Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
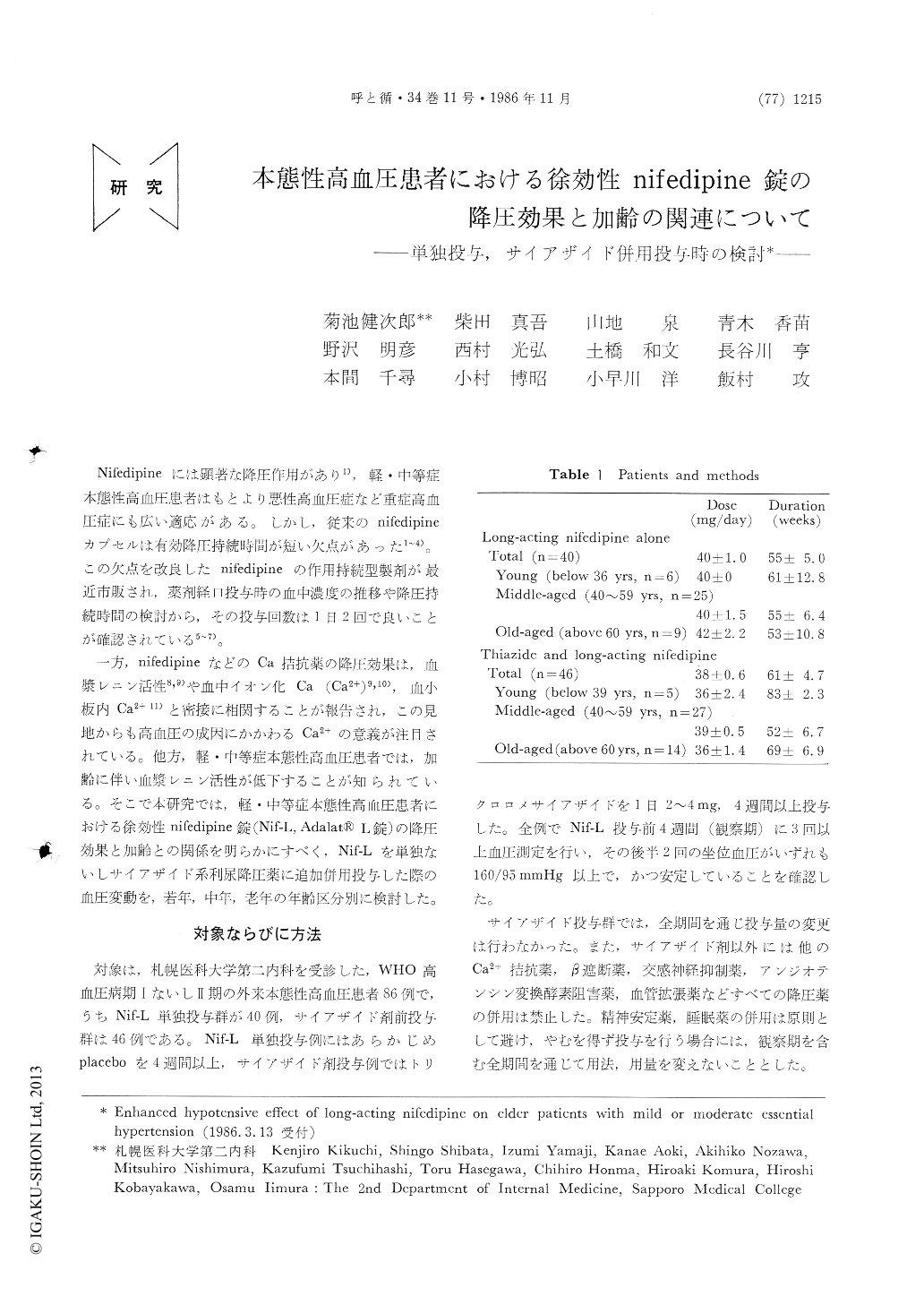
Nifedipineには顕著な降圧作用があり1),軽・中等症本態性高血圧患者はもとより悪性高血圧症など重症高血圧症にも広い適応がある。しかし,従来のnifedipineカプセルは有効降圧持続時間が短い欠点があった1〜4)。この欠点を改良したnifedipineの作用持続型製剤が最近市販され,薬剤経口投与時の血中濃度の推移や降圧持続時間の検討から,その投与回数は1日2回で良いことが確認されている5〜7)。
一方,nifedipineなどのCa拮抗薬の降圧効果は,血漿レニン活性8,9)や血中イオン化Ca (Ca2+)9,10),血小板内Ca2+ 11)と密接に相関することが報告され,この見地からも高血圧の成因にかかわるCa2+の意義が注目されている。他方,軽・中等症本態性高血圧患者では,加齢に伴い血漿レニン活性が低下することが知られている。そこで本研究では,軽・中等症本態性高血圧患者における徐効性nifedipine錠(Nif-L,Adalat®L錠)の降圧効果と加齢との関係を明らかにすべく,Nif-Lを単独ないしサイアザイド系利尿降圧薬に追加併用投与した際の血圧変動を,若年,中年,老年の年齢区分別に検討した。
The antihypertensive efficacy of long-acting nifedipine, monotherapy (n=40) and combined therapy with thia-ride diuretics (n=46), was investigated in young adult (be-low 40 years, n=11), middle-aged (40-59 years, n=52) and elderly (above 60 years, n=23) out-patients with mild or moderate essential hypertension. No significant difference of arterial pressure (MAP) before nifedipine treatment, its dose or the duration of nifedipine therapy was found in the patients receiving monotherapy (126± O.9mmHg, 40±1.Omgjday, 55±5.0 weeks) and those having a combined therapy (126±0.8mmHg, 38±0.6 mg day, 61±4.7 weeks, respectively ). No significant difference in these parameters was also observed among the three age-groups. Mean value of age and the distribution of age were similar in patients receiving monotherapy and combined therapy.
Following nifedipine therapy, the blood pressure significantly (p< 0.001) decreased in all patients' groups. Changes (ΔJMAP 1 and percent changes in MAP (%ΔJMAP) of nifedipine monotherapy (-25±1.1 mmHg,-19.8±0.8%) were more remarkable than those of the combined therapy (-21±1.3mmHg, -16.7±1.0%). Mean values in ΔJMAP and %ΔMAPof combined therapy were significantly greater in the middle-aged (-23±1.7mmHg, p<0.025,-17±1.3%, p<0.05) and elderly patients' group (-22±1.8mmHg, p<0.025,-17±1.2%, p<0.025) than in the young adult group (-12±4.0mmHg,-9.9±3.3%). A simi-lar tendency was observed for monotherapy. Incidence of decrements or % decrements in MAP above 25mmHg or 20% by nifedipine in both monotherapy and com-bined therapy significantly (p<0.05) higher in the older (middle-aged plus elderly) patients (45.3%, 45.3 %, respectively) than in young adult group (9.1%, 9.1%, respectively).
These results indicate that the antihypertensive effi-cacy of long-acting nifedipine was marked in the older essential hypertensives. In addition, the hypotensive response to nifedipine seems to be remarkable in mono-therapy as compared with combined therapy.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


