Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.緒言
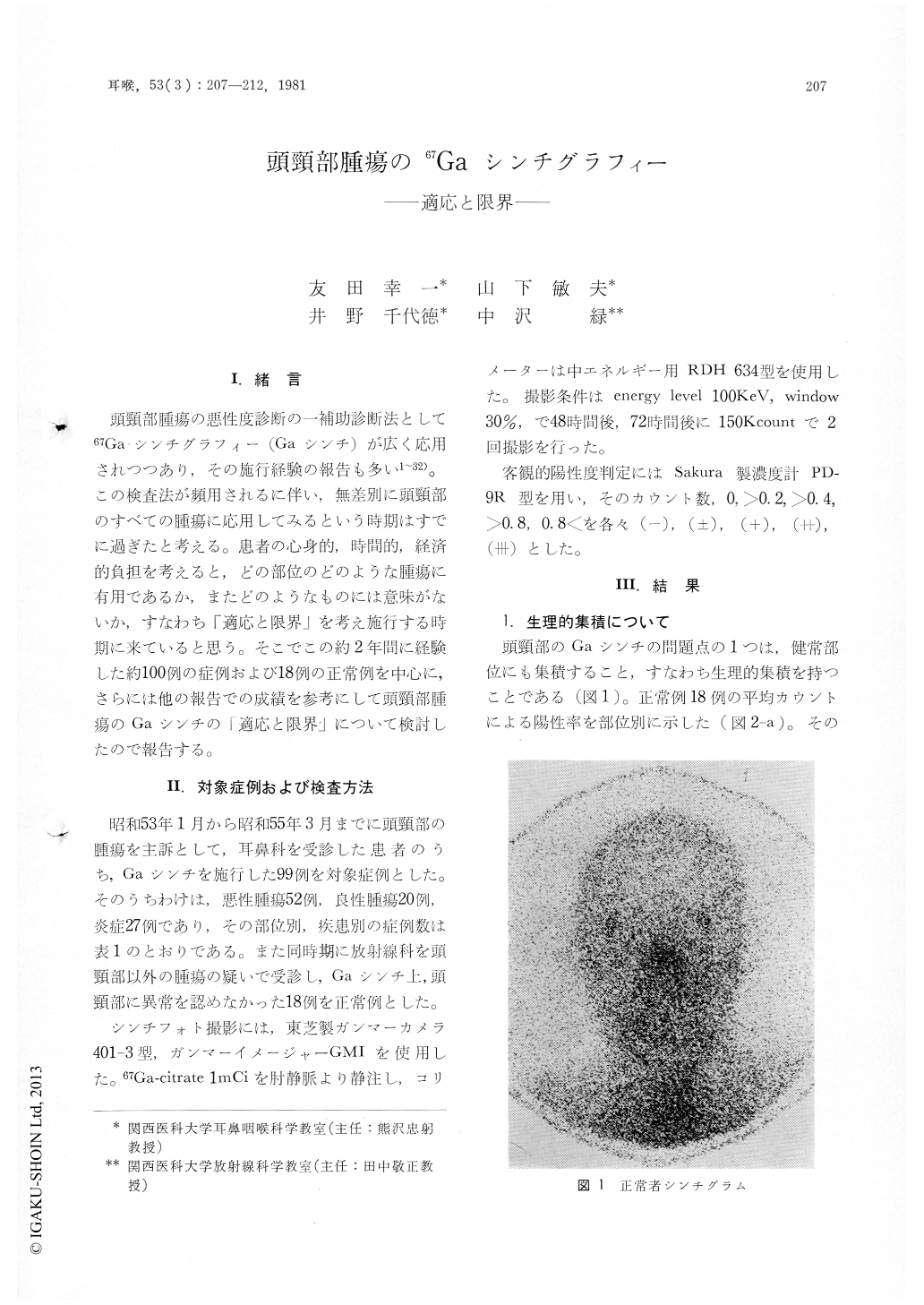
頭頸部腫瘍の悪性度診断の補助診断法として67Gaシンチグラフィー(Gaシンチ)が広く応用されつつあり,その施行経験の報告も多い1〜32)。この検査法が頻用されるに伴い,無差別に頭頸部のすべての腫瘍に応用してみるという時期はすでに過ぎたと考える。患者の心身的,時間的,経済的負担を考えると,どの部位のどのような腫瘍に有用であるか,またどのようなものには意味がないか,すなわち「適応と限界」を考え施行する時期に来ていると思う。そこでこの約2年間に経験した約100例の症例および18例の正常例を中心に,さらには他の報告での成績を参考にして頭頸部腫瘍のGaシンチの「適応と限界」について検討したので報告する。
67 Ga-scintigraphy (Ga-Scin) was used to confirm the diagnosis of head and neck tumors in 99 patients. Scintigraphic accuracy in tumor diagnosis and location ("positive-rate") was evaluated.
Total body scans of patients without tumor in the head and neck provided "control" information on physiological accumulation of 67Ga in this area. High "positive rate" was recorded in malignant tumors of the parotid glands or other organs.
Considering "positive rate" in conjunction with other diagnostic methods and in a context of determined physiological accumulation, Ga-Scin is indicated in the evaluation of head and neck tumors as follows : 1. Parotid gland tumors, tumors of the neck, and suspected malignant lymphomas are the best subjects for Ga-Scin. 2. Ga-Scin is of limited use in tumors of the paranasal sinuses and thyroid gland. 3. Ga-Scin is of little value in tumors of the nasal cavity, tongue, oral cavity, pharynx and larynx.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


