Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
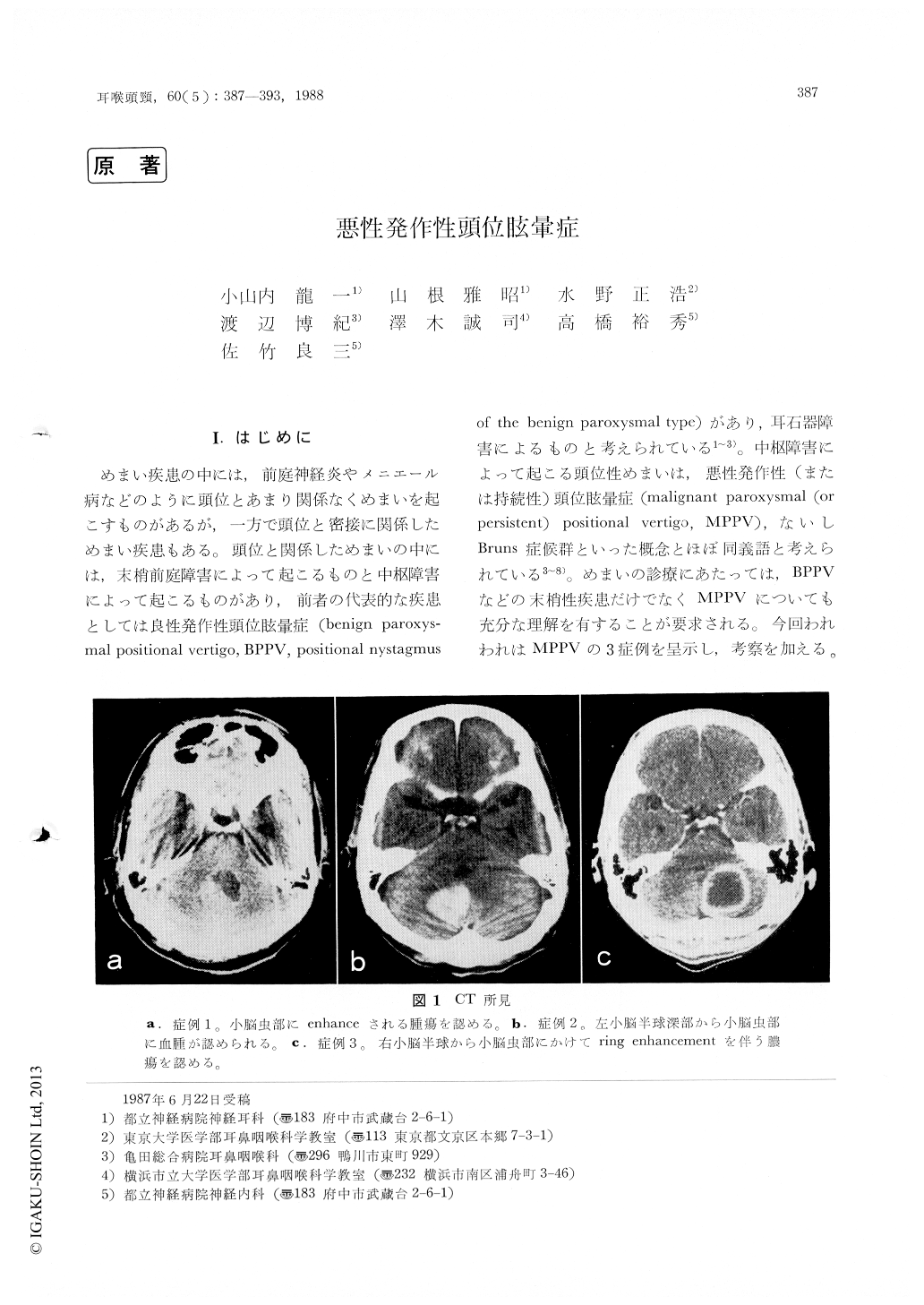
めまい疾患の中には,前庭神経炎やメニエール病などのように頭位とあまり関係なくめまいを起こすものがあるが,一方で頭位と密接に関係しためまい疾患もある。頭位と関係しためまいの中には,末梢前庭障害によって起こるものと中枢障害によって起こるものがあり,前者の代表的な疾患としては良性発作性頭位眩(benign paroxys—mal positional vertigo, BPPV, positional nystagmusof the benign paroxysmal type)があり,耳石器障害によるものと考えられている1〜3)。中枢障害によって起こる頭位性めまいは,悪性発作性(または持続性)頭位眩暈症(malignant paroxysmal (orpersistent)positional vertigo, MPPV),ないしBruns症候群といった概念とほぼ同義語と考えられている3〜8)。めまいの診療にあたっては,BPPVなどの末梢性疾患だけでなくMPPVについても充分な理解を有することが要求される。今回われわれはMPPVの3症例を呈示し,考察を加える。
Three cases of positional nystagmus of malignant paroxysmal type (Sakata) were reported.
All three patients complained of vertigo which was induced by change of head position and exhibited direction changing positional nystagmus whose quick phase was toward the uppermost ear. Astrocytoma of cerebellar vermis, hematoma of deeper portion of cerebellar hemisphere and vermis, and abscess of cerebellar hemisphere and vermis were disclosed in each case by CT scan and sur-gical intervention.
Neurotological findings including positional and positioning nystagmus, saccadic pattern in eye tracking test and impaired optokinetic nystagmus were of great value to clarify the disturbance of central vestibular system.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


