- 有料閲覧
- 文献概要
- 1ページ目
1.重曹注射の発見 船酔や乗物酔など動揺によつておこる疾患は,従来一般には動揺病,更に嚴格には加速度病9)と呼ばれ,これが発生に内耳の耳石器官が主役を演ずることは,すでに幾多の実験によつて明らかにされている。従来本疾患の対策としては,アトロピン,バルビタールの類や抗ヒスタミン剤が試みられるにすぎなかつたが,1947年長谷川8)によつて発表せられた重曹注射は正に画期的な方法として迎えられ,藤崎3)(20例),豊島33)(21例),古代16)(72例),牟田22)(100例)の臨床実験により効果が確認せられるに至つた。
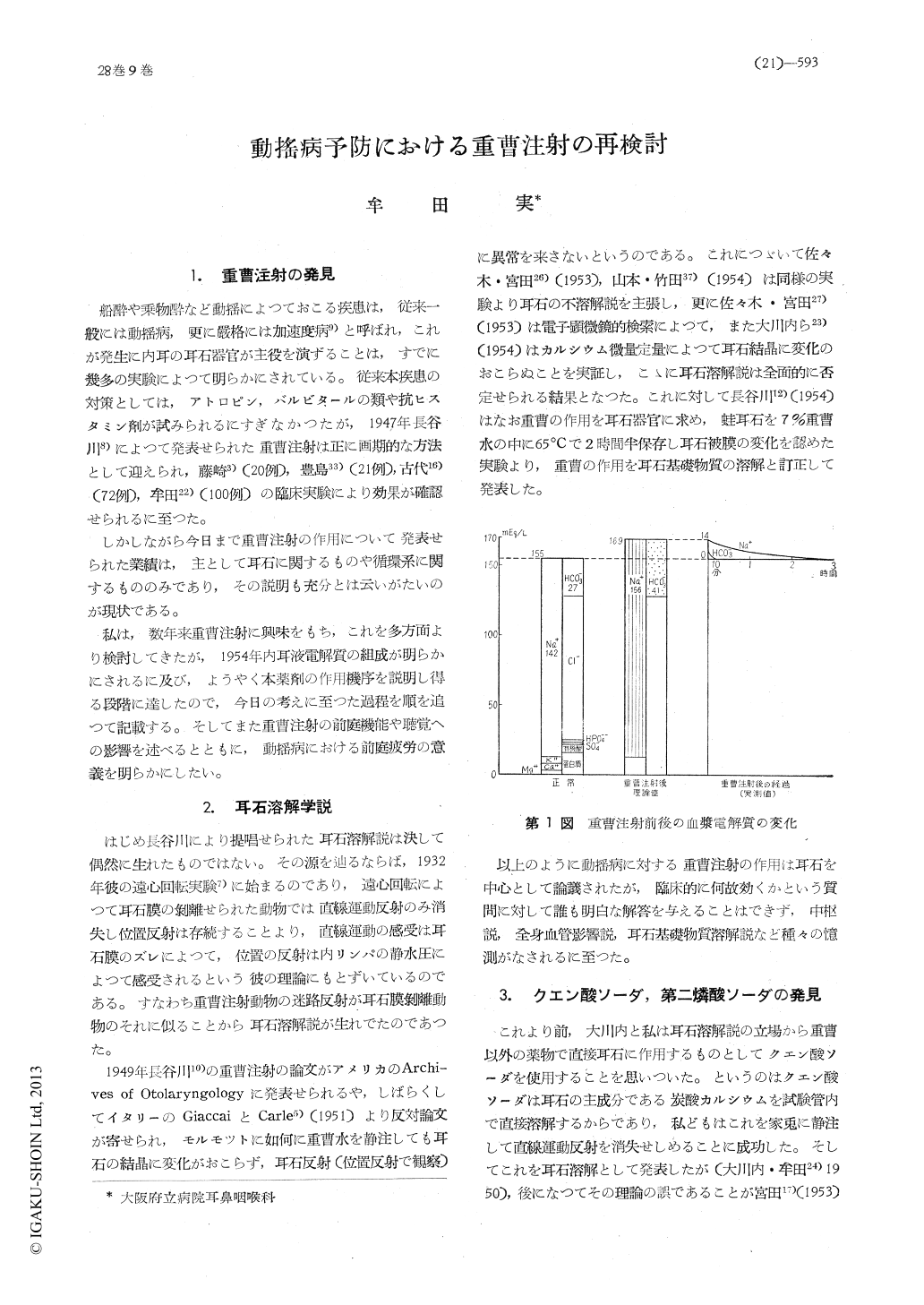
しかしながら今日まで重曹注射の作用について発表せられた業績は,主として耳石に関するものや循環系に関するもののみであり,その説明も充分とは云いがたいのが現状である。
That Na ion concentration is increased and metabolic alkalosis is produced in the blood stre-am when sodium bicarbonate solution is admi-nistered intravenously are facts that have been established. For this reason the circulatory K ion concentration would be decreased with conse-quent depressive effect on the vestibular func-tion. The mechanism by which sodium bicarbo-nate solution becoming effective towards allay-ing of symptoms of motion sickness may be explained by the element, vestibular fatigue. The action of sodium bicarbonate solution is found to be a depressant not only to otolithic organs but also to cristae and Corti's organ as well. To the agents that might cause decrease of K ion concentration in the endolymph such as, sodium bicarbonate, sodium sulphate, sodium citrate and atropine, the author proposes the term, endolymphatic inner ear depressant, to be applied.
Copyright © 1956, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


