Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.緒言
computerized tomography(CT)の導入以来,頭蓋内病巣の診断は,近年飛躍的な進歩を遂げてきた。とくに頭部外傷症例の頭蓋内血腫合併の有無に関する診断は一目瞭然であり,しかも血腫量やその部位まで正確に把握することが可能となっている。しかしながら,このCTを用いても,頭部外傷症例における頭蓋内病巣のすべてを知りえないことも事実である,すなわち,受傷初期にはCT上から,脳挫傷の有無を診断することが困難なこともある。そのため,このような症例では,その治療方針決定や予後判定のために脳組織の損傷程度を客観的にとらえうる手段の必要性が痛感されている。
これまで脳組織の損傷程度を定量的に把握するには,脳組織より髄液中へ逸脱した各種酵素の活性値測定が試みられてきた。たとえば髄液中のglutamic oxaloacetictransaminase(GOT)やlactic dehydrogenasc(LDH)などの活性値は,脳組織損傷時に上昇し,その損傷程度とも相関しているのではないかと報告されている(古本,196217);牧野,196218);高倉,196333);明石,19661);Kaltiala,196816)。
Abstract
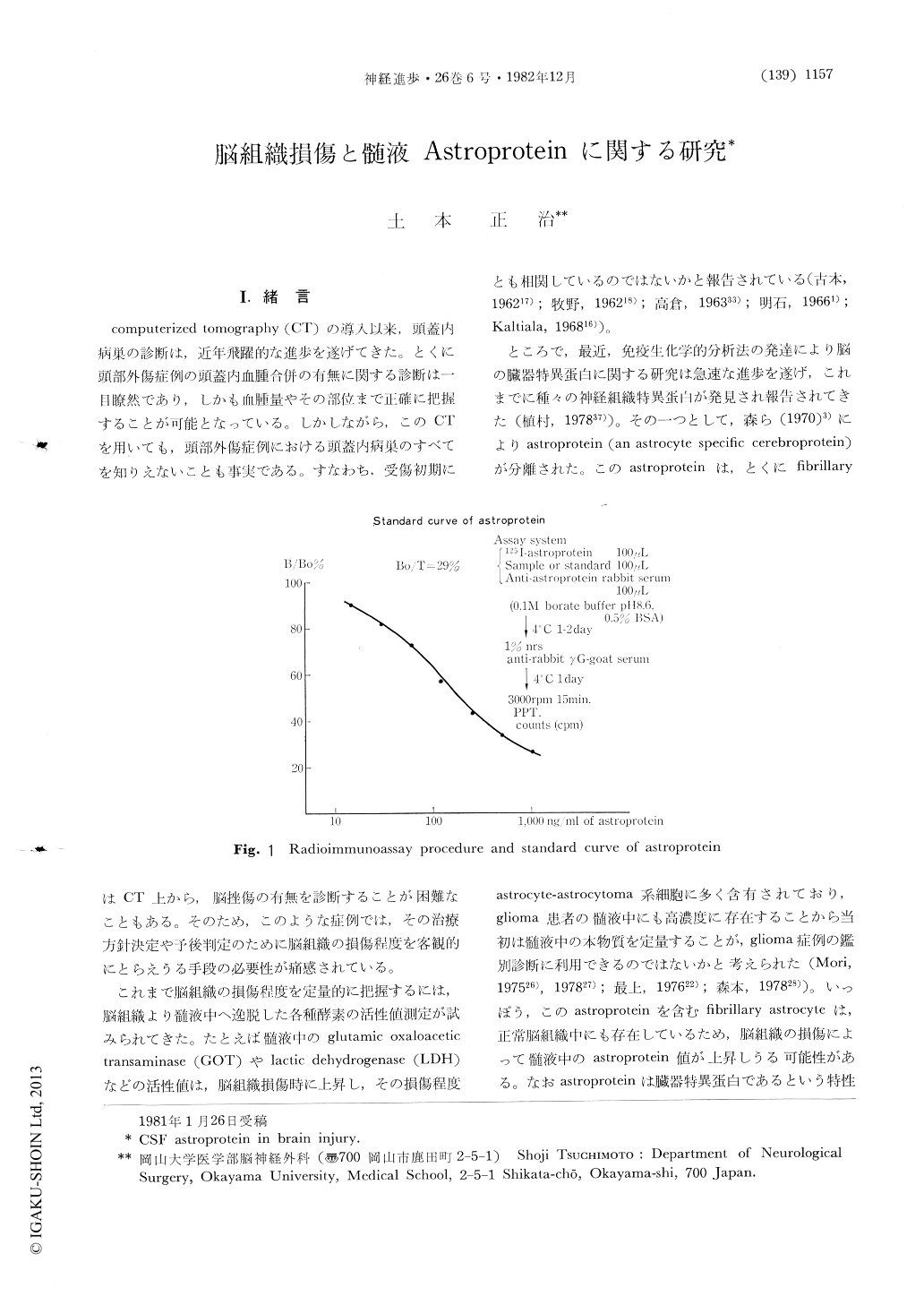
Amounts of astroprotein (astrocyte-specific cerebroprotein) measured by radioimmunoassay was reported to increase remarkably in cerebrospinal fluid and tumorous cystic fluid of patients with glioma. While astroprotein was also detected in normal fibrillary astrocytes, therefore it is presumed that astroprotein increases in CSF following fibrillary astrocytes breakdown.
This study concerns interreationships between CSF astroprotein and severity of brain injury.
The mateials were CSF samples from 63 patients with head injuries and 38 patients without any cerebral damages.
Copyright © 1982, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


