Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
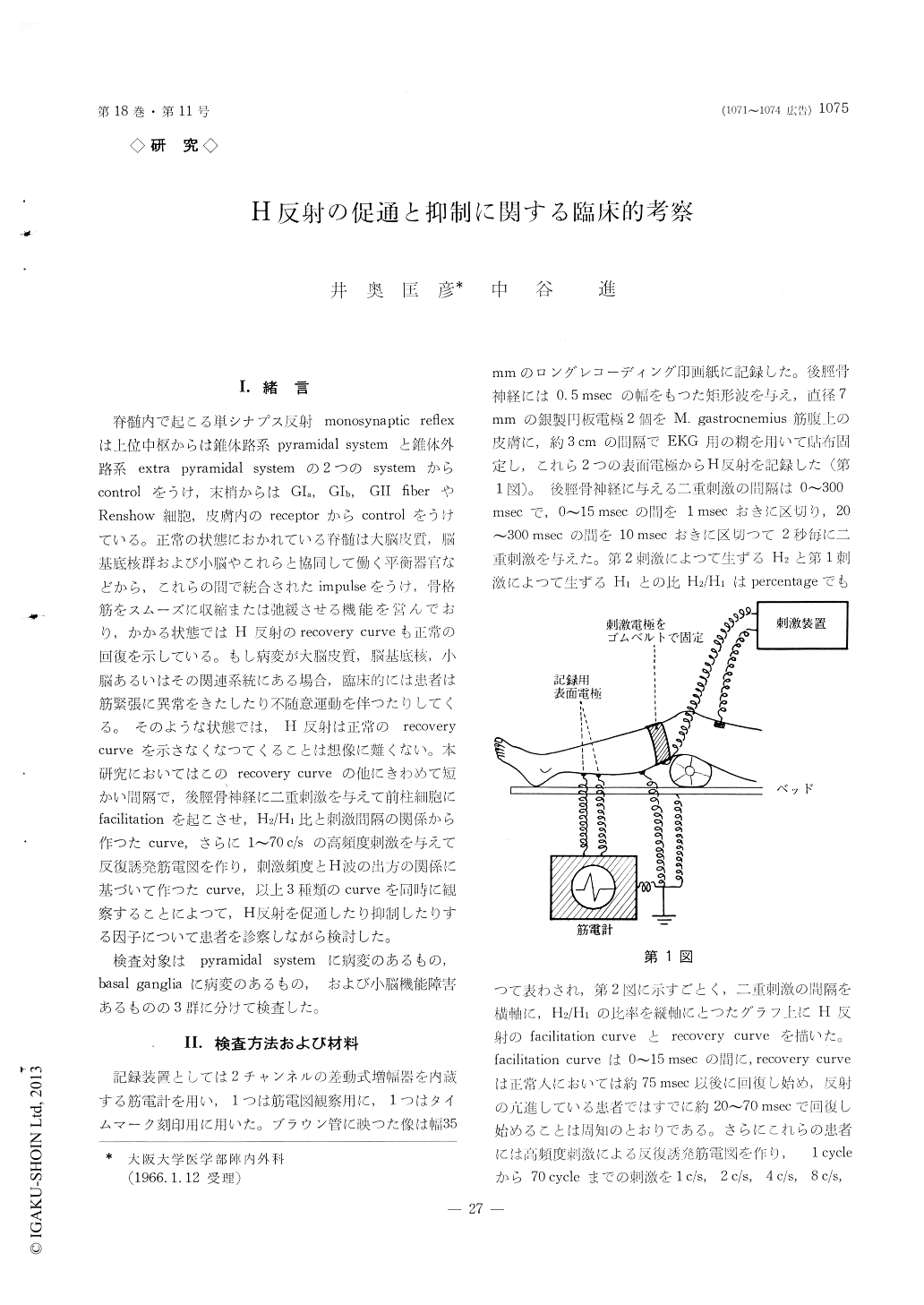
I.緒言
脊髄内で起こる単シナプス反射monosynaptic reflexは上位中枢からは錐体路系pyramidal systemと錐体外路系extra pyramidal systemの2つのsystemからcontrolをうけ,末梢からはGIa, GIb, GII fiberやRenshow細胞,皮膚内のreceptorからcontrolをうけている。正常の状態におかれている脊髄は大脳皮質,脳基底核群および小脳やこれらと協同して働く平衡器官などから,これらの間で統合されたimpulseをうけ,骨格筋をスムーズに収縮または弛緩させる機能を営んでおり,かかる状態ではH反射のrecovery curveも正常の回復を示している。もし病変が大脳皮質,脳基底核,小脳あるいはその関連系統にある場合,臨床的には患者は筋緊張に異常をきたしたり不随意運動を伴つたりしてくる。そのような状態では,H反射は正常のrecovery curveを示さなくなつてくることは想像に難くない。本研究においてはこのrecovery curveの他にきわめて短かい間隔で,後脛骨神経に二重刺激を与えて前柱細胞にfacilitationを起にさせ,H2/H1比と刺激間隔の関係から作つたcurve,さらに1〜70c/sの高頻度刺激を与えて反復誘発筋電図を作り,刺激頻度とH波の出方の関係に某ついて作つたcurve,以上3種類のcurveを同時に観察するにとによつて,H反射を促通したり抑制したりする因子について患者を診察しながら検討した。
検査対象はpyramidal systemに病変のあるもの,basal gangliaに病変のあるもの,および小脳機能障害あるものの3群に分けて検査した。
Studies of the monosynaptic reflex by means of three kinds of analysis were carried out in neurologi-cal disorders.
Using Magladery's method recovery curves were plotted utilizing the relationship of the H-waves ob-tained after each of two succesive stimuli (H2/H1).In addition, a personal modification by loku consisting of recording the facilitatory conditions of the lower mo-tor neuron, using again two succesive stimuli in 1~15 msec range was determined at the same time. Furthermore in this study, the curve made with plotting the average value of the first 10 stimuli of the frequency in 1~70 c/s was investigated. The curve H2/Hi ratio obtained in the long interval double volley method (over 20 msec) is called as the recovery cur-ve. The curve of H2/H1 ratio, in contrast, obtained in the short interval double volley method (within 15 or so msec) is called as the facilitation curve. In the normal case, the H2/H1 ratio in the facilitation curve fell between 5080%. The curve made by repetitive stimulation dropped at the frequency of about 30 c/s. Comparison of the normals and neurological disorders led to the following conclusions :
(1) Pyramidal disorders
The facilitation curve took higher ratio than the normal and the recovery curve showed the faster onset than the normal. The curve plotting the average value of the first 10 volleys of repetitive stimulation took higher level at the frequency less than 30 c/s and almost normal level at the frequency over 30 msec.
(2) Extrapyramidal disorders
This group was divided into 2 groups.
a) Severe rigidity cases such as rigid type of par-kinsonism showed low facilitation curve in case of having severe muscle atrophy in the extremities and showed high facilitation curve in case of having no muscle atrophy. Fast onset was seen in the recovery curve of this group than the normal. The curve made with repetitive stimulation took higher level both in low and high frequencies.
b) Patient without rigidity but only having invo-luntary movement such as tremor type of parkinson-ism, chorea and intention tremor showed low facili-tation curve in case of having muscle atrophy and showed high facilitation curve in case of having no muscle atrophy. The recovery curve took delayed onset than the normal. The curve made with repetitive stimulation dropped in lower frequency than the nor-mal.
(3) Cerebellar disorders
The facilitation curve showed various hight depend-ing upon severity of muscle atrophy. The recovery curve had delayed onset and the curve made with repetitive stimulation dropped in lower frequency than the normal.
Our method, analysis of the curve plotting the average value of the first 10 volleys of repetitive stimulation is obviously proper method to make de-tailed analysis of severity of rigidity, muscle tone and/or balance disturbance.
Copyright © 1966, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


