Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
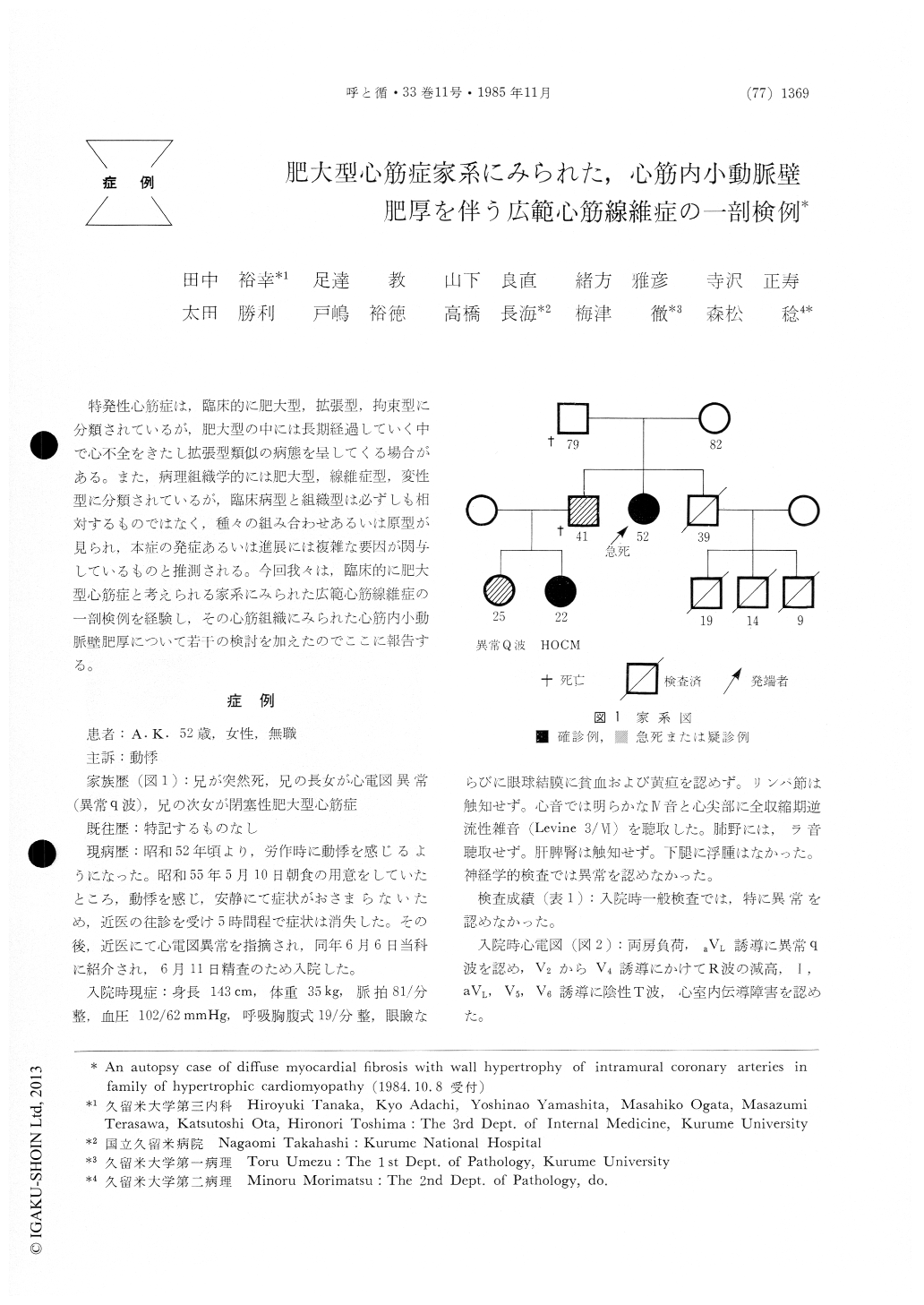
特発性心筋症は,臨床的に肥大型,拡張型.拘束型に分類されているが,肥大型の中には長期経過していく中で心不全をきたし拡張型類似の病態を呈してくる場合がある。また,病理組織学的には肥大型,線維症型,変性型に分類されているが,臨床病型と組織型は必ずしも相対するものではなく.種々の組み合わせあるいは原型が見られ,本症の発症あるいは進展には複雑な要因が関与しているものと推測される。今回我々は,臨床的に肥大型心筋症と考えられる家系にみられた広範心筋線維症の一剖検例を経験し,その心筋組織にみられた心筋内小動脈壁肥厚について若干の検討を加えたのでここに報告する。
An autopsy case of progressed form of hypertro-phic cardiomyopathy showing marked diffuse fibrosis of the myocardium with intimal and medial hyper-trophy of intramural small arteries is presented in this report.
A 52-year-old woman, who had a brother died of sudden death, one niece diagnosed with hyper-trophic obstructive cardiomyopathy confirmedly and another niece with abnormal Q wave on the ECG, was admitted to our hospital because of palpitation. She did not have prior angina pectoris or old myocardial infarction. The chest X-ray film showed cardiomegaly. The ECG revealed ab-normal Q wave in Lead aVL; the R waves low in Leads V2 through V4. The echocardiogram revealed hypokinesis and thinning of the intra-ventricular septum and anterior wall except that the posterior and lateral walls, which were rather thickened, moved normally. The coronary arterio-graphy revealed no significant organic stenosis and the left ventriculogram showed severely reduced motion of the anterior wall of left ventricle. Percu-taneous right ventricular endomyocardial biopsies demonstrated myocellular disarrangement with mod-erate interstitial fibrosis. Finally, the clinical di-agnosis of progressed form of hypertrophic cardio-myopathy was made. Two years and 4 months later, she suffered from irreversible congestive heart failure and fetal ventricular arrhythmia, then she died soon. At necropsy, the interventricular septum and anterior wall were markedly thinned and showed diffuse interstitial fibrosis with thickening of the wall of intramural small coronary arteries. Distributing more compact in the fibrotic area, the thickened small arteries spread over almost entire ventricular walls.
From these observations, we suggested that the presence of thickened small arteries in hypertro-phic cardiomyopathy may be strongly related with certain pathogenesis of cardiomyopathy, and that the progression from typical form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy to dilated one may be accelerated by the decreased intramural blood flow due to narrowing of the lumen of these small arteries.
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


