Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
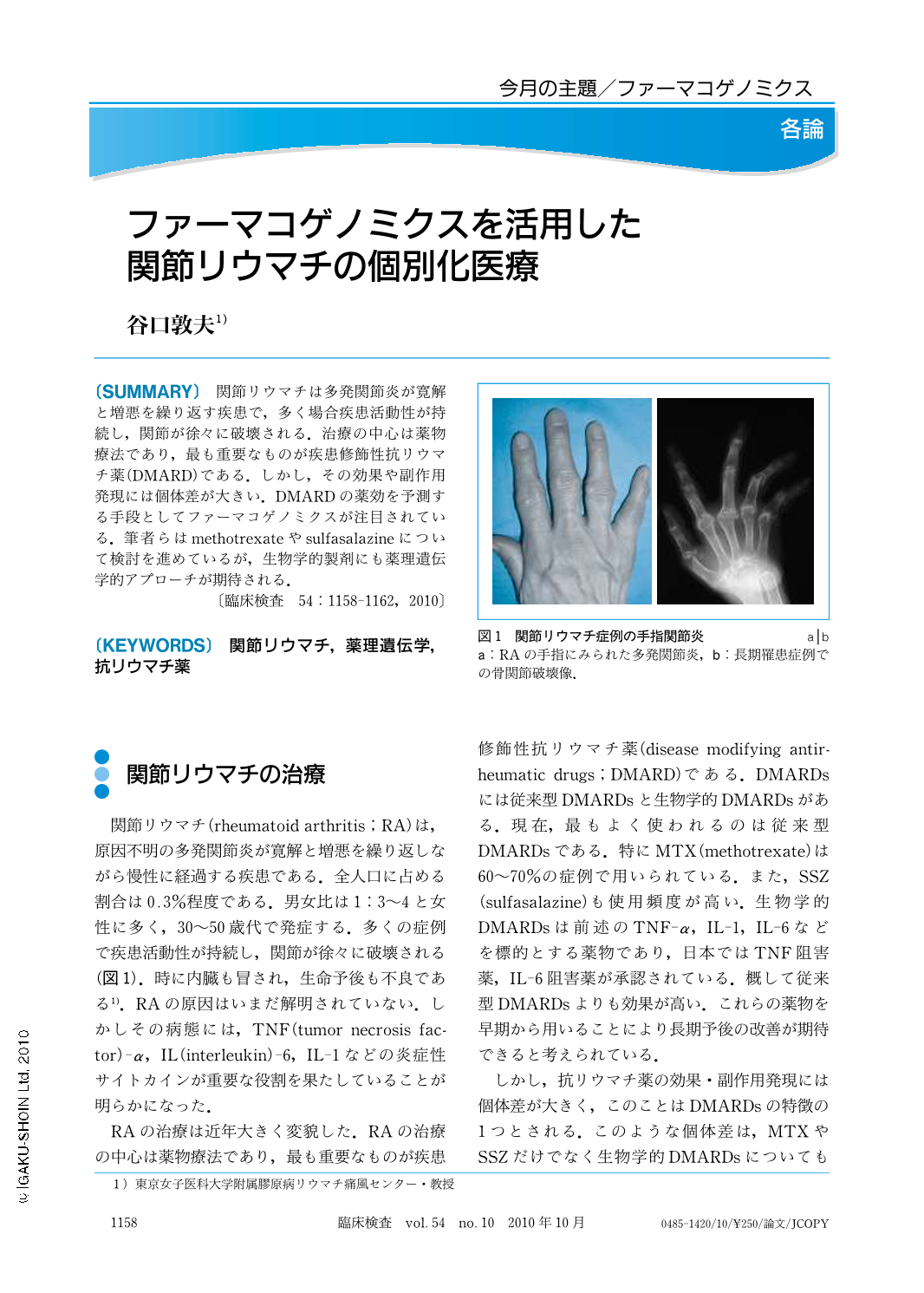
関節リウマチは多発関節炎が寛解と増悪を繰り返す疾患で,多く場合疾患活動性が持続し,関節が徐々に破壊される.治療の中心は薬物療法であり,最も重要なものが疾患修飾性抗リウマチ薬(DMARD)である.しかし,その効果や副作用発現には個体差が大きい.DMARDの薬効を予測する手段としてファーマコゲノミクスが注目されている.筆者らはmethotrexateやsulfasalazineについて検討を進めているが,生物学的製剤にも薬理遺伝学的アプローチが期待される.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease. The inflammatory process of the joint destroys articular architecture and causes a significant disability. The efficacy of disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs is widely accepted. However, the outcome of the treatment with these agents is known to vary among patients. the pharmacogenomic studies on methotrexate, sulfasalazine and tumor necrosis factor-ainhibitors have been reported. These investigations suggest that the pharmacogenomic approach is useful for the treatment of RA although there are points to be considered before the translation of the pharmacogenomic date into clinical practice.
Copyright © 2010, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


