Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
輸血後GVHD(transfusion associated graftversus host disease)は,移植片(graft)である輸血血液中のリンパ球が宿主(host)である患者体内で生着・増殖して体組織を攻撃して生じる病態である。臨床症状は,輸血後1〜2週で発熱・紅斑が出現し,肝障害・下痢・下血・意識障害などの症状が続く。最終的には骨髄無形成・汎血球減少を呈し,敗血症・肺炎などの重症感染,あるいは大量の出血により死亡するのが典型的な経過である1)。
輸血後GVHDは,1965年にHathawayら2)が免疫不全小児例に認められて以来,出現頻度は少ないものの輸血後の予後不良な合併症として胸部外科領域を中心に報告がある3-5)。以前は輸血血液の生着を拒絶する能力のない重症の免疫不全患者に発症すると考えられていたが,近年免疫学的に異常のない患者にも発症が相次ぎ注目を浴びている6)。耳鼻咽喉科頭頸部外科領域では峯田ら7)が臨床症状より報告をしているが,診断が確定したという報告はされていない。われわれは臨床症状と皮膚組織像より輸血後GVHDが強く疑われ,最終的にはDNA分析にて本疾患が証明された1症例を経験したので報告する。
A 62-year-old male with carcinoma of the hy-popharynx developed a blood transfusion asso-ciated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GVHD). The patient presented with fever and skin rash 14 days after laryngo-pharyngo-esophagectomy, follwed by liver dysfunction, diarrhea, pancytopenia, bone marrow aplasia, and disturbance of consciousness. The diagnosis of TA-GVHD was made by DNAsequence polymorphism analysis. The results de-monstrated the replacement of patient DNA types with donor types at the time of GVHD.
For preventing TA-GVHD, irradiation in a dose of 15~50 Gy to blood products before transfusion was recommended.
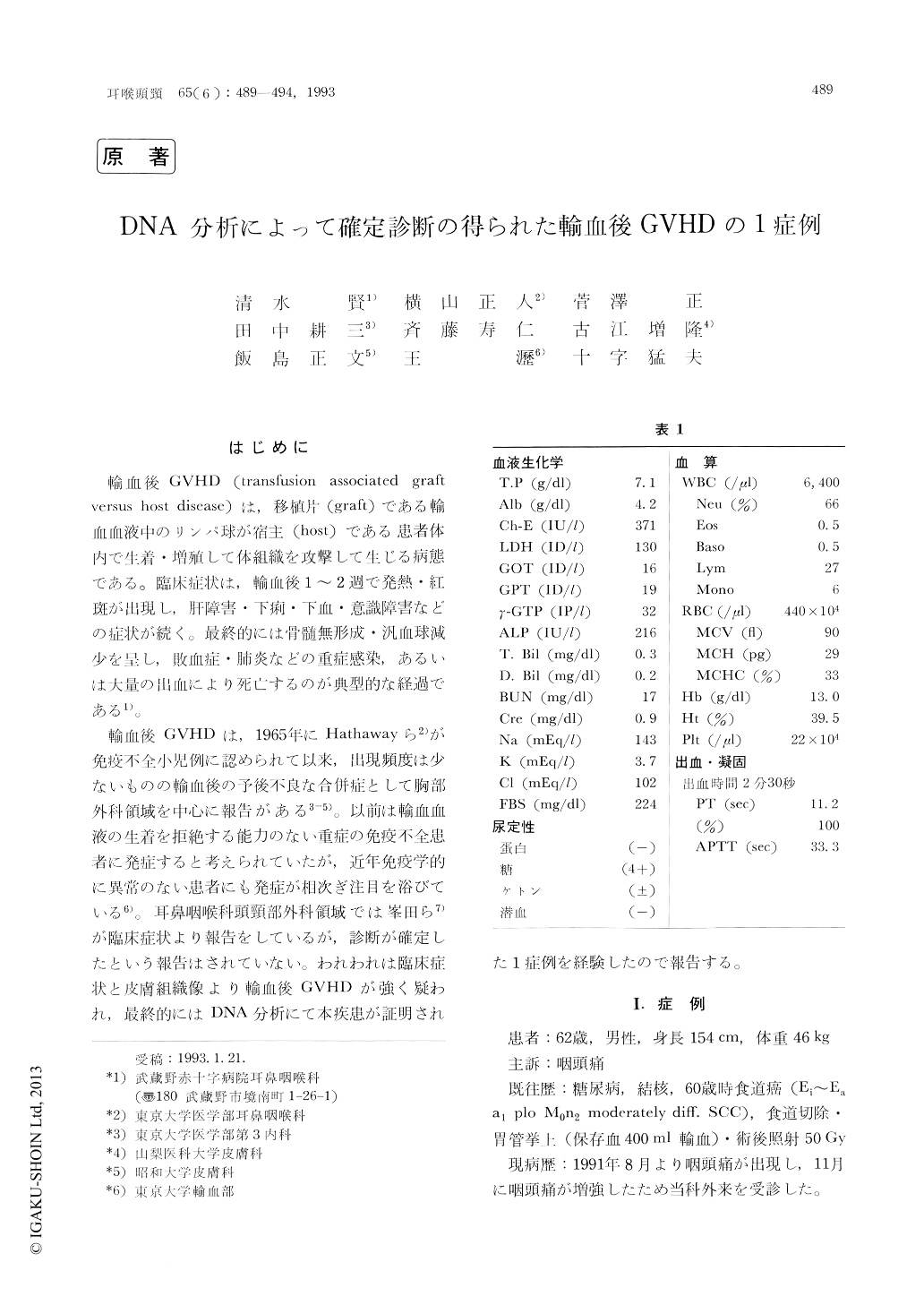
Copyright © 1993, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


