Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
良性頭蓋内圧亢進症(benign intracranial hyperten—sion)はpseudotumor cerebriともよばれ頭蓋内に占拠性病変が存在しないにもかかわらず頭蓋内圧亢進症状を示す症候群である.特異的な所見に乏しいため診断はしばしば因難であるが,今回われわれは頭蓋内圧連続測定が診断および治療に有用であった1例を経験したので報告する.
The authors report a case of benign intracranial hypertension (BIH) treated with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt.
A 62-year-old man was referred to the Kobe City General Hospital with several episodes of transient visual obscuration. Neurological examination on admis-sion revealed bilateral papilledema and a right lower quadrantic homonymous hemianopsia. Computed tomography (CT) showed normalized ventricles and a low-density area in the left occipital lobe without mass effects. From the findings of magnetic resonance im-ages (MRIs) the occipital lesion was diagnosed as a chronic intracerebral hematoma. Because the hematoma did not show mass effects, BIH was suspected to be re-sponsible for the papilledema. In spite of intravenous administration of dexamethasone and glycerol for a week, a lumbar puncture showed an opening pressure of 360mm H2O. Several subsequent lumbar punctures failed to improve intracranial hypertension. The mean opening pressure of the last 6 punctures was 392mm H2O. The mean terminal pressure dropped to 32mm H2O after removal of 10ml of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). A spinal subarachnoid drainage was inserted at the level of L4-L5 interspace for continuous CSF pres-sure monitoring. The mean CSF pressure ranged from 20 to 40mmHg. The continuous recording showed typical B waves frequently and plateau waves (A waves) occasionally. Removal of only 8ml of CSF caused significant pressure reduction immediately. Then, pressure returned to the predrainage level about 35 minutes later. These findings supported the diagno-sis of BIH. A ventriculoperitoneal shunt was inserted, which resulted in rapid and complete resolution of the papilledema. Postoperative CSF monitoring returned to normal pressure and waves.
This case emphasizes the usefulness of continuousCSF pressure recording for the diagnosis and subse-quent therapy of BIH.
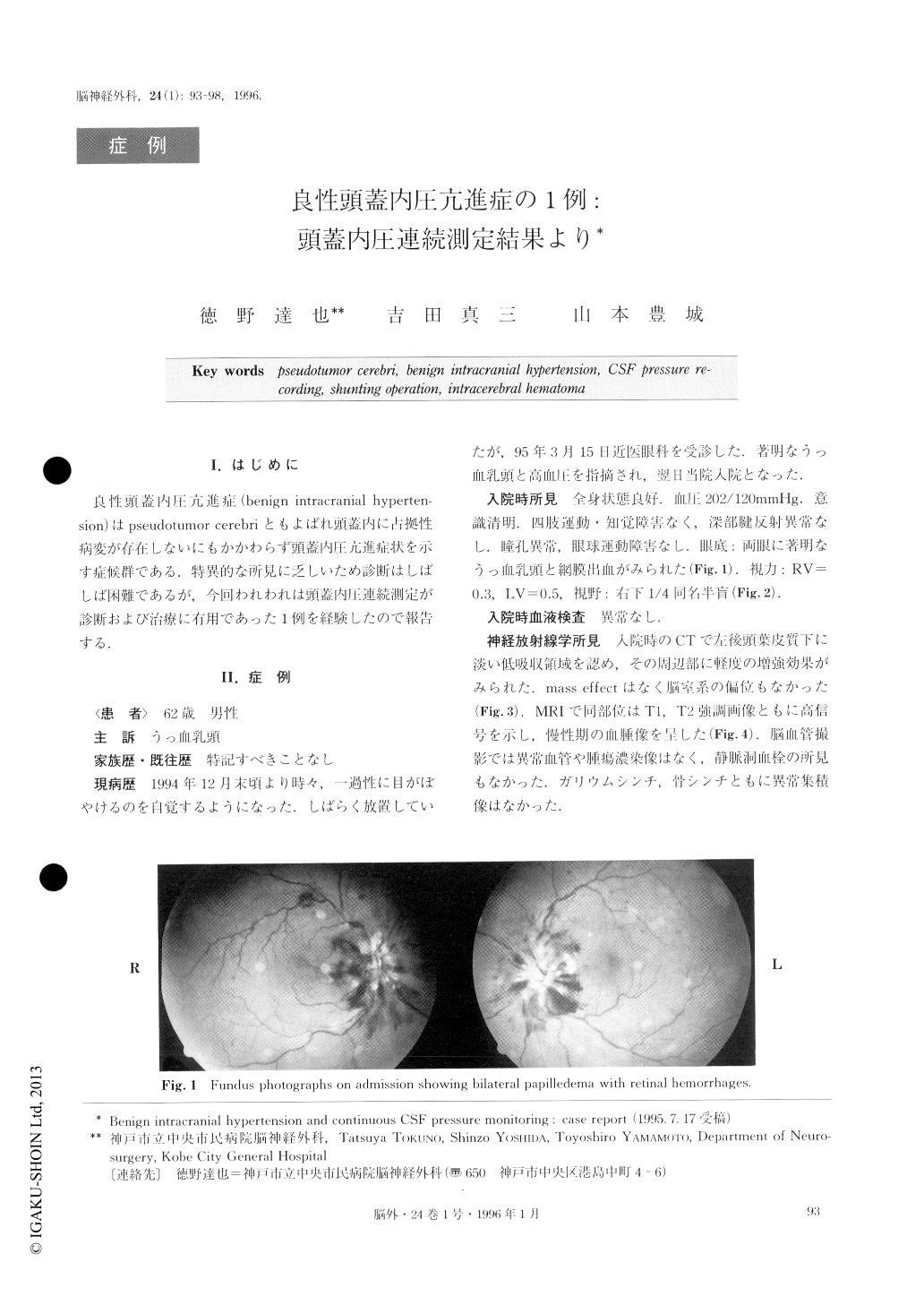
Copyright © 1996, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


