Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
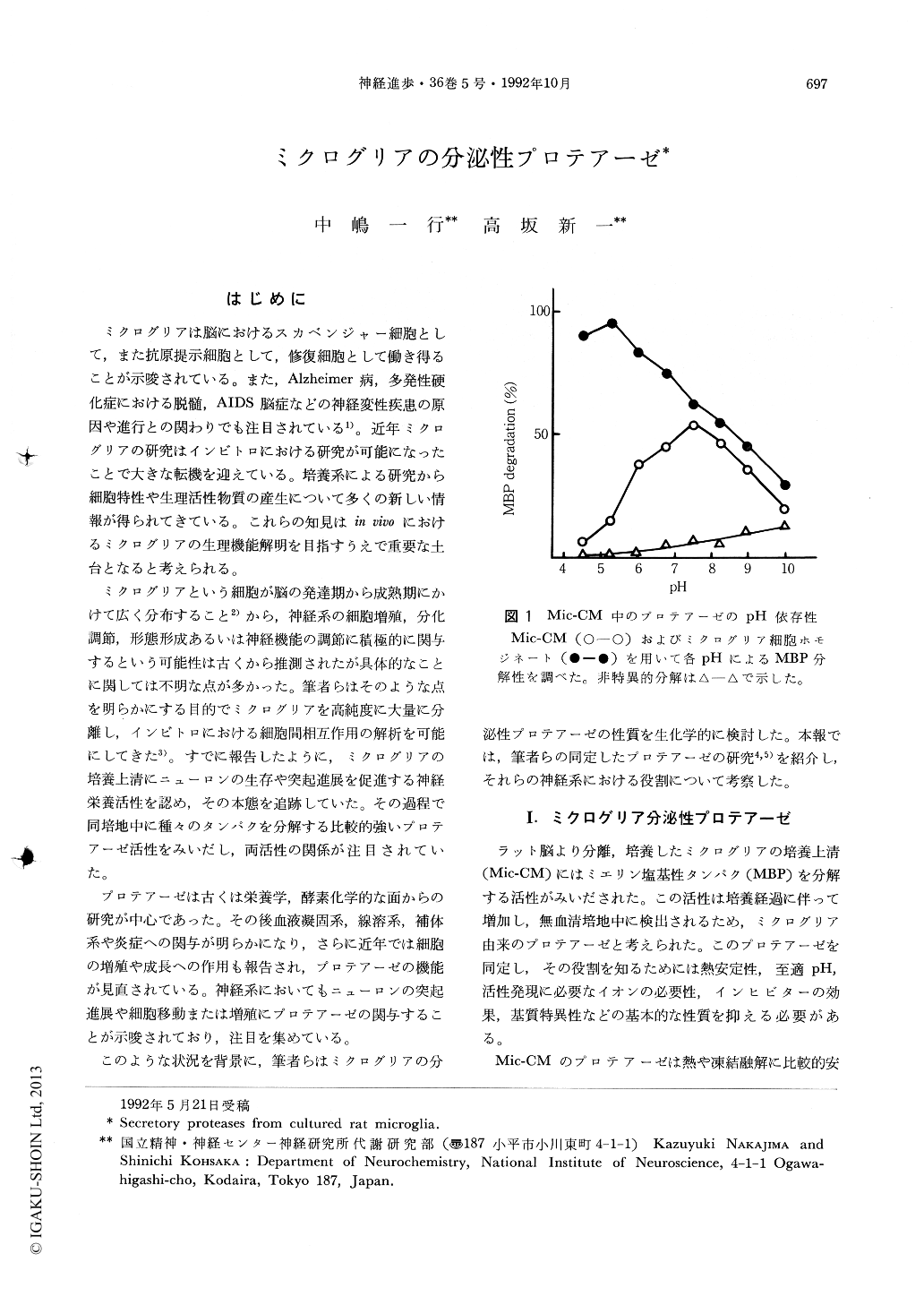
はじめに
ミクログリアは脳におけるスカベンジャー細胞として,また抗原提示細胞として,修復細胞として働き得ることが示唆されている。また,Alzheimer病,多発性硬化症における脱髄,AIDS脳症などの神経変性疾患の原因や進行との関わりでも注目されている1)。近年ミクログリアの研究はインビトロにおける研究が可能になったことで大きな転機を迎えている。培養系による研究から細胞特性や生理活性物質の産生について多くの新しい情報が得られてきている。これらの知見はin vivoにおけるミクログリアの生理機能解明を目指すうえで重要な土台となると考えられる。
ミクログリアという細胞が脳の発達期から成熟期にかけて広く分布すること2)から,神経系の細胞増殖,分化調節,形態形成あるいは神経機能の調節に積極的に関与するという可能性は古くから推測されたが具体的なことに関しては不明な点が多かった。筆者らはそのような点を明らかにする目的でミクログリアを高純度に大量に分離し,インビトロにおける細胞間相互作用の解析を可能にしてきた3)。すでに報告したように,ミクログリアの培養上清にニューロンの生存や突起進展を促進する神経栄養活性を認め,その本態を追跡していた。その過程で同培地中に種々のタンパクを分解する比較的強いプロテアーゼ活性をみいだし,両活性の関係が注目されていた。
Microglia are histochemically found to be widely distributed throughout the perinatal and matured brain and are considered to act in normal homeostasis involving a regulation of neuronal activity and extracellular environment. When microglia were activated in injured site or pathological state, they proliferate, migrate and are thought to work as scavenger cells. However the direct role or function of microglia in the brain has been remained unclear.
In recent years, the methods for isolating microglia have been developed wnich made it possible to study the properties of microglia and intercellular interaction between microglia and other cells. In vitro studies demonstrated that microglia have on ability of antigen presentation and produce cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, TNF and growth factors like NGF and bFGF. We also showed cultured micro-glia secrete relatively strong proteolytic enzymes into the medium. These proteases were biochemically characterized and now three kinds of proteases were identified, elastase, plasminogen activator and plasminogen.
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


