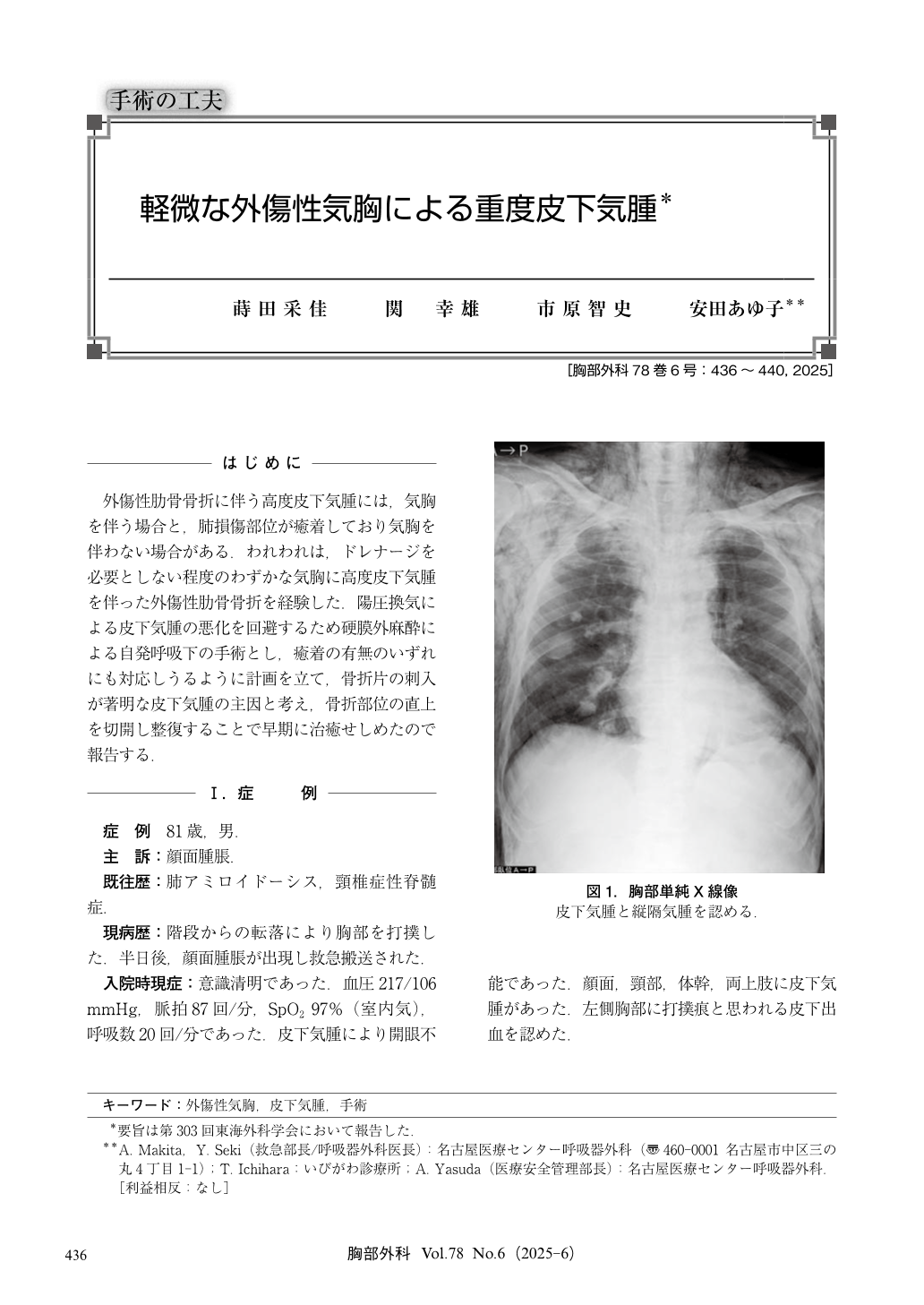
外傷性肋骨骨折に伴う高度皮下気腫には,気胸を伴う場合と,肺損傷部位が癒着しており気胸を伴わない場合がある.われわれは,ドレナージを必要としない程度のわずかな気胸に高度皮下気腫を伴った外傷性肋骨骨折を経験した.陽圧換気による皮下気腫の悪化を回避するため硬膜外麻酔による自発呼吸下の手術とし,癒着の有無のいずれにも対応しうるように計画を立て,骨折片の刺入が著明な皮下気腫の主因と考え,骨折部位の直上を切開し整復することで早期に治癒せしめたので報告する.
An 81-year-old man with chest trauma presented with facial swelling and eyes shut due to subcutaneous emphysema. Computed tomography (CT) scans revealed extensive emphysema from the face to the pelvis, including mediastinal emphysema, fractures of the left 6th and 7th ribs, minor left pneumothorax, and slight hemothorax. Emphysema was likely caused by lung adhesions or fractured bone fragments penetrating the lung. Surgery was performed under epidural anesthesia in the right lateral decubitus position. The 6-cm incision above the fracture site allowed access to the extrapleural cavity. The lung penetration was relieved, and the fractured bones were realigned. Thoracoscopy revealed no adhesions, and two drains were placed. The patient was discharged on postoperative day nine. Although transfer to general anesthesia was considered, the surgery was successfully completed under epidural anesthesia. Epidural anesthesia may be a viable option for patients with severe subcutaneous emphysema, thereby avoiding the risks associated with positive pressure ventilation.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2025