Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
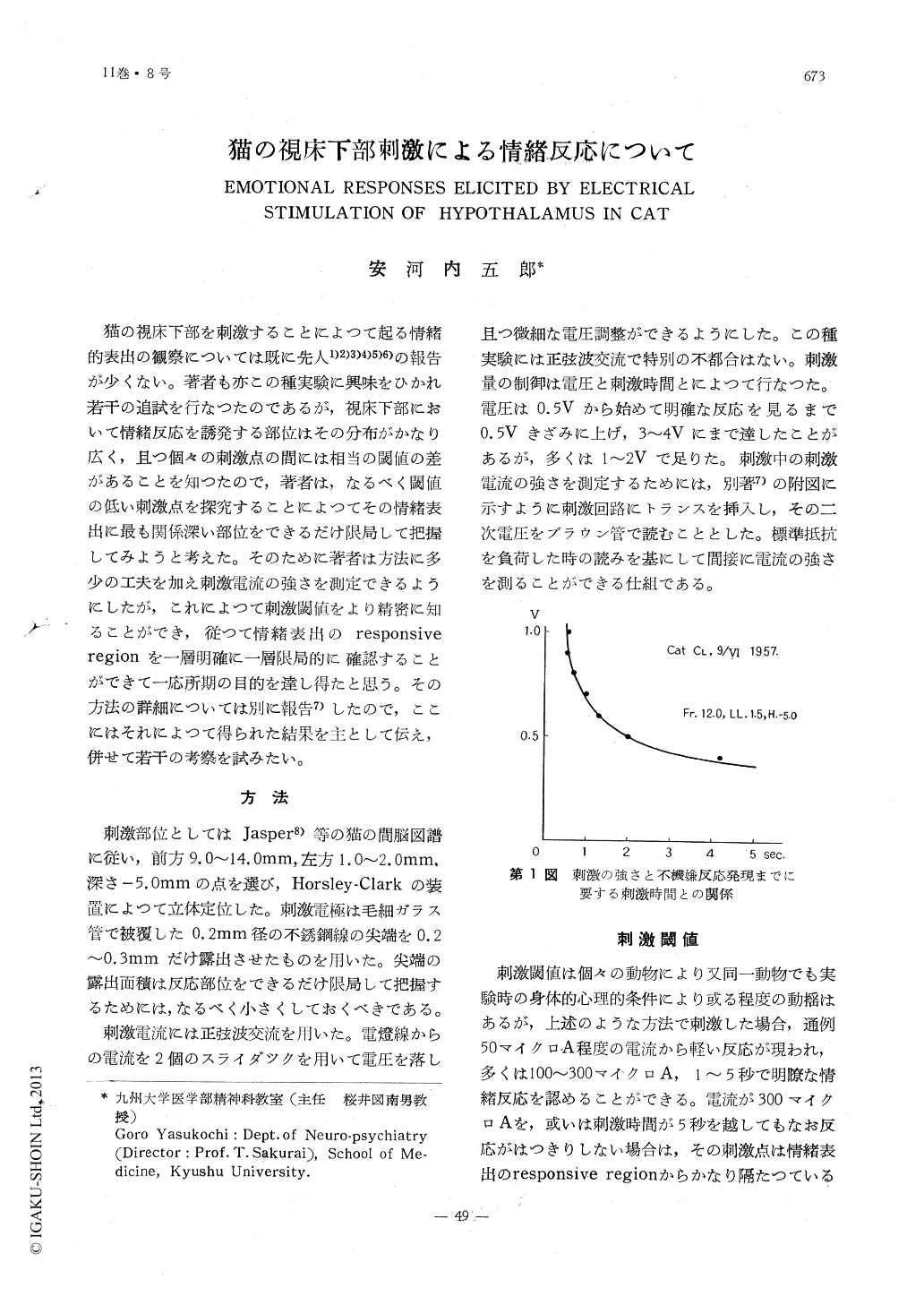
猫の視床下部を刺激することによつて起る情緒的表出の観察については既に先人1)2)3)4)5)6)の報告が少くない。著者も亦この種実験に興味をひかれ若干の追試を行なつたのであるが,視床下部において情緒反応を誘発する部位はその分布がかなり広く,且つ個々の刺激点の間には相当の閾値の差があることを知つたので,著者は,なるべく閾値の低い刺激点を探究することによつてその情緒表出に最も関係深い部位をできるだけ限局して把握してみようと考えた。そのために著者は方法に多少の工夫を加え刺激電流の強さを測定できるようにしたが,これによつて刺激閾値をより精密に知ることができ,従つて情緒表出のresponsive regionを一層明確に一層限局的に確認することができて一応所期の目的を達し得たと思う。その方法の詳細については別に報告7)したので,ここにはそれによつて得られた結果を主として伝え,併せて若干の考察を試みたい。
The emotional responses elicited by electri-cal stimulation of hypothalamus were obser-ved in unanesthetized and unrestrained cats. The needle electrodes were streotaxically implanted by means of Horsley-Clark's ap-paratus. Stimulus threasholds were exactly studied by measuring the intensity of stimu-lating currents. Responsible region for each type of emotional responses might have been thus more precisely and more localizedly de-cided. As the stimulating current, sinusoidal A. C. of 60c/s was used, which showed itself, at least in this experiment, not inferior to rectangular wave current. Stimulating vol-tage was 1-4V, and duration of current was 1-5 sec., while the intensity of it was 50-300micro-A.
Stimulation of the anterior part of hypo-thalamus was responsible for anxiety respo-nse, middle part for ill temper, or irritabi-lity, and postero-dorsal part for curious ea-gerness. Especially the stimulation of Nucl. hypothalam. ventromed., lying in the middle part of hypothalamus usually elicited remar-kable response of furios aggression.
Copyright © 1959, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


