Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
Ⅰ.はじめに
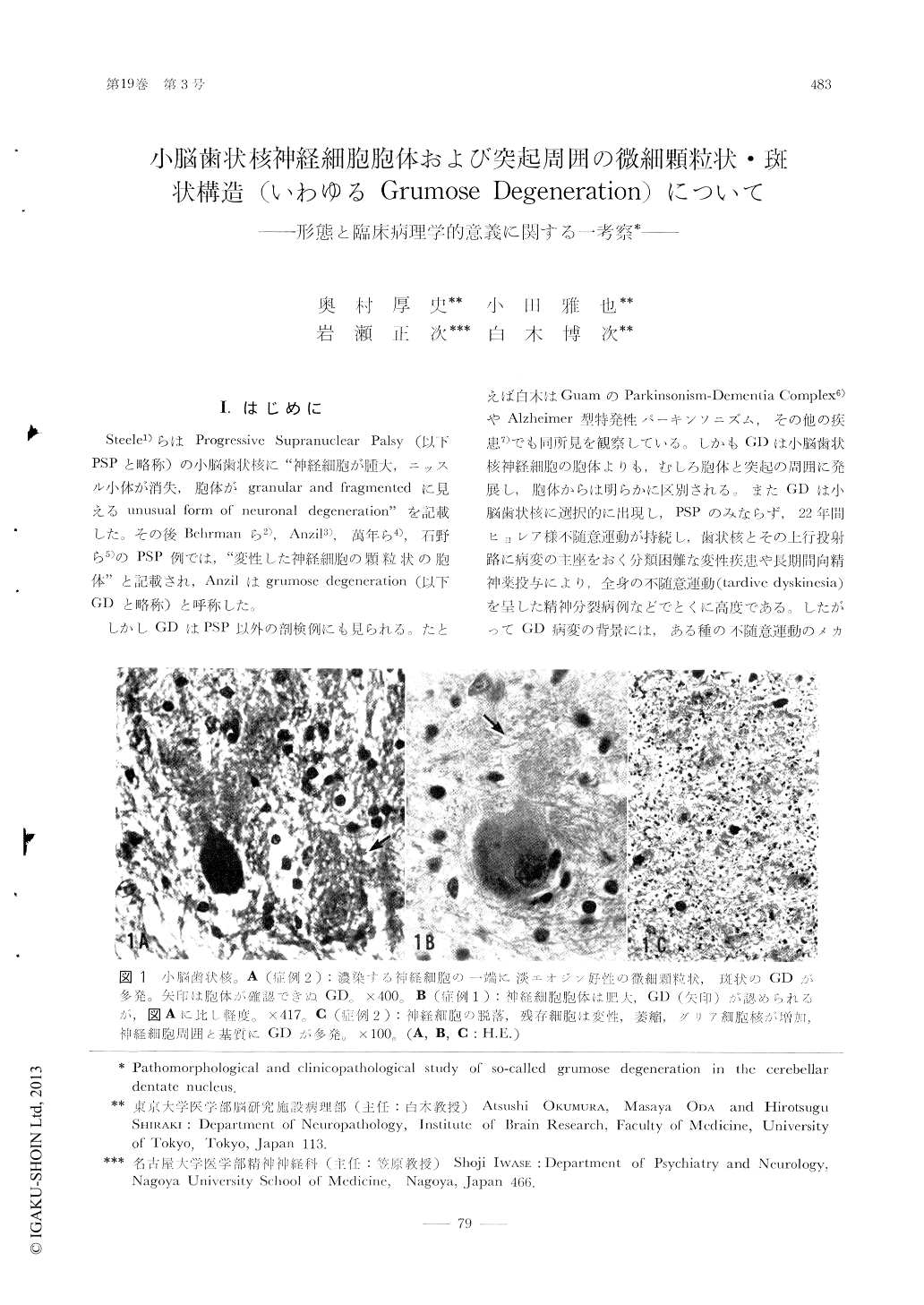
Steele1)らはProgressive Supranuclear Palsy(以下PSPと略称)の小脳歯状核に"神経細胞が腫大,ニッスル小体が消失,胞体がgranular and fragmentedに見えるunusual form of neuronal degeneration"を記載した。その後Behrmanら2),Anzil3),萬年ら4),石野ら5)のPSP例では,"変性した神経細胞の顆粒状の胞体"と記載され,Anzilはgrumose degeneration(以下GDと略称)と呼称した。
しかしGDはPSP以外の剖検例にも見られる。たとえば白木はGuamのParkinsonism-Dementia Complex6)やAlzheimer型特発性パーキンソニズム,その他の疾患7)でも同所見を観察している。しかもGDは小脳歯状核神経細胞の胞体よりも,むしろ胞体と突起の周囲に発展し,胞体からは明らかに区別される。またGDは小脳歯状核に選択的に出現し,PSPのみならず,22年間ヒョレア様不随意運動が持続し,歯状核とその上行投射路に病変の主座をおく分類困難な変性疾患や長期間向精神薬投与により,全身の不随意運動(tardive dyskinesia)を呈した精神分裂病例などでとくに高度である。
So-called grumose degeneration (abbreviated as GD) in the cerebellar dentate nucleus was examined both light- and electronmicroscopically in 7 cases of various human diseases including progressive supranuclear palsy. The clinico-neuropathological features of them were summarized in Tables 1 and 2.
Copyright © 1975, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


