Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
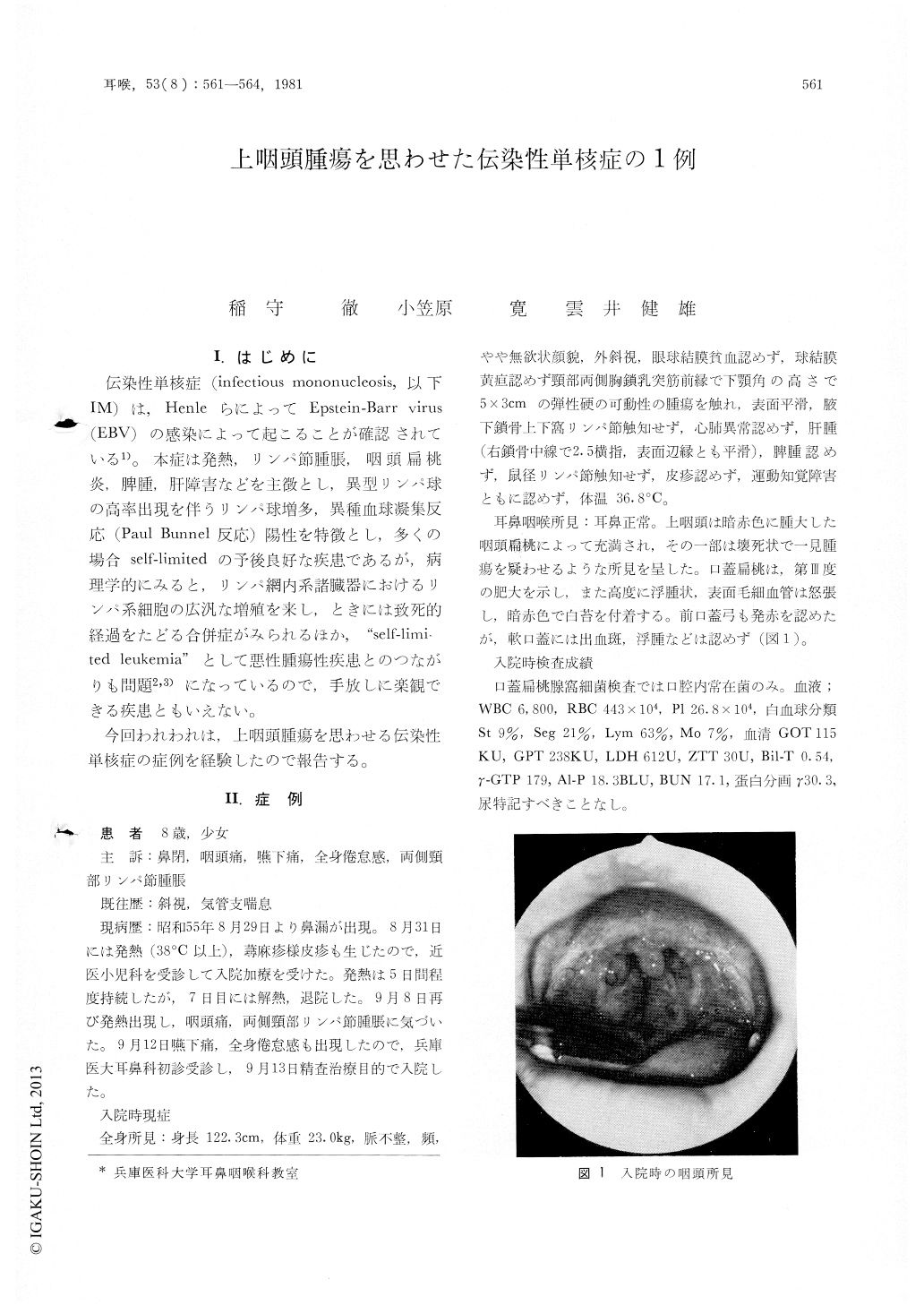
伝染性単核症(infectious mononucleosis,以下IM)は,HenleらによってEpstein-Barr virus(EBV)の感染によって起こることが確認されている1)。本症は発熱,リンパ節腫脹,咽頭扁桃炎,脾腫,肝障害などを主徴とし,異型リンパ球の高率出現を伴うリンパ球増多,異種血球凝集反応(Paul Bunnel反応)陽性を特徴とし,多くの場合self-limitedの予後良好な疾患であるが,病理学的にみると,リンパ網内系諸臓器におけるリンパ系細胞の広汎な増殖を来し,ときには致死的経過をたどる合併症がみられるほか,"self-limited leukemia"として悪性腫瘍性疾患とのつながりも問題2,3)になっているので,手放しに楽観できる疾患ともいえない。
今回われわれは,上咽頭腫瘍を思わせる伝染性単核症の症例を経験したので報告する。
A 8-year-old girl developed fever of 38℃, progressive dysphagia and severe nasal obstruction.
Examination of the oropharynx showed inflammed pharyngeal mucosa with marked enlargement of the tonsils covered with exudate. Nasopharyngeal examination showed markedly enlarged and inflammed adenoids with partial necrosis. Bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy and hepatomegaly were found. Leucocyte count was 6,800/mm3 with 63% lymphocytes and many atypical lymphocytes were seen. On the fifth day of admission, Paul-Bunnel test was positive (titre 1,792) and Monospot test was positive with specific Davidsohn reaction. She was treated conservatively with intravenous fluid administration, and she was gradually improved symptomatically and the tonsils, adenoids and liver returned to normal size.
The diagnostic significance of infectious mononucleosis in E.N.T. practice was also discussed.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


