Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
非侵襲的な脳機能の画像化の方法の一つとしてとりあげられるfunctional MRI(fMRI)は,3年程まえにその可能性が示されて以来1-3)多くの脳機能研究分野から興味と期待がよせられている。高い磁場内での測定という制限はあるが,高分解度の空間情報の的確さおよび秒単位のやや遅い応答時間を持つとはいえ,画像の経時的変化を追えるといった特長を持っ測定である。MRIとしての現象の理解が深まるとともに測定技術や画像情報の抽出法の進歩度合からして,この方法の諸方面への応用の将来は非常にあかるい。
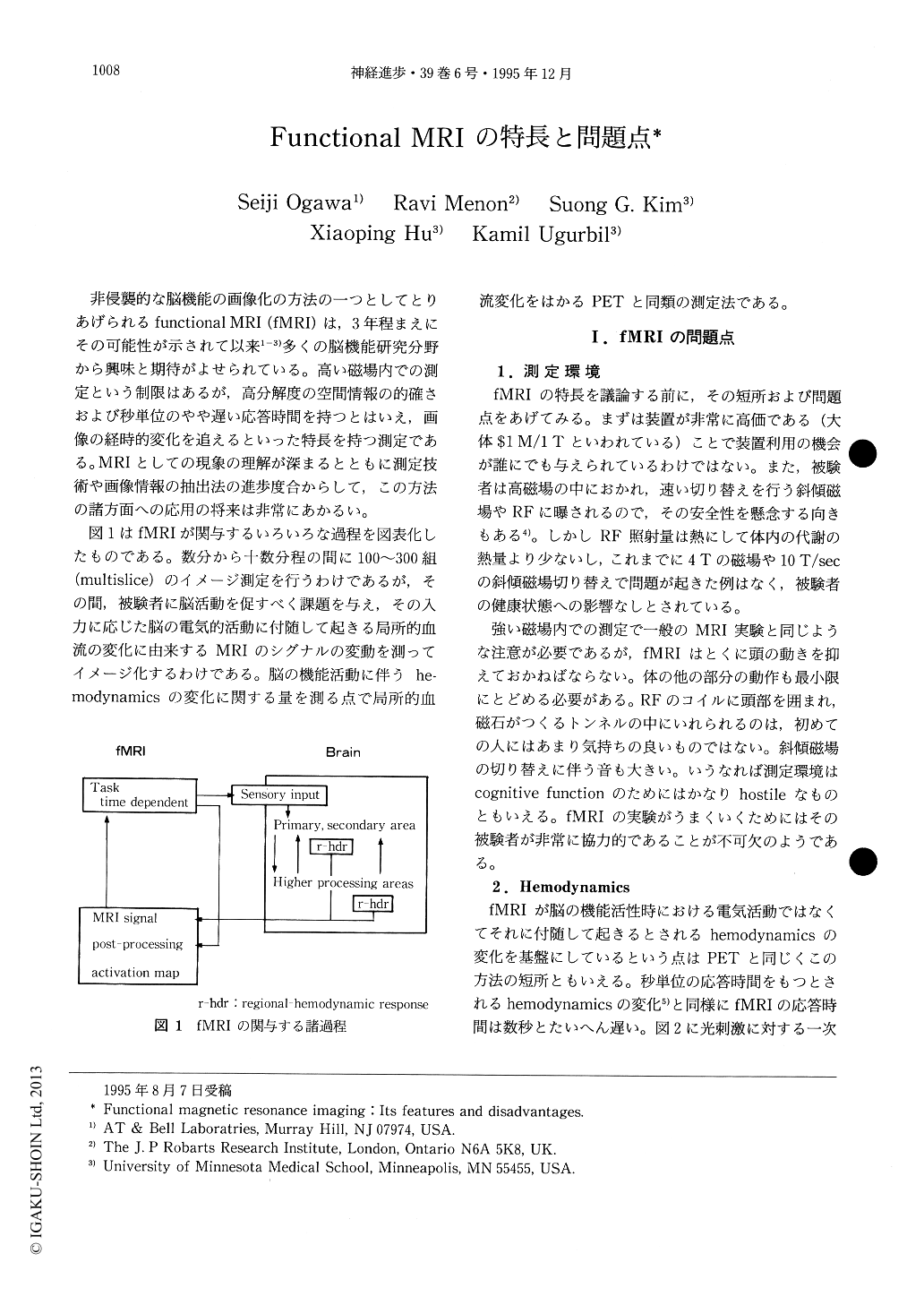
図1はfMRIが関与するいろいろな過程を図表化したものである。数分から十数分程の間に100~300組(multislice)のイメージ測定を行うわけであるが,その間,被験者に脳活動を促すべく課題を与え,その入力に応じた脳の電気的活動に付随して起きる局所的血流の変化に由来するMRIのシグナルの変動を測ってイメージ化するわけである。脳の機能活動に伴うhemodynamicsの変化に関する量を測る点で局所的血流変化をはかるPETと同類の測定法である。
Various features of functional MRI together with some shortcomings and current problems are summarized. One major problem of fMRI is the signal fluctuation along the time course of the measurement. It exceeds often those of weak functional activation signals. The fluctuation is mainly due to physiological noise with cardiac and respiratory origin in addition to small brain motion during the experiment. Various ways to cope with the problem are known but not completely satisfactory yet. fMRI is based upon the hemodynamic response to the neuro-activation and therefore the response time is rather slow (several seconds).
Copyright © 1995, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


