Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
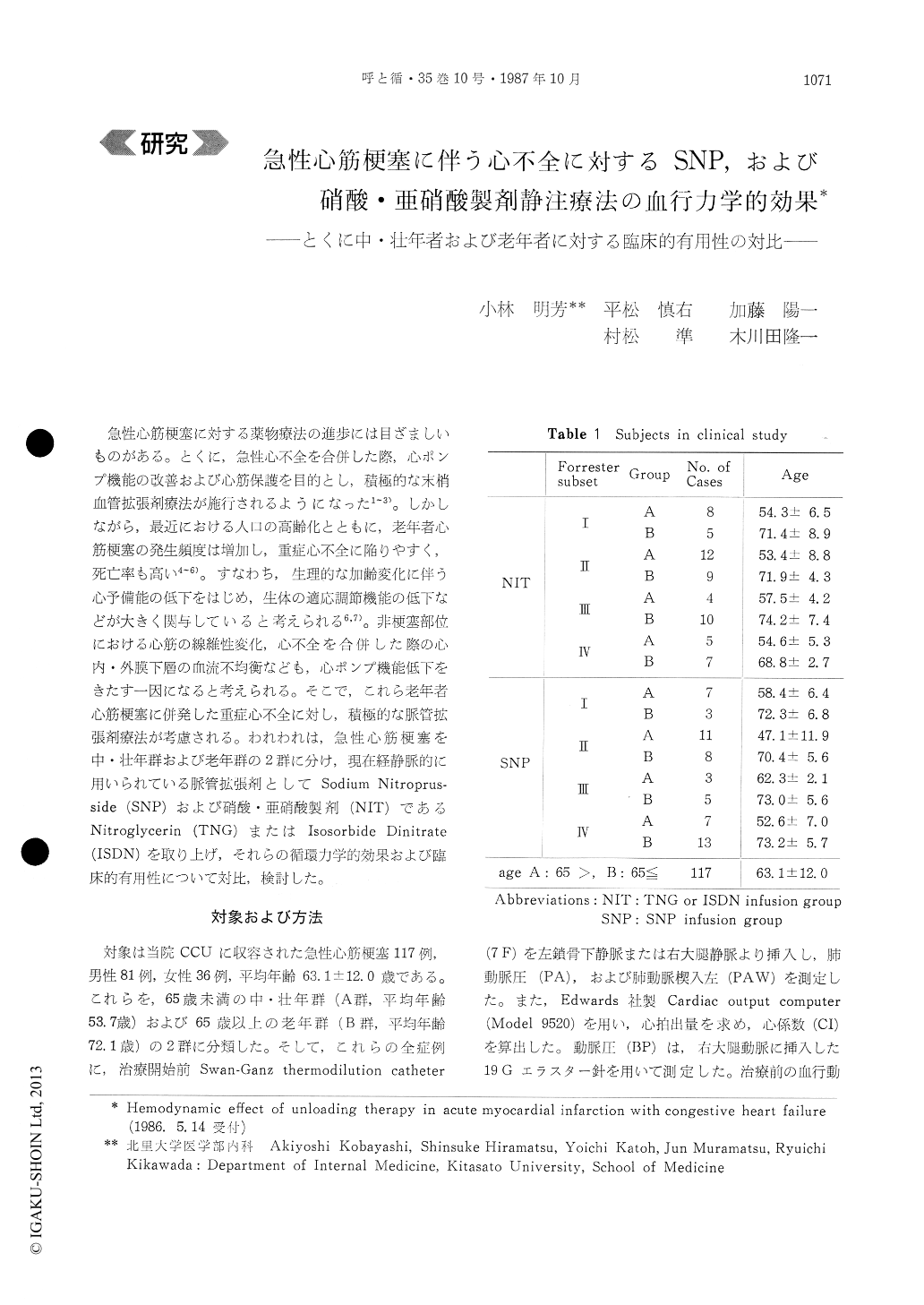
急性心筋梗塞に対する薬物療法の進歩には目ざましいものがある。とくに,急性心不全を合併した際,心ポンプ機能の改善および心筋保護を目的とし,積極的な末梢血管拡張剤療法が施行されるようになった1〜3)。しかしながら,最近における人口の高齢化とともに,老年者心筋梗塞の発生頻度は増加し,重症心不全に陥りやすく,死亡率も高い4〜6)。すなわち,生理的な加齢変化に伴う心予備能の低下をはじめ,生体の適応調節機能の低下などが大きく関与していると考えられる6,7)。非梗塞部位における心筋の線維性変化,心不全を合併した際の心内・外膜下層の血流不均衡なども,心ポンプ機能低下をきたす一因になると考えられる。そこで,これら老年者心筋梗塞に併発した重症心不全に対し,積極的な脈管拡張剤療法が考慮される。われわれは,急性心筋梗塞を中・壮年群および老年群の2群に分け,現在経静脈的に用いられている脈管拡張剤としてSodium Nitroprus—side (SNP)および硝酸・亜硝酸製剤(NIT)であるNitroglycerin (TNG)またはIsosorbide Dinitrate(ISDN)を取り上げ,それらの循環力学的効果および臨床的有用性について対比,検討した。
To evaluate the effectiveness of vasodilator the-rapy in acute myocardial infarction, Nitroglycerine (TNG), Isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN) or Sodium Nit-roprusside (SNP) were administrated by intravenous infusion to 117 patients with congestive heart fai-lure. The patients were divided into two groups according to the age. The elder group (above 65 years old, Group B) consisted of 57 patients and the younger group (below 64, Group A), 60 patients. The hemodynamic parameters were measured by Swan-Ganz catherer before and after therapy. We used also the Forrester classification as hemodyna-mic subset.
After the administration of TNG, ISDN or SNP, pulmonary wedge pressure and systemic vascular resistance decreased significantly in Forrester subset II and IV. In these subsets of Group A, cardiac index elevated from 2. 86±0. 71 to 3. 17.+0. 61, 1.85 ±0. 29 to significant change in that of Group B. On the other hand, after TNG or ISDN injection, cardiac index elevated from 2. 51±0. 24 to 3. 01±0. 43, 1. 94±0. 16 to 2. 59±0.43 l/min/m2 in Forrester subsets II and IV of Group B, respectively.
These fingings suggested that the TNG or ISDN therapy may be suitable for elder patients with congestive heart failure in acute myocardial infarc-tion.
Copyright © 1987, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


