Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
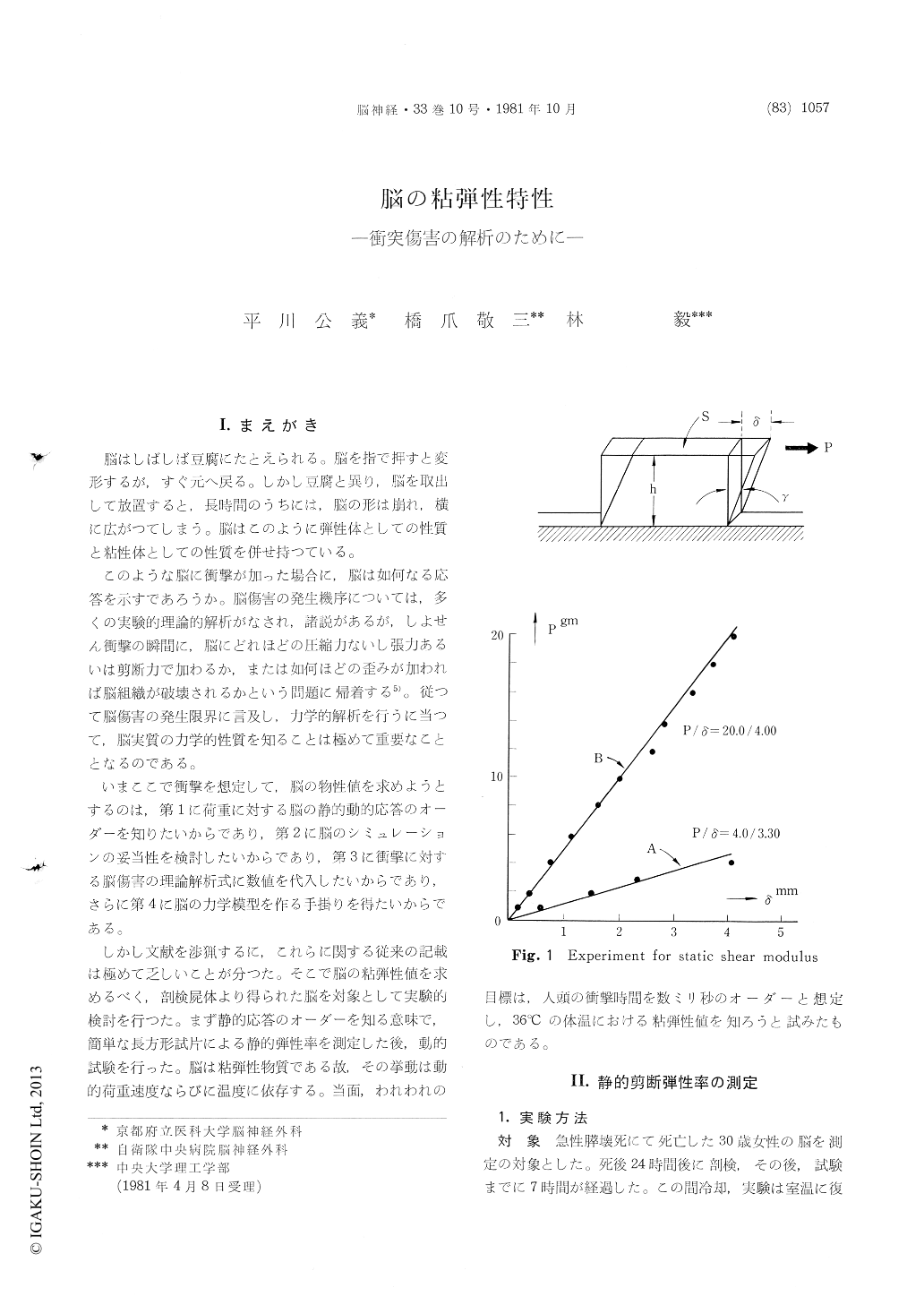
1.まえがき
脳はしばしば豆腐にたとえられる。脳を指で押すと変形するが,すぐ元へ戻る。しかし豆腐と異り,脳を取出して放置すると,長時間のうちには,脳の形は崩れ,横に広がつてしまう。脳はこのように弾性体としての性質と粘性体としての性質を併せ持つている。
このような脳に衝撃が加った場合に,脳は如何なる応答を示すであろうか。脳傷害の発生機序については,多くの実験的理論的解析がなされ,諸説があるが,しよせん衝撃の瞬間に,脳にどれほどの圧縮力ないし張力あるいは剪断力で加わるか,または如何ほどの歪みが加われば脳組織が破壊されるかという問題に帰着する5)。従つて脳傷害の発生限界に言及し,力学的解析を行うに当つて,脳実質の力学的性質を知ることは極めて重要なこととなるのである。
1. Viscoelasticity of the human brain was in-vestigated in order to understand the physical pro-perties of the brain and to apply it to the analysis of the head injury mechanisms.
2. Static shear modulus (G) of the human white matter was 2.4×103dyne/cm2.
3. Complex Young's modulus (E*(ω)=E´+iE") of the white matter, the gray matter, and the brain stem was measured in the range of 3-36℃ and 3-35Hz using the dynamic viscoelastometer. Storage Young's modulus (E′) of both white and gray matters of human brain was in the figures of 105 dyne/cm2 and loss Young's modulus (E") of those showed 104-155dyne/cm2.
4. The viscoelasticity of human brain is illustrat-ed in Fig. 4 on the assumption of the equivalence of time and temperature. In case of head injury with impact duration of 5msec it is proper to use the following value: E′=4×105dyne/cm2, E"=2×105dyne/cm2 in the white matter and E′=3×105dyne/cm2, in the gray matter.
5. The viscoelasticity of gelatin and bean curds were also examined to know whether or not simu-lation of the brain was possible. The viscoelasticity of 5-15% gelatin with an addition of 5% formalin was decreased 1-2 figures compared with that of the brain. The viscoelasticty of bean curds was about the same as that of the brain.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


