Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
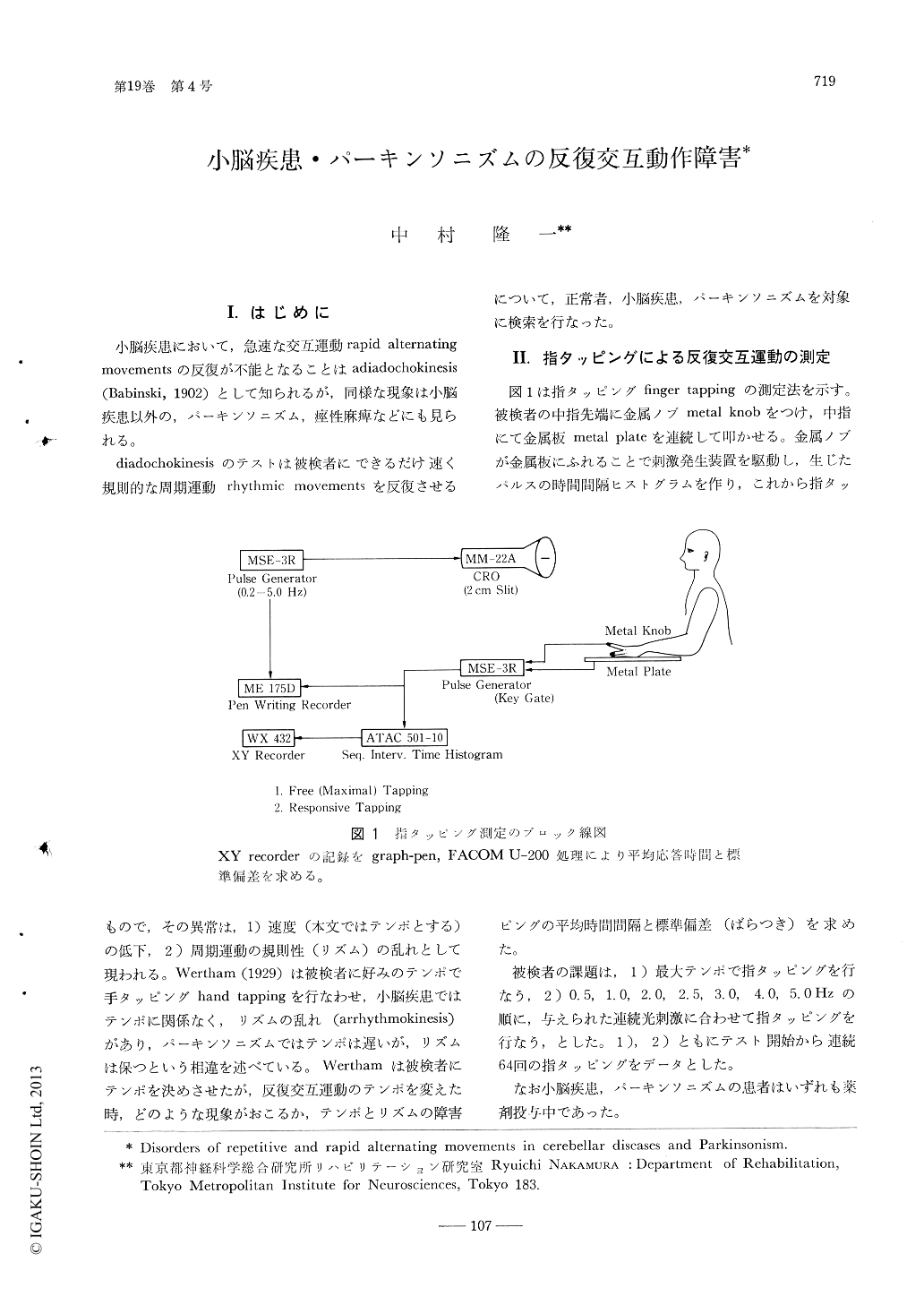
I.はじめに
小脳疾患において,急速な交互運動rapid alternating movementsの反復が不能となることはadiadochokinesis(Babinski,1902)として知られるが,同様な現象は小脳疾患以外の,パーキンソニズム,痙性麻痺などにも見られる。
diadochokinesisのテストは被検者にできるだけ速く規則的な周期運動rhythmic movementsを反復させるもので,その異常は,1)速度(本文ではテンポとする)の低下,2)周期運動の規則性(リズム)の乱れとして現われる。Wertham(1929)は被検者に好みのテンポで手タッピングhand tappingを行なわせ,小脳疾患ではテンポに関係なく,リズムの乱れ(arrhythmokinesis)があり,パーキンソニズムではテンポは遅いが,リズムは保つという相違を述べている。Werthamは被検者にテンポを決めさせたが,反復交互運動のテンポを変えた時,どのような現象がおこるか,テンポとリズムの障害について,正常者,小脳疾患,パーキンソニズムを対象に検索を行なった。
Mean time interval and standard deviation were calculated from 64 sequential trials of finger tapping triggered by the photic stimulation in normal subjects and patients with cerebellar diseases and Parkinsonism.
Disorder of finger tapping in cerebellar diseases and Parkinsonism was the irregularity of rhythmdepending on tempo.
Copyright © 1975, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


