Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
梅毒患者数は社会的背景と鋭敏に反応し,とくに戦争によつて大きく左右されることはよく知られている。最近でも第2次大戦終戦後の急激な増加は驚異的なものであつた。その後世相の安定するに従い,またペニシリンの登場によつて,顕症梅毒はほとんどあとを絶つにいたつたのであるが,昭和35年項より再び早期梅毒患者をみるようになり,その後次第に増加の傾向を示している。今梅毒,軟下疳の地理的分布の実態について考えてみると,はなはだ興味深い問題であると同時に今後の性病対策の上からいつても非常に重要な点であると考える。今回西日本各地の臨床医の協力の下に,昭和40年7月より41年6月迄の1年間にわたり報告してもらつた資料に基いて検討考察を加えたので報告する。
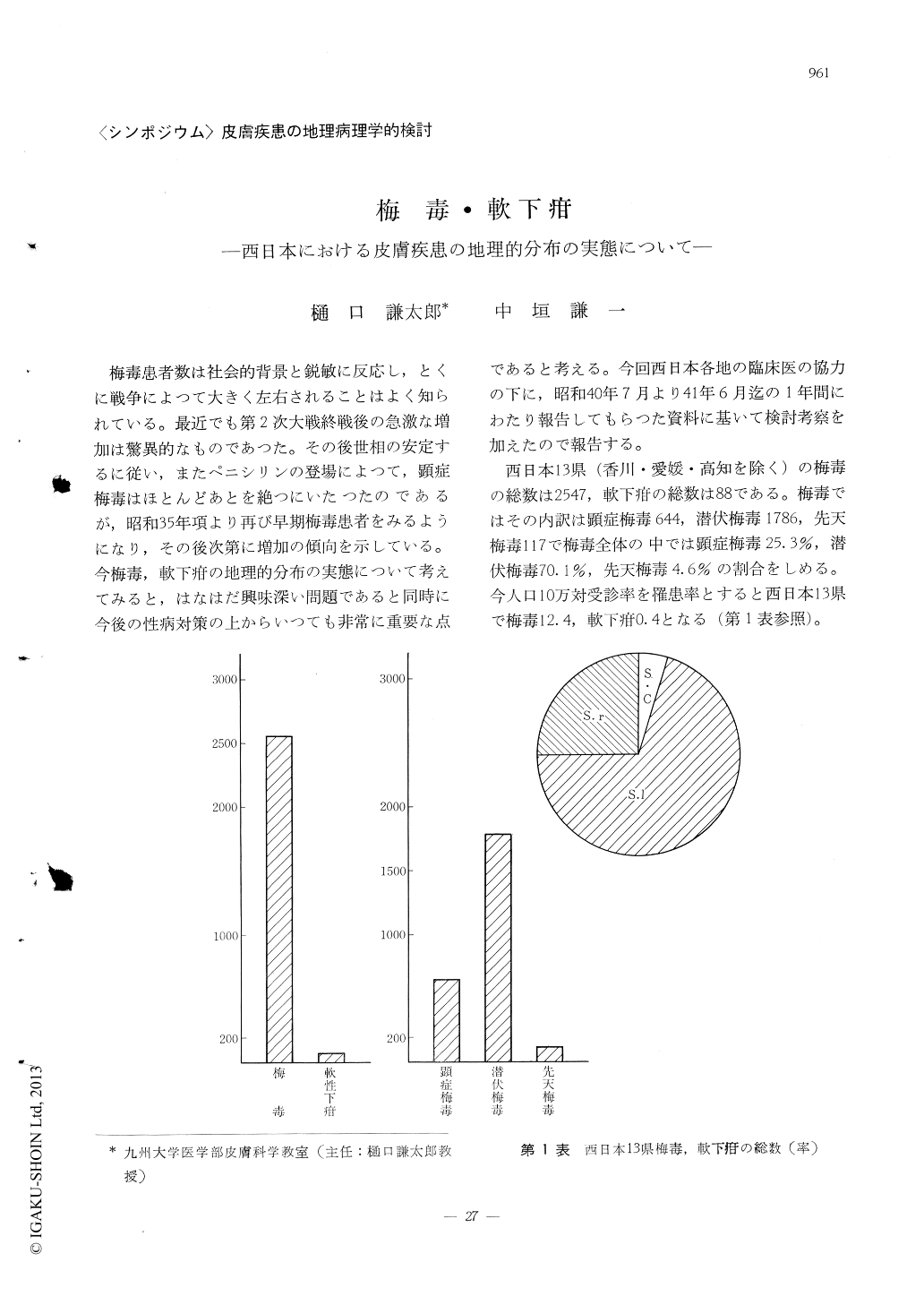
西日本13県(香川・愛媛・高知を除く)の梅毒の総数は2547,軟下疳の総数は88である。梅毒ではその内訳は顕症梅毒644,潜伏梅毒1786,先天梅毒117で梅毒全体の中では顕症梅毒25.3%,潜伏梅毒70.1%,先天梅毒4.6%の割合をしめる。今人口10万対受診率を罹患率とすると西日本13県で梅毒12.4,軟下疳0.4となる(第1表参照)。
Statistic studies on syphilis and chancroid in 13 prefectures of the west Japan for 1 year (from July of 1965 to June of 1966) were performed.
Total number of syphilis was 2547 ……… syphilis with lesion (644), latent syphilis (1786), and congenital syphilis (117). Total number of chancroid was 88.
Incidence ratio (number of patient per 105 population) of syphilis and chancroid was 12.4 and 0.4 respectively in these prefectures.
Total number and incidence ratio of syphilis and chancroid were larger in the urban area than in the rural. Those were also higher in the coastal than in the mountainous arca.
Copyright © 1967, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


