Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
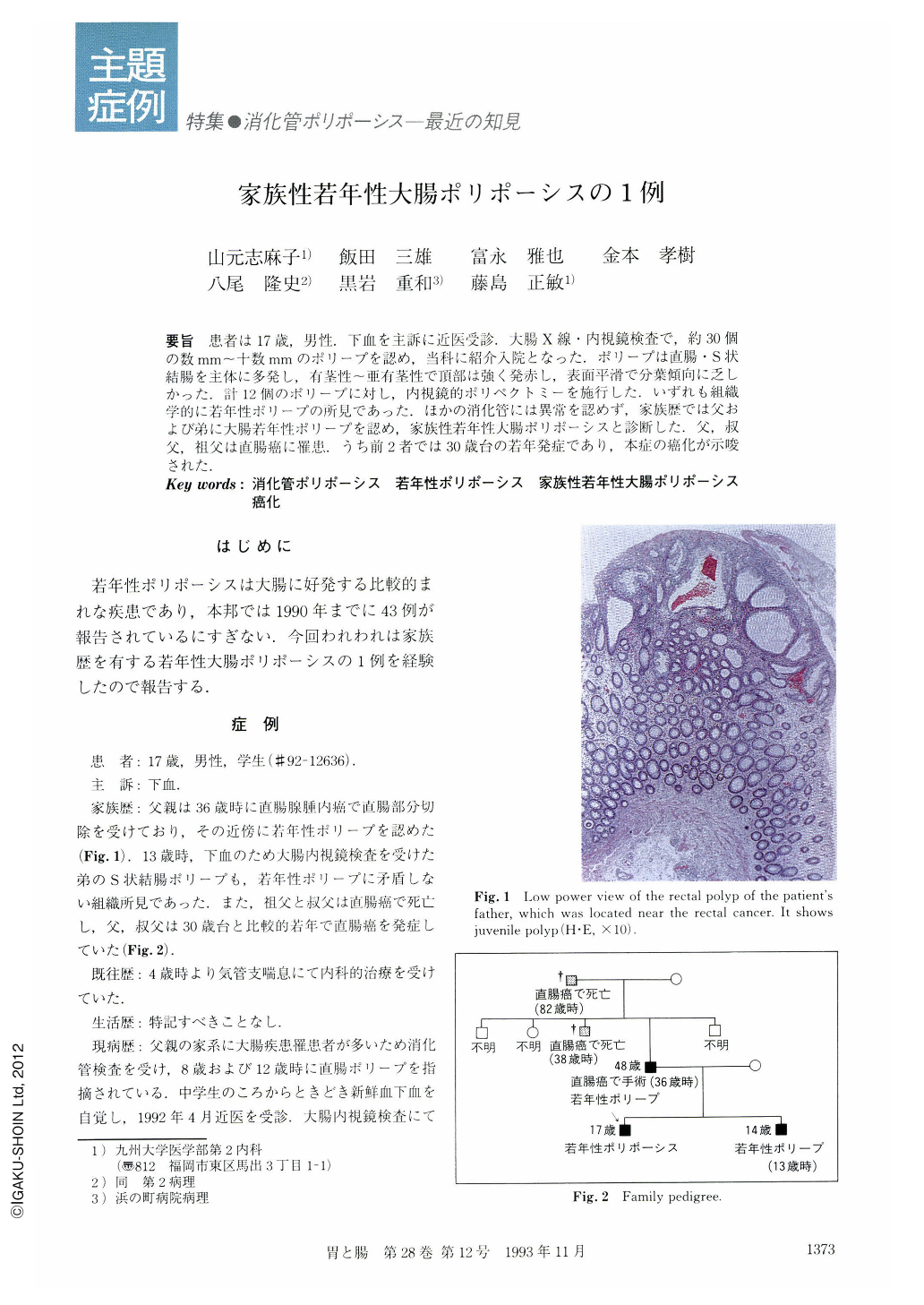
要旨 患者は17歳,男性.下血を主訴に近医受診.大腸X線・内視鏡検査で,約30個の数mm~十数mmのポリープを認め,当科に紹介入院となった.ポリープは直腸・S状結腸を主体に多発し,有茎性~亜有茎性で頂部は強く発赤し,表面平滑で分葉傾向に乏しかった.計12個のポリープに対し,内視鏡的ポリペクトミーを施行した.いずれも組織学的に若年性ポリープの所見であった.ほかの消化管には異常を認めず,家族歴では父および弟に大腸若年性ポリープを認め,家族性若年性大腸ポリポーシスと診断した.父,叔父,祖父は直腸癌に罹患.うち前2者では30歳台の若年発症であり,本症の癌化が示唆された.
A 17-year-old boy visited our hospital because of anal bleeding. Barium enema radiography and colonoscopy showed multiple sessile or pedunculated polyps in the colon and rectum, predominantly in the sigmoid colon and rectum. The polyp had a smooth, reddish surface. Twelve polyps were removed endoscopically. All of these polyps were histologically compatible with juvenile polyposis. There was no polyp in the oter parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Family history revealed that the patient's father and younger brother had undergone endoscopic polypectomy for colonic juvenile polyps. The diagnosis of familial juvenile polyposis coli was confirmed. In addition, his father, uncle, and grandfather had suffered from rectal cancer. Therefore, patients with familial juvenile polyposis coli are considered to require careful periodic gastrointestinal examination because of the high risk of colonic cancer.
Copyright © 1993, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


