Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
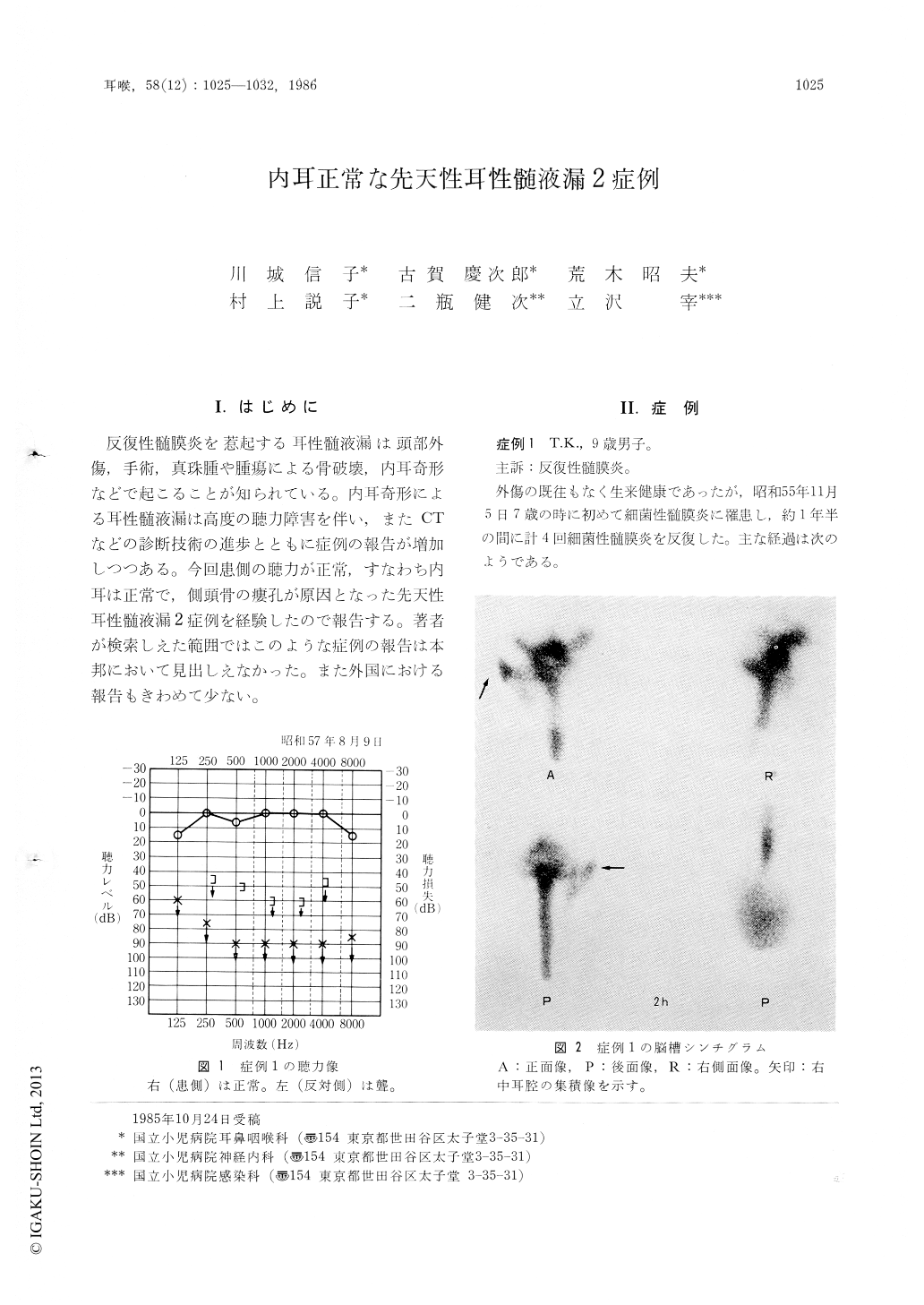
反復性髄膜炎を惹起する耳性髄液漏は頭部外傷,手術,真珠腫や腫瘍による骨破壊,内耳奇形などで起こることが知られている。内耳奇形による耳性髄液漏は高度の聴力障害を伴い,またCTなどの診断技術の進歩とともに症例の報告が増加しつつある。今回患側の聴力が正常,すなわち内耳は正常で,側頭骨の痩孔が原因となった先天性耳性髄液漏2症例を経験したので報告する。署者が検索しえた範囲ではこのような症例の報告は本邦において見出しえなかった。また外国における報告もきわめて少ない。
It has well been known that one of the causes of recurrent meningitis is cerebrospinal otorrhea through the malformed inner ears of Mondini type. We, however, had two cases of congenital cerebrospinal otorrhea with normal hearing acuity, which suggested their labyrinths were normally developed. They suffered from recurrent bacterial meningitis. The cause of recurrent meningitis was infection spread by cerebrospinal otorrhea through a fistula of the temporal bone, which was diagnosed by RI cisternography. A 9-year-old boy had deafness on the non-affected side and the fistula was supposed to be Hyrtl's fissure. He underwent surgery twice without success. A 5-year-old boy had facial paralysis with canal paralysis in the left side. Congenital leakage was occurred through the fistula opening to the facial canal. The fistula was packed with temporal fascia, Lyodura and pieces of bones, and the successful result was obtained.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


