Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
現代医学の発展は,19世紀に始まる自然科学的方法の導入によるところが多い。長い間にわたって人類を苦しめてきた細菌による伝染病の原因はその多くが明らかにされ,化学療法や抗生物質による治療法も確立された。
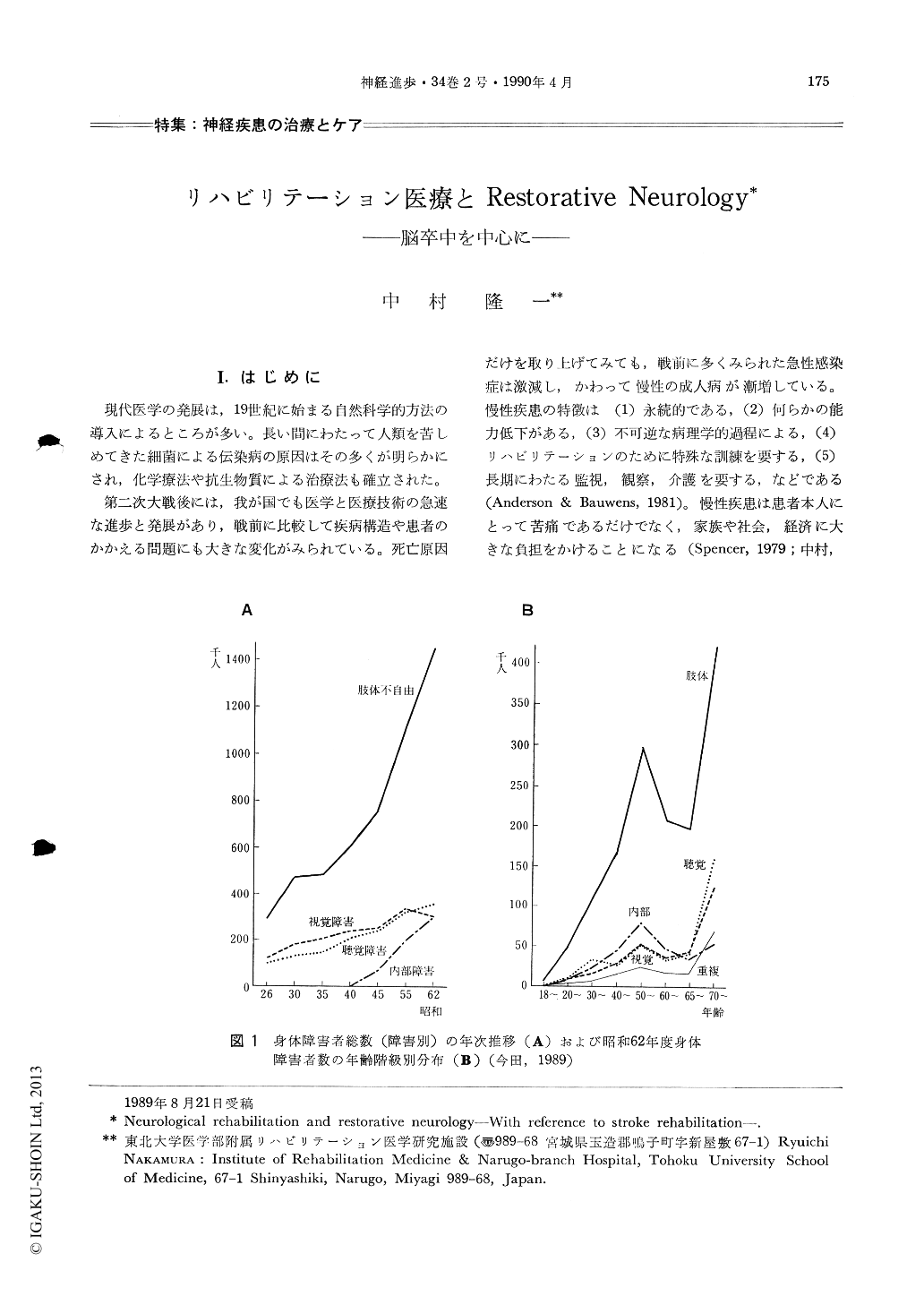
第二次大戦後には,我が国でも医学と医療技術の急速な進歩と発展があり,戦前に比較して疾病構造や患者のかかえる問題にも大きな変化がみられている。死亡原因だけを取り上げてみても,戦前に多くみられた急性感染症は激減し,かわって慢性の成人病が漸増している。慢性疾患の特徴は(1)永続的である,(2)何らかの能力低下がある,(3)不可逆な病理学的過程による,(4)リハビリテーションのために特殊な訓練を要する,(5)長期にわたる監視,観察,介護を要する,などである(Anderson & Bauwens,1981)。慢性疾患は患者本人にとって苦痛であるだけでなく,家族や社会,経済に大きな負担をかけることになる(Spencer,1979;中村,1983a)。
The number one health problem in the modern societies including Japan is chronic disease. Recent survey on the disabled in Japan indicated that the number of disabled due to chronic neurological disease were increasing, whereas those due to trauma and infection decreasing. Patients with chronic disease require special training for rehabilitation, a long period of supervision, observation and care, since the disease is permanent and leaves residual disability. In this paper we report recent progress in stroke rehabilitation and restorative neurology as new horizon in rehabilitation technology.
Copyright © 1990, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


