Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
- サイト内被引用 Cited by
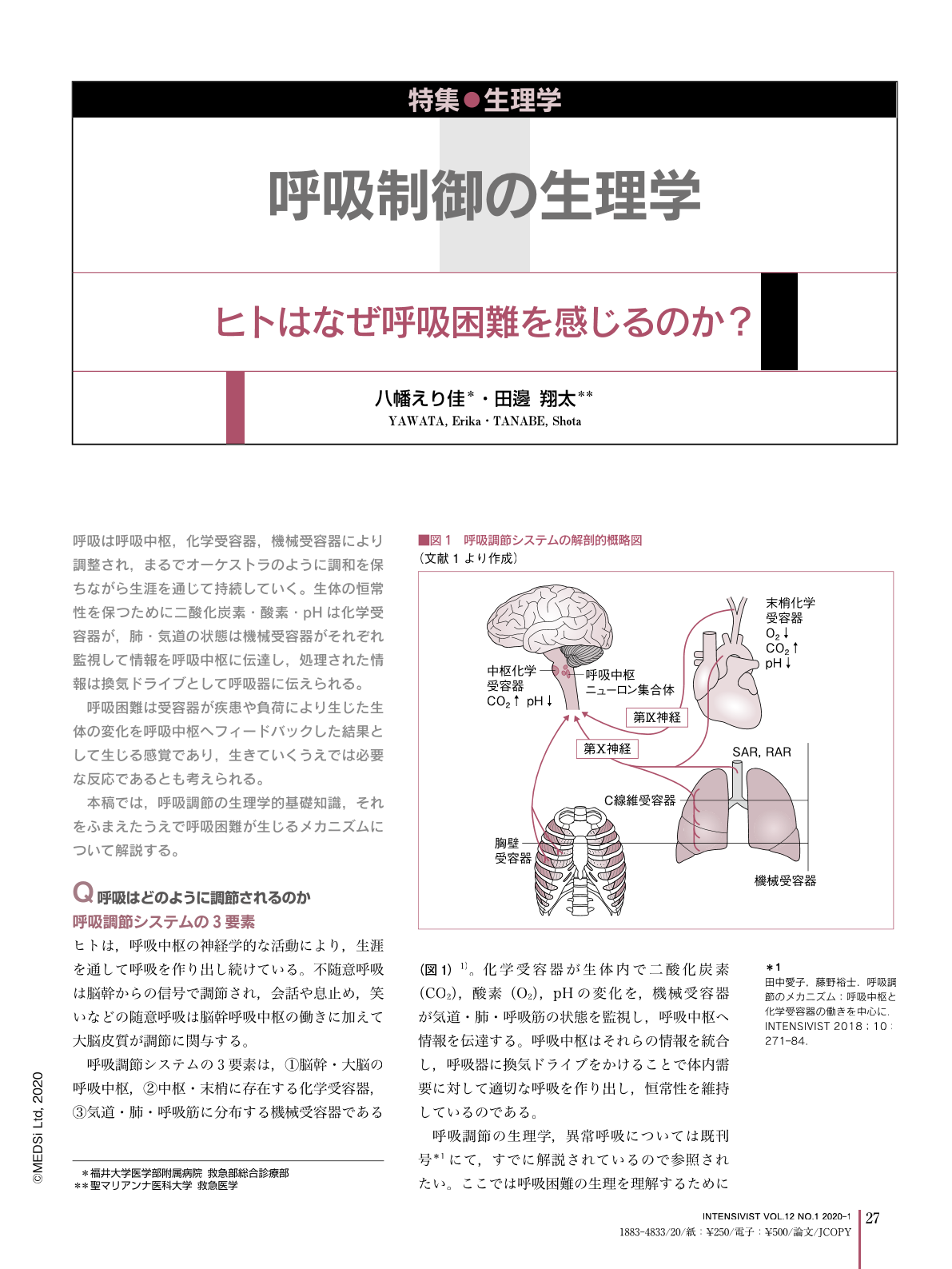
呼吸は呼吸中枢,化学受容器,機械受容器により調整され,まるでオーケストラのように調和を保ちながら生涯を通じて持続していく。生体の恒常性を保つために二酸化炭素・酸素・pHは化学受容器が,肺・気道の状態は機械受容器がそれぞれ監視して情報を呼吸中枢に伝達し,処理された情報は換気ドライブとして呼吸器に伝えられる。
呼吸困難は受容器が疾患や負荷により生じた生体の変化を呼吸中枢へフィードバックした結果として生じる感覚であり,生きていくうえでは必要な反応であるとも考えられる。
本稿では,呼吸調節の生理学的基礎知識,それをふまえたうえで呼吸困難が生じるメカニズムについて解説する。
The components of respiratory control include a neural network in the respiratory center, chemoreceptors and mechanoreceptors. Respiratory rhythm and ventilation are generated by the brainstem extending from the pons to the lower medulla. Chemoreceptors sense changes in CO2, O2 and pH, then the afferent signals from the chemoreceptors travel to the brainstem via the vagus nerves. Sensory information regarding bronchoconstriction, pulmonary stretch, and chest wall muscular action is sent from mechanoreceptors to the brainstem. Breathing is regulated to maintain homeostasis in the blood and tissues. Dyspnea is caused by a mismatch between motor commands and incoming afferent information from sensory receptors and plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis. We describe the pathophysiology of respiratory control to better understand dyspnea,in addition to the mechanism of dyspnea.
Copyright © 2020, MEDICAL SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, LTD. All rights reserved.


