Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
神経疾患の中には慢性進行性の経過を示すものが多く,有効な治療法や薬剤を見出されず,予後不良の経過をとるものが少なくない。脳血管障害の一部や外傷ないし先天異常に伴う脳脊椎障害を除けば,外科的治療法によって完治する神経疾患はきわめて限られている。このような慢性進行性の経過をとるものは神経疾患に限らず,一般の内科疾患などにもみられるが,かなりのものは特定疾患,いわゆる「難病」という枠の下で医療補助を受けられる体制になっている。しかしながら神経疾患の場合には,歩行や四肢筋の麻痺,さらには呼吸や嚥下など,直接生命維持に必要な神経系統の障害を伴って進行してくる点が特異である。すなわち,治療によって治癒する機会や回復をする可能性がなく,進行し,重症化することを予測して治療を続けなければならない点が問題なのである。
一方,医療の面からみると,特別の治療法がなく慢性の看護のみを主体とするような医療は,現在の保険診療下では最も歓迎されない患者であり,いわゆる慢性療養を中心とした医療は医療採算の合わない疾患対象群を相手にしているといってよい。筋ジストロフィーなどきわめて限られた疾患に対しては,国立療養所が長期療養施設として用意されているが,疾患の種類,そのベッドの数もきわめて限られていて,一般の需要には応じられないのが実状であろう。
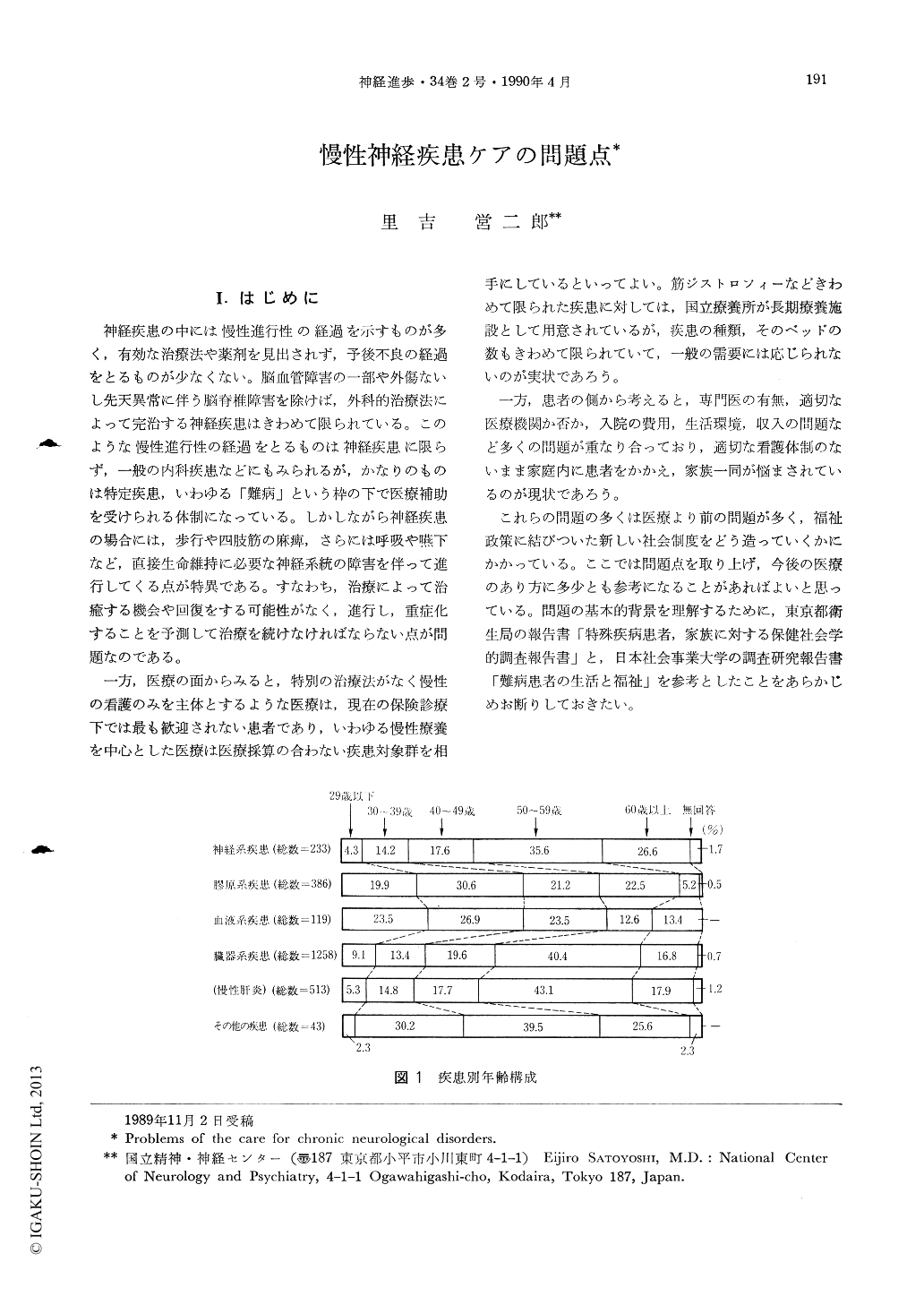
Social and medical factors of the 2,038 patients with “so called” incurable diseases (Nanbyo) living Tokyo City were analysed. And the state of the neurological disorders were compared with the other incurable disease groups. 233 patients of various neurological diseases showed higher onset of the disease, predominantly male patients and chiefly economical supporting person. Therefore, chronic neurological diseases brought up the economical and medical unfavourable state in the process of the disease. On the other hand, these chronic patients care does not pay so well to the hospitals economics.
Copyright © 1990, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


