Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
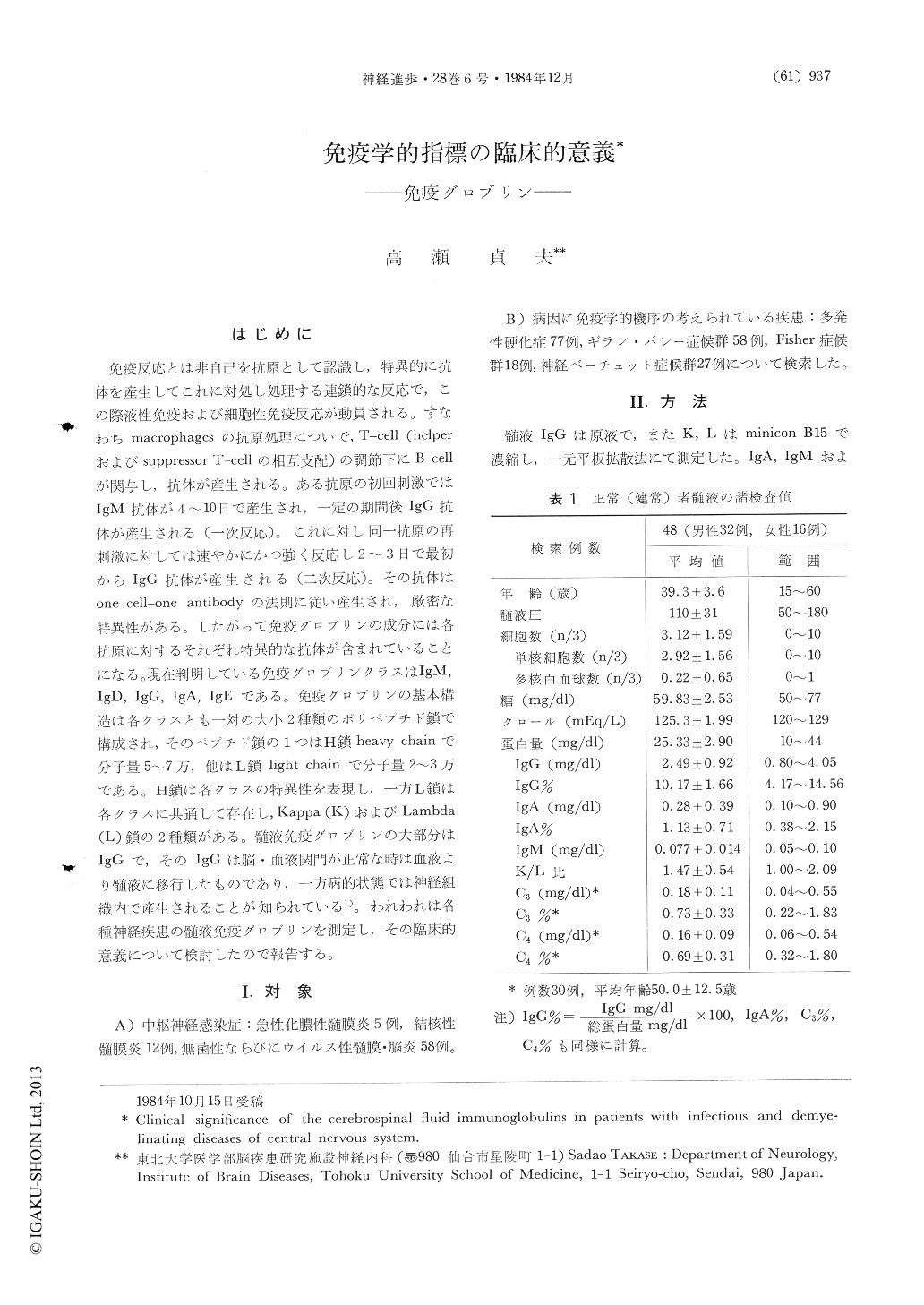
はじめに
免疫反応とは非自己を抗原として認識し,特異的に抗体を産生してこれに対処し処理する連鎖的な反応で,この際液性免疫および細胞性免疫反応が動員される。すなわちmacrophagesの抗原処理についで,T-cell(helperおよびsuppressor T-cellの相互支配)の調節下にB-cellが関与し,抗体が産生される。ある抗原の初回刺激ではIgM抗体が4〜10日で産生され,一定の期間後IgG抗体が産生される(一次反応)。これに対し同一抗原の再刺激に対しては速やかにかつ強く反応し2〜3日で最初からIgG抗体が産生される(二次反応)。その抗体はone cell-one antibodyの法則に従い産生され,厳密な特異性がある。したがって免疫グロブリンの成分には各抗原に対するそれぞれ特異的な抗体が含まれていることになる。現在判明している免疫グロブリンクラスはIgM,IgD,IgG,IgA,IgEである。免疫グロブリンの基本構造は各クラスとも一対の大小2種類のポリペプチド鎖で構成され,そのペプチド鎖の1つはH鎖heavy chainで分子量5〜7万,他はL鎖light chainで分子量2〜3万である。H鎖は各クラスの特異性を表現し,一方L鎖は各クラスに共通して存在し,Kappa(K)およびLambda(L)鎖の2種類がある。
The significance of immunoglobulins was studied in the infection of the central nervous system, demyelinating diseases and neuro-Behcet's syndrome.
(Method)
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimens were obtained from patients with each disorders and the relationship between these data and clinical courses of each disorders was studied. IgG and IgA were determined by immunodiflusion method. IgM, C3 and C4 were determined by Laser nephelometry. The ratio of K/L was examined by immunodiffusion method using concentrated CSF specimens.
(Results)
Copyright © 1984, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


