Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
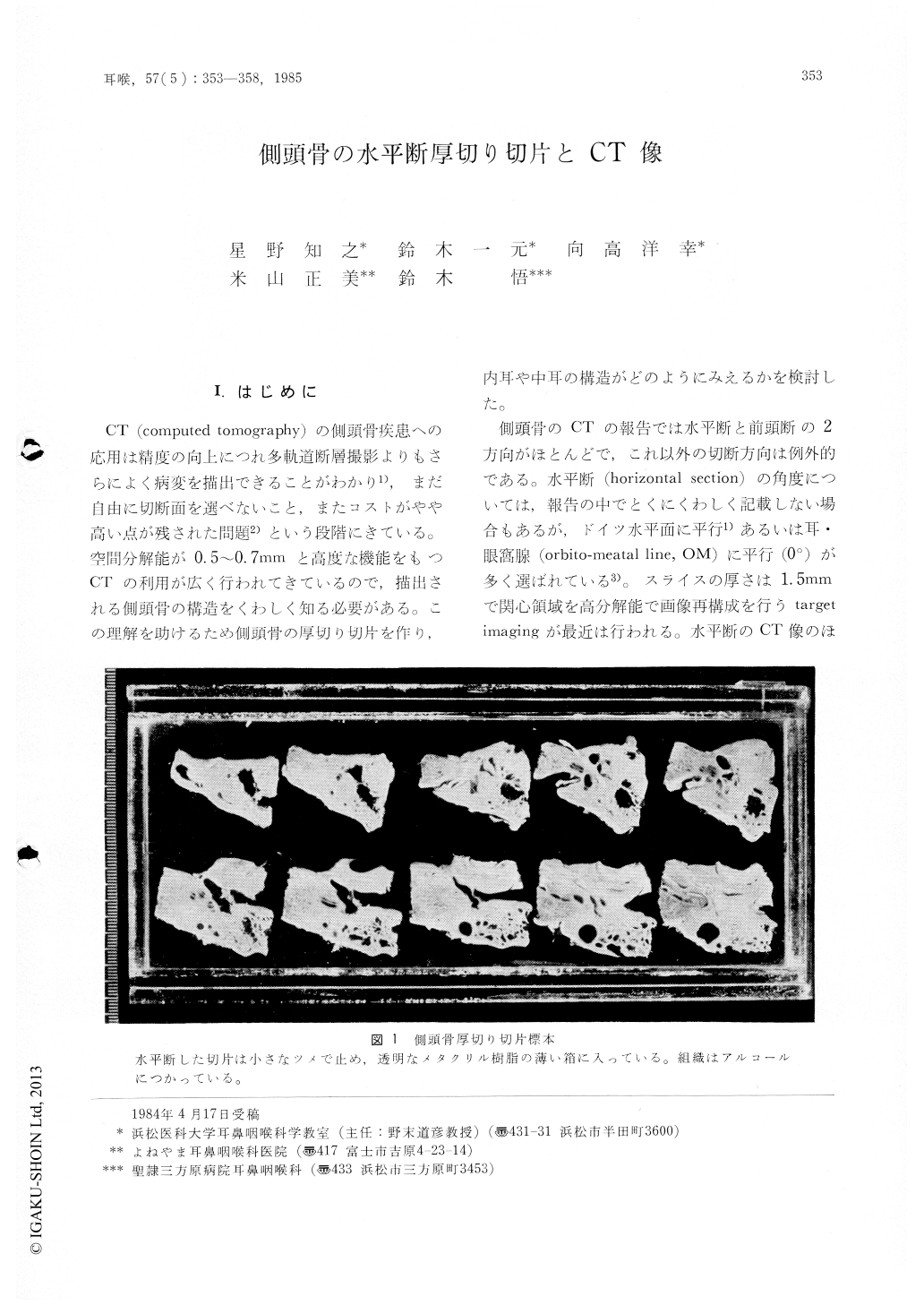
CT(computed tomography)の側頭骨疾患への応用は精度の向上につれ多軌道断層撮影よりもさらによく病変を描出できることがわかり1),まだ自由に切断面を選べないこと,またコストがやや高い点が残された問題2)という段階にきている。空間分解能が0.5〜0.7mmと高度な機能をもつCTの利用が広く行われてきているので,描出される側頭骨の構造をくわしく知る必要がある。この理解を助けるため側頭骨の厚切り切片を作り,内耳や中耳の構造がどのようにみえるかを検討した。
側頭骨のCTの報告では水平断と前頭断の2方向がほとんどで,これ以外の切断方向は例外的である。水平断(horizontal section)の角度については,報告の中でとくにくわしく記載しない場合もあるが,ドイツ水平面に平行1)あるいは耳・眼窩腺(orbitomeatal line,OM)に平行(0°)が多く選ばれている3)。スライスの厚さは1.5mmで関心領域を高分解能で画像再構成を行うtargetimagingが最近は行われる。水平断のCT像のほとんどに共通する目立つ点は外側半規管が全周にわたり横断されその輪が広い前庭腔に開くのがみられることである(図3A)。したがって標本の切断面は外側半規管が水平に切り出される角度を選び厚さはCTと同じ1.5mmとした。
A temporal bone specimen was sliced horizontally into sections of 1.5mm thickness, and each section was compared with CT images taken in the same plane and of the same thickness. Before cutting, the temporal bone was embedded in celloidin, and these sections showed excellent preservation of membranous structures. Target imaging CT pictures were taken by a GE CT/T 8800 at a CT number range of-1000-+2500 with a window width of 4000. The CT pictures of 9 normal ears were compared to the temporal bone sections. Most structures appearing in the pictures were found to correspond with the structures in the histological sections, except for the jugular bulb and the external auditory meatus which showed considerable individual variation.
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


