Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
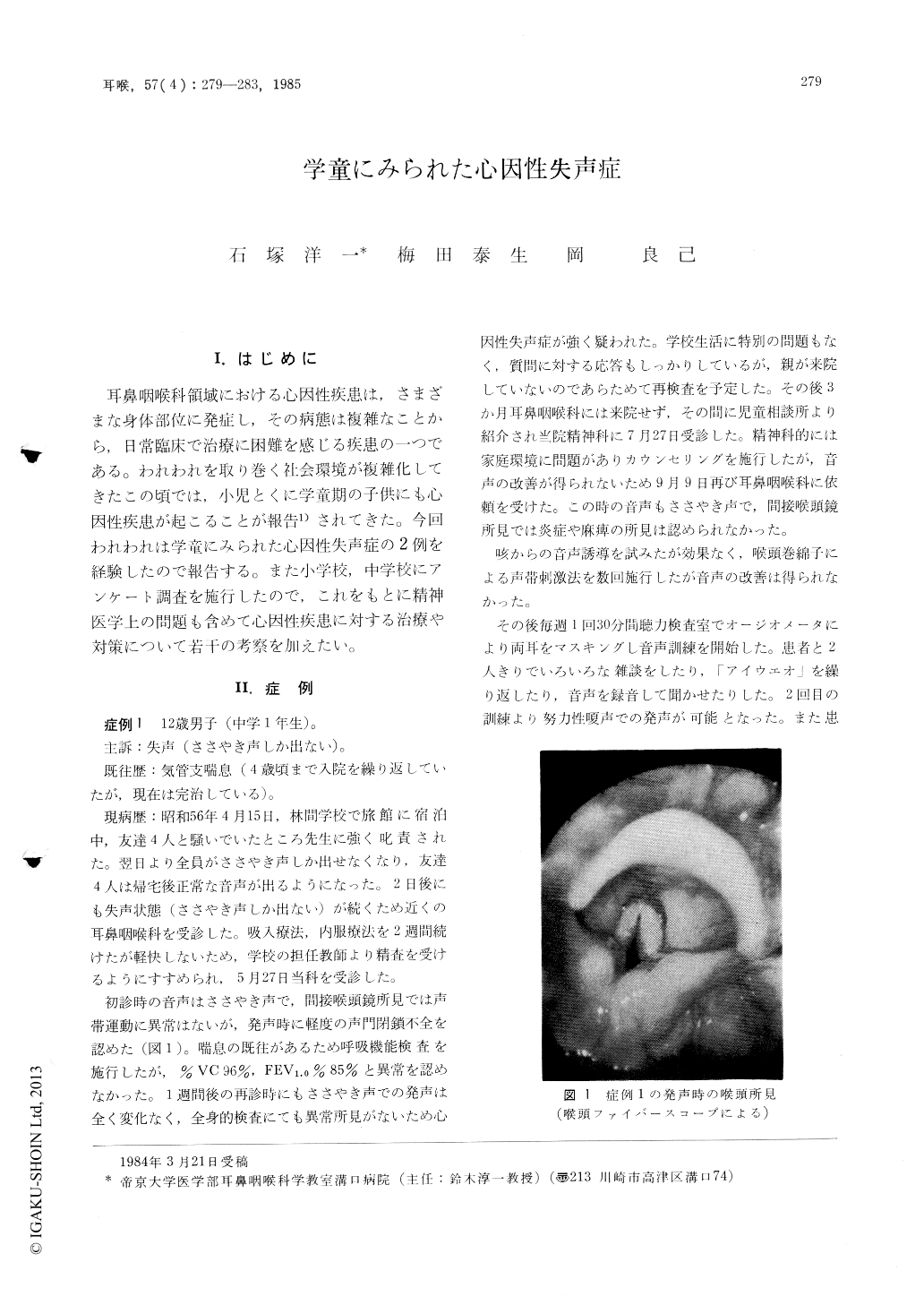
耳鼻咽喉科領域における心因性疾患は,さまざまな身体部位に発症し,その病態は複雑なことから,日常臨床で治療に困難を感じる疾患の一つである。われわれを取り巻く社会環境が複雑化してきたこの頃では,小児とくに学童期の子供にも心因性疾患が起こることが報告1)されてきた。今回われわれは学童にみられた心因性失声症の2例を経験したので報告する。また小学校,中学校にアンケート調査を施行したので,これをもとに精神医学上の問題も含めて心因性疾患に対する治療や対策について若干の考察を加えたい。
Two cases of psychogenic aphonia in children were reported. A 12-year-old boy became aphonic after severe scold by a school teacher. His parents were divorced and it is assumed that he became aphonic because the complex familial environment such as a fatherless family caused psychogenic factors. By voice training connected with mental therapy he recovered in 2 months. A 13-year-old boy became aphonic after severe scold by his father. The aphonia was thought to be the result of refusal reaction from introvert character. He was strongly suspected as having a psychogenic reaction and examined by a psychiatrist, and treated with psychotropic drugs. Psychogenic aphonia should be clarified its psychogenic reaction in patients' background. A close connection of communications with patients and long-term therapies are necessary.
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


