Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.発作発射活動と細胞内電位
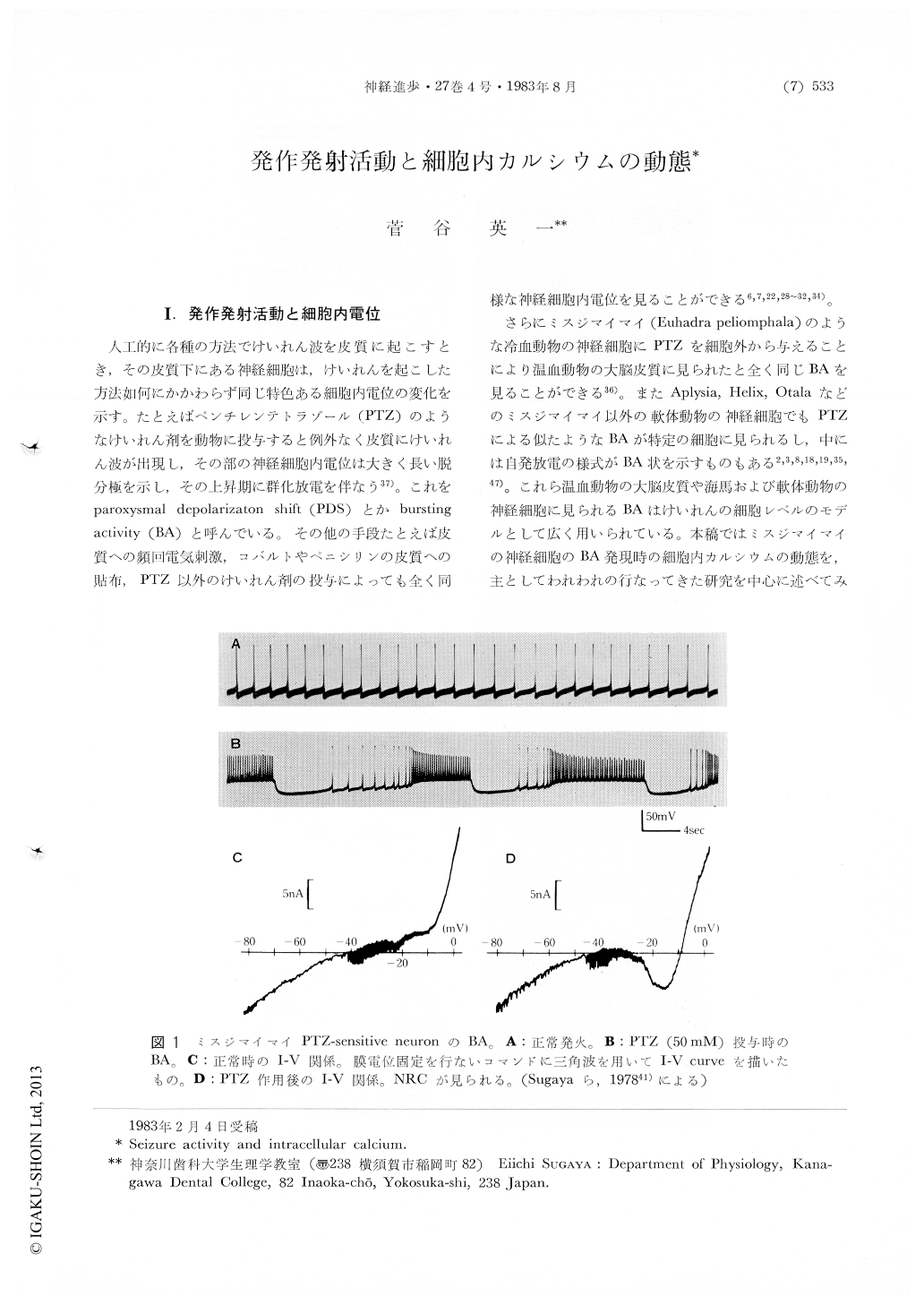
人工的に各種の方法でけいれん波を皮質に起こすとき,その皮質下にある神経細胞は,けいれんを起こした力法如何にかかわらず同じ特色ある細胞内電位の変化を示す。たとえばペンチレンテトラゾール(PTZ)のようなけいれん剤を動物に投与すると例外なく皮質にけいれん波が出現し,その部の神経細胞内電位は大きく長い脱分極を示し,その上昇期に群化放電を伴なう37)。これをparoxysmal depolarizaton shift(PDS)とかburstingactivity(BA)と呼んでいる。その他の手段たとえば皮質への頻回電気刺激,コバルトやペニシリンの皮質への貼布,PTZ以外のけいれん剤の投与によっても全く同様な神経細胞内電位を見ることができる6,7,22,28〜32,34)。
さらにミスジマイマイ(Euhadra peliomphala)のような冷血動物の神経細胞にPTZを細胞外から与えることにより温血動物の大脳皮質に見られたと全く同じBAを見ることができる36)。またAplysia,Helix,Otalaなどのミスジマイマイ以外の軟体動物の神経細胞でもPTZによる似たようなBAが特定の細胞に見られるし,中には自発放電の様式がBA状を示すものもある2,3,8,18,19,35,47)。これら温血動物の大脳皮質や海馬および軟体動物の神経細胞に見られるBAはけいれんの細胞レベルのモデルとして広く用いられている。
Summary
In the case of seizure discharge, the mammalian cerebral cortical neuron shows a characteristic intracellular potential change, i.e. a long-lasting huge depolarization shift with a burst-like action potential on its rising phase coincident with the cortical surface seizure wave. This is called bursting activity (BA) or paroxysmal depolarization shift (PDS). The same intracellular potential change, BA, can be observed in the isolated special neurons of the Japanese land snail, Euhadra peliomphala, when pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) is applied extracellularly.
Copyright © 1983, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


