Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
- サイト内被引用 Cited by
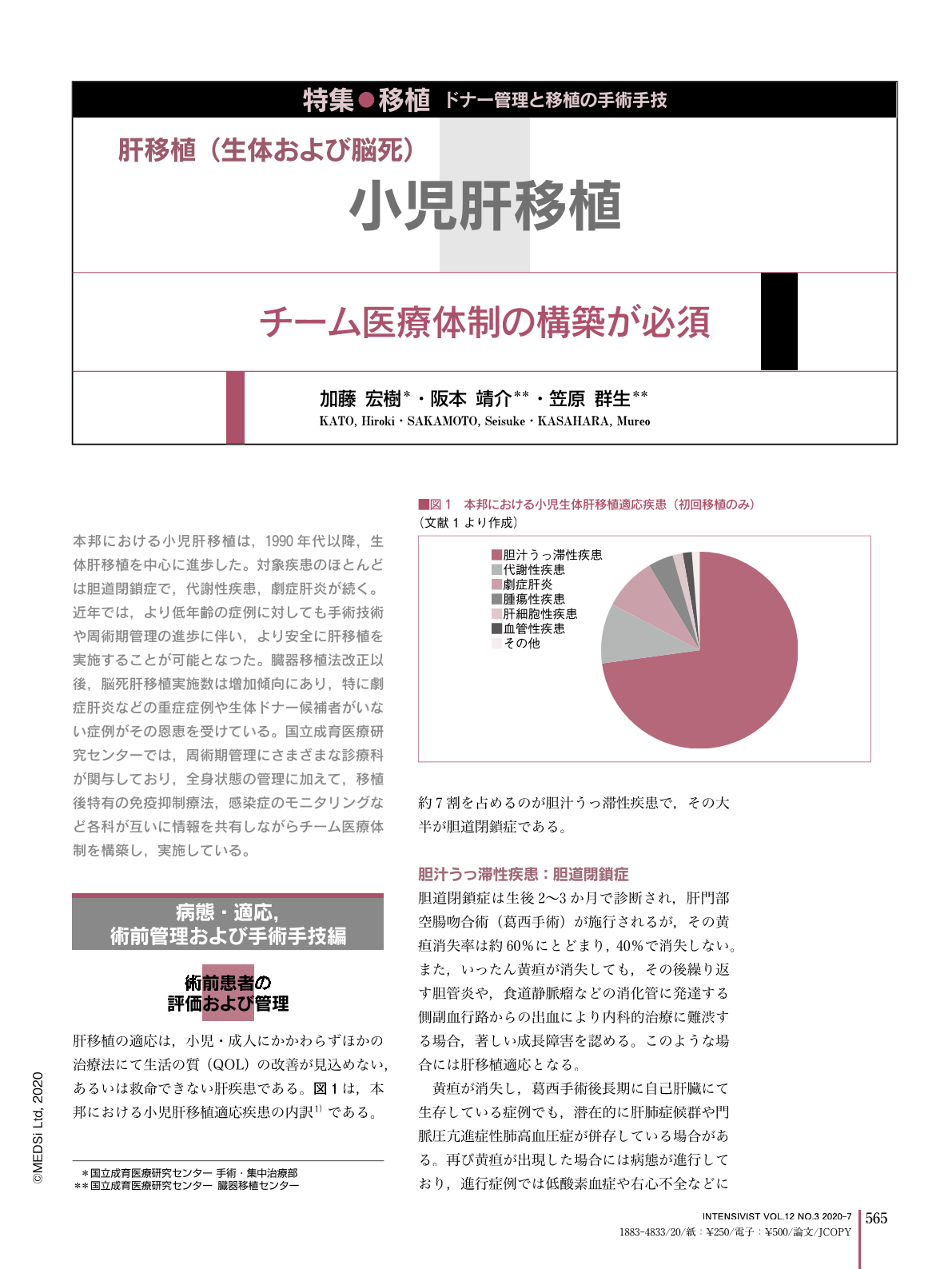
本邦における小児肝移植は,1990年代以降,生体肝移植を中心に進歩した。対象疾患のほとんどは胆道閉鎖症で,代謝性疾患,劇症肝炎が続く。近年では,より低年齢の症例に対しても手術技術や周術期管理の進歩に伴い,より安全に肝移植を実施することが可能となった。臓器移植法改正以後,脳死肝移植実施数は増加傾向にあり,特に劇症肝炎などの重症症例や生体ドナー候補者がいない症例がその恩恵を受けている。国立成育医療研究センターでは,周術期管理にさまざまな診療科が関与しており,全身状態の管理に加えて,移植後特有の免疫抑制療法,感染症のモニタリングなど各科が互いに情報を共有しながらチーム医療体制を構築し,実施している。
Pediatric liver transplantation (LT) has been developing in Japan since living donor LT was initiated in the 1990s. The underlying liver diseases in patients undergoing LT include biliary atresia, followed by metabolic liver disease and fulminant hepatic failure. In recent years, LT is safely performed in small infants due to advances in surgical technique and perioperative management. Deceased donor LT has been also used in pediatric patients, especially in critically ill patients. The care of these patients includes medical specialists and healthcare professionals dedicated to pediatric care and others to manage a variety of issues including immunosuppression and infection control, as a team.
Copyright © 2020, MEDICAL SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, LTD. All rights reserved.


