- 有料閲覧
- 文献概要
- 1ページ目
緒言
ジフテリアの流行を決定ずけるものは,病原菌の発育増殖力や毒素産生力の他に,人体の免疫乃至抵抗力,社会経済的条件などの複雑な因子の函数であると見做すことが出来る。然し,我々実地医家は,むしろ流行伝播の真相を手近かに知ることに関心を抱きやすい。例えば,患者の発生が一都市において,如何に分布するかを知ることなどは,流行の真相解明の一助ともなり得るのであるが,寡聞にも,我が国ジフテリアの文献中,この点に論及したものは甚だ少ないようである。
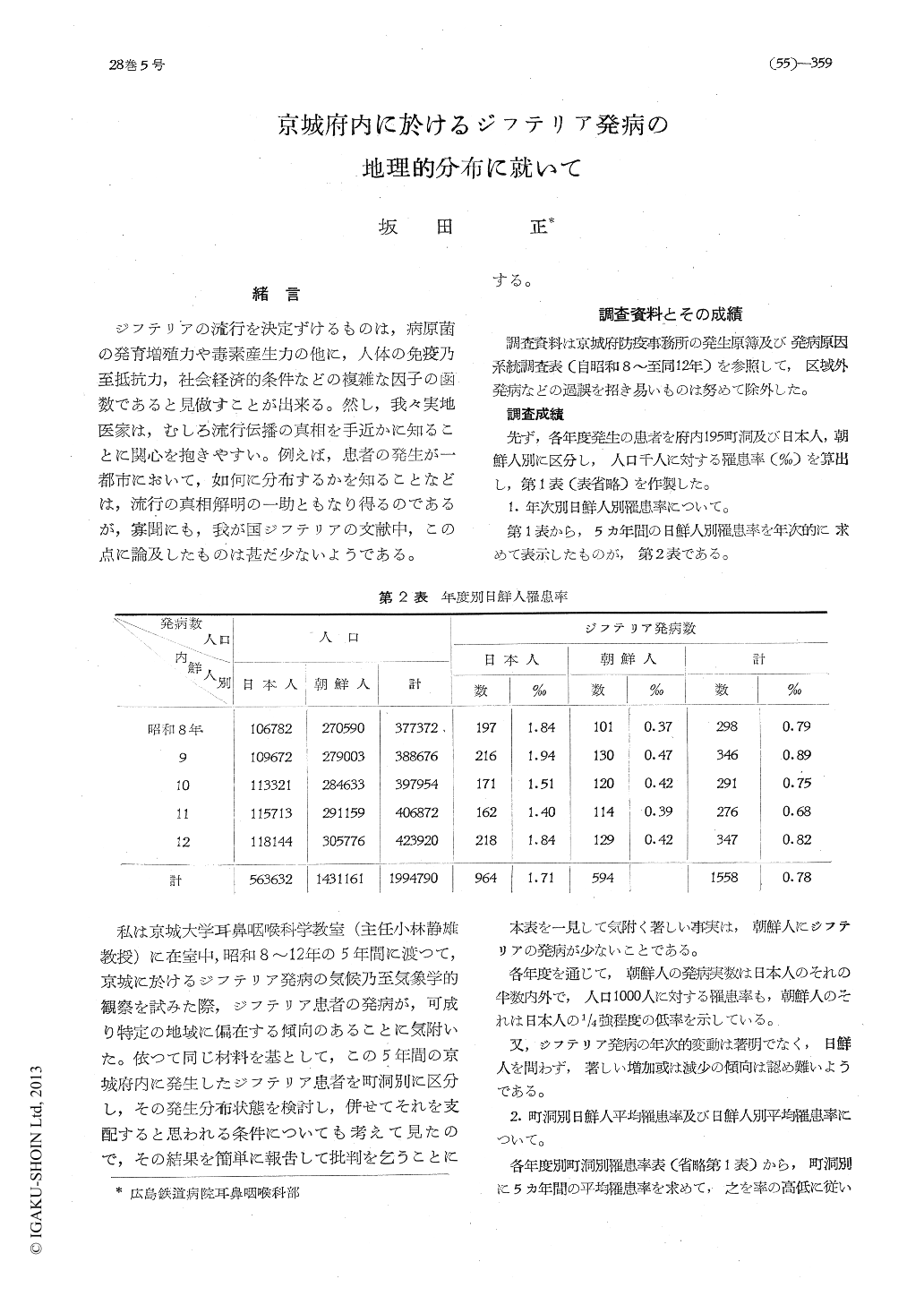
私は京城大学耳鼻咽喉科学教室(主任小林静雄教授)に在室中,昭和8〜12年の5年間に渡つて,京城に於けるジフテリア発病の気候乃至気象学的観察を試みた際,ジフテリア患者の発病が,可成り特定の地域に偏在する傾向のあることに気附いた。依つて同じ材料を基として,この5年間の京城府内に発生したジフテリア患者を町洞別に区分し,その発生分布状態を検討し,併せてそれを支配すると思われる条件についても考えて見たので,その結果を簡単に報告して批判を乞うことにする。
Sakata presents a statistical review of diph-theria mobidity gathered from the record of cases reported to the Department of Infectious Disease Control at Seoul Korea during the per-iod of 4 years, 1933 to 1936. It showed that the incidence of disease occurring among the Japa-nese 1.7% to be exceeding that of the Korea-ns 0.7%; and geographically the distribution in numbers in some area exceeded those of others. It appeared that in few localities the disease existed endemically without causing actual mor-bidity among its residents. With environmen-tal influence, it seemed that among the Japa-nese who lived in a mixed abode with the Kor-ean populace the incidence of disease appeared to be higher, 2.9%, as against 1.9% with those who lived in sections that were purely Japa-nese.
Copyright © 1956, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


