Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.緒言
緑内障の早期発見の必要が叫ばれて以来,緑内障検出のための集団検診が,これまでに多数行なわれてきており,それ自体が非常に意義のあることであった。しかし,そのさいに検出された緑内障は別として,ある検査のみが陽性のもの,あるいは疑似緑内障として検出された例が,いかなる経過をとり,どのような症例が真性の緑内障に発展するのかという点に着目し,長期にわたり追跡し分析することは,さらに緑内障集団検診の意義を深めるものである。このような点に関する報告は著者の調べ得た範囲では,外国に少数1)〜5)のものがみられるのみで,わが国には見当たらない。
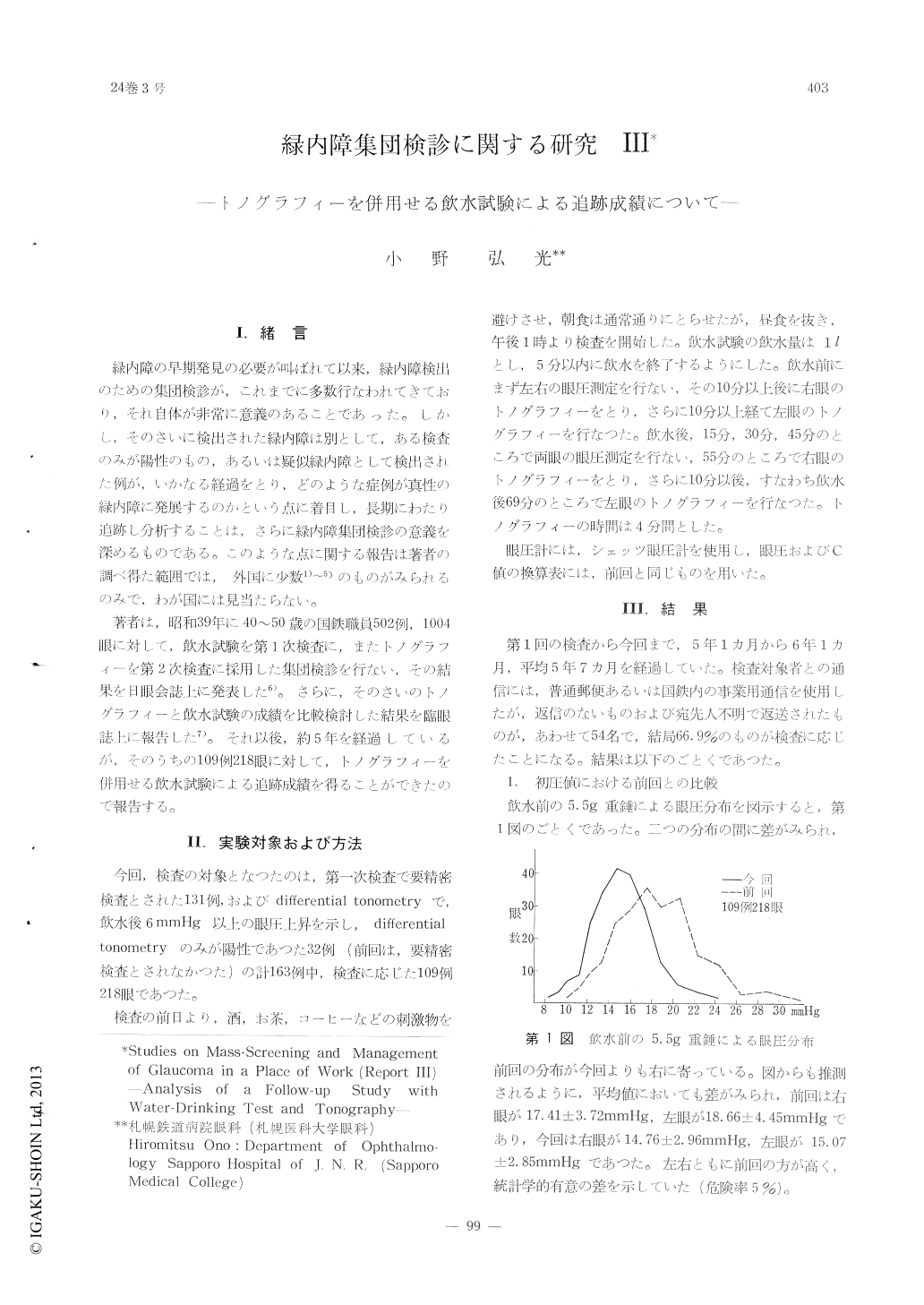
著者は,昭和39年に40〜50歳の国鉄職員502例,1004眼に対して,飲水試験を第1次検査に,またトノグラフィーを第2次検査に採用した集団検診を行ない,その結果を日眼会誌上に発表した6)。さらに,そのさいのトノグラフィーと飲水試験の成績を比較検討した結果を臨眼誌上に報告した7)。それ以後,約5年を経過しているか,そのうちの109例218眼に対して,トノグラフィーを併用せる飲水試験による追跡成績を得ることができたので報告する。
109 cases (218 eyes) selected in the previous report were examined by water provocative test and tonography. About 5 years had passed since the previous test. On the average, initial pressure recorded in the previous test was sig-nificantly higher than that in this report. At 15 minutes after water, the same was concluded.In both examinations, a significant rise of pres-sure was recorded at 15 minutes after water.
For 83 per cent of the water provocative test the maximum change of pressure was recorded within the first 30 minutes. After water ingestion, 8 cases (11 eyes) reacted by a rise 6mm Hg or more.
Copyright © 1970, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


