Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
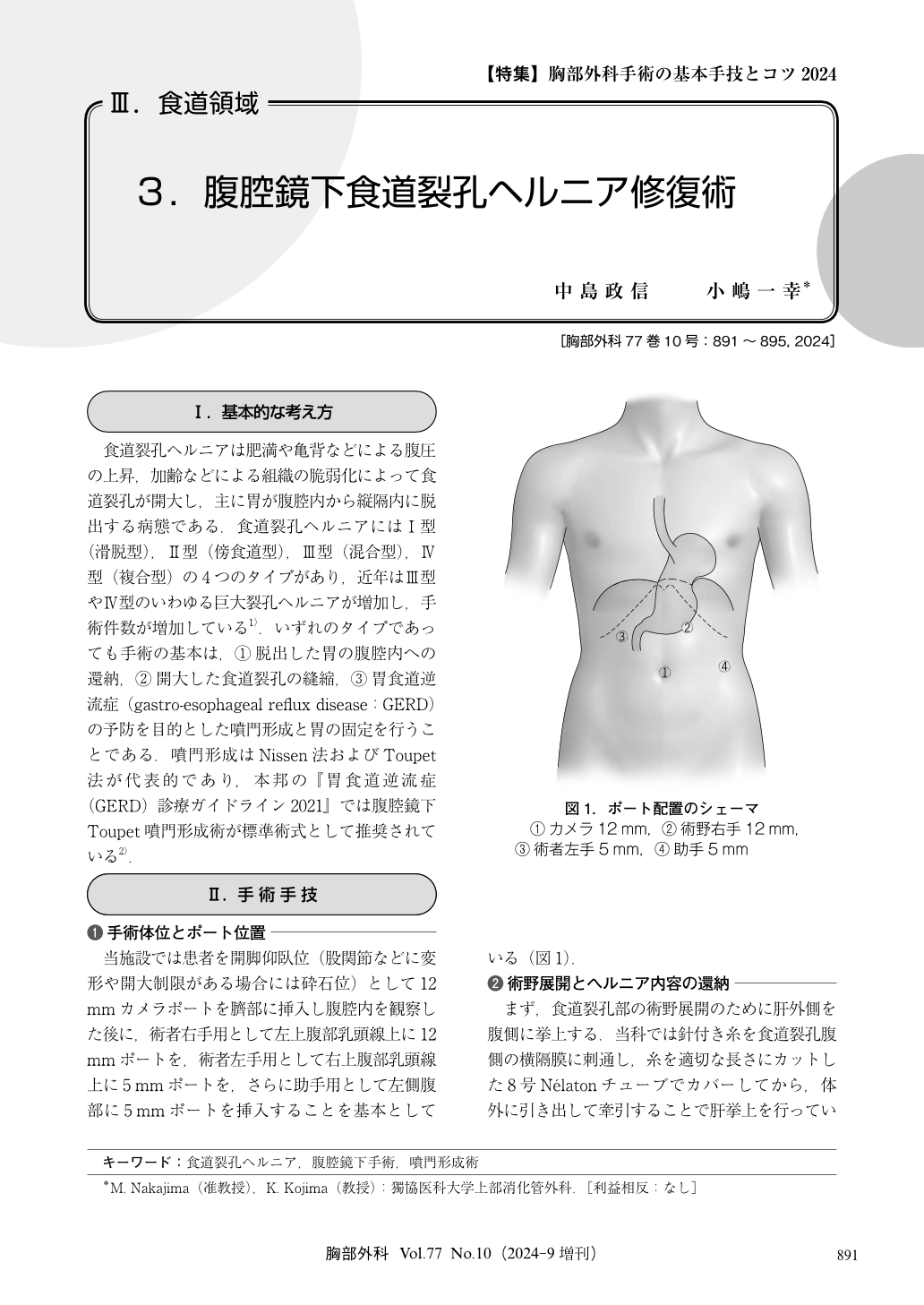
食道裂孔ヘルニアは肥満や亀背などによる腹圧の上昇,加齢などによる組織の脆弱化によって食道裂孔が開大し,主に胃が腹腔内から縦隔内に脱出する病態である.食道裂孔ヘルニアにはⅠ型(滑脱型),Ⅱ型(傍食道型),Ⅲ型(混合型),Ⅳ型(複合型)の4つのタイプがあり,近年はⅢ型やⅣ型のいわゆる巨大裂孔ヘルニアが増加し,手術件数が増加している1).いずれのタイプであっても手術の基本は,①脱出した胃の腹腔内への還納,②開大した食道裂孔の縫縮,③胃食道逆流症(gastro-esophageal reflux disease:GERD)の予防を目的とした噴門形成と胃の固定を行うことである.噴門形成はNissen法およびToupet法が代表的であり,本邦の『胃食道逆流症(GERD)診療ガイドライン2021』では腹腔鏡下Toupet噴門形成術が標準術式として推奨されている2).
Esophageal hiatal hernia is a condition in which the esophageal hiatus opens and the stomach escapes from the abdominal cavity into the mediastinum. The basic surgical procedures are 1) return of the prolapsed stomach into the abdominal cavity, 2) suture of the dilated esophageal hiatus, and 3) fundoplication and fixation of the stomach to prevent gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The Japanese guidelines for the treatment of GERD recommend laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication as the standard procedure, which we also follow. It is important to determine the position of ports by considering the angle at which the esophageal hiatus can be easily approached. The dissection of the hernia sac from the left side enables effective surgical procedure. In Toupet fundoplication, loosening the wrapping for the elderly is important to prevent dysphagia. Postoperative complications include aspiration pneumonia, delayed gastric emptying, and esophageal stricture. It is important to accurately understand the normal anatomy and the situation causing the hernia, and to perform a careful repair operation.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2024


