Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
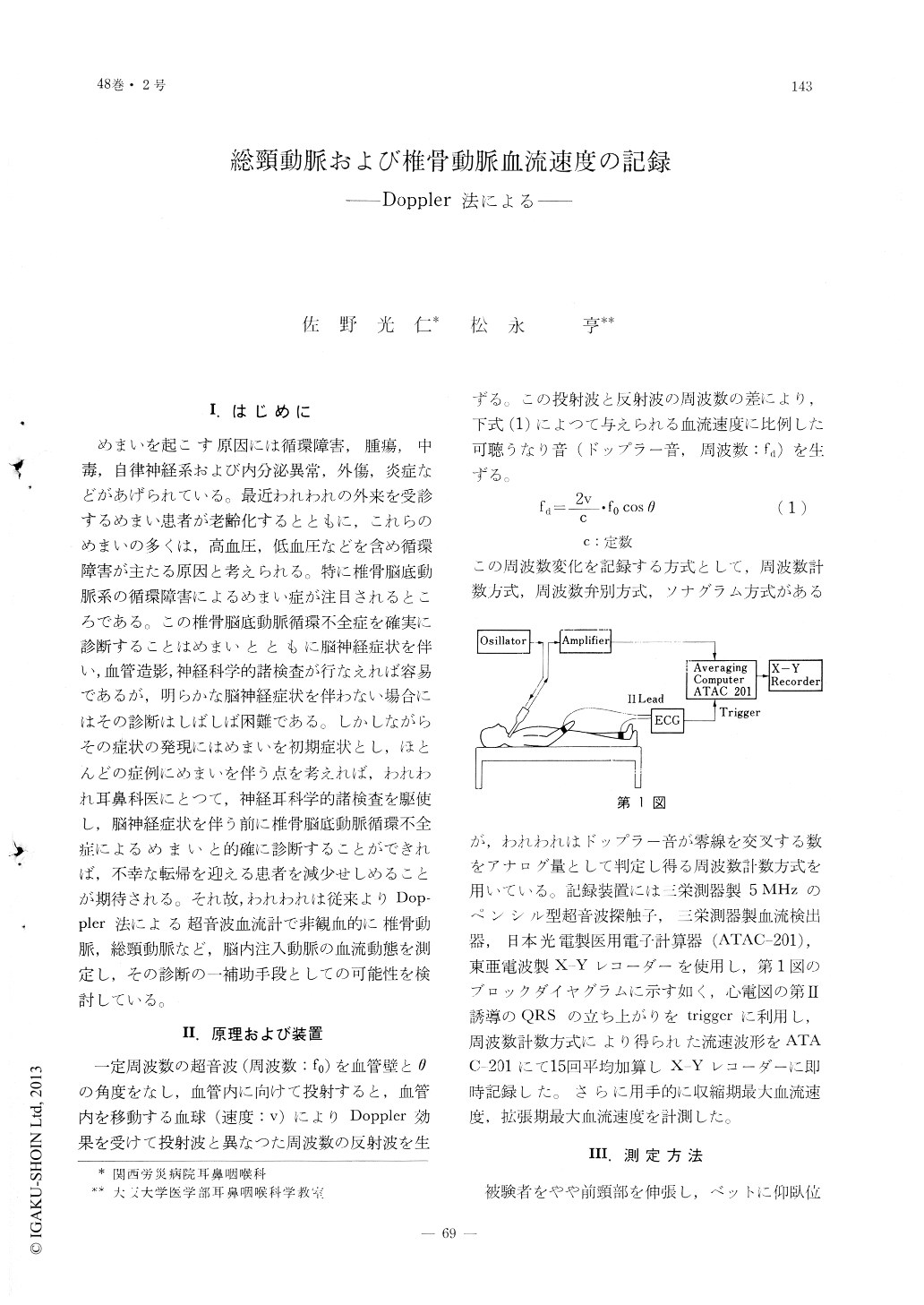
めまいを起こす原因には循環障害,腫瘍,中毒,自律神経系および内分泌異常,外傷,炎症などがあげられている。最近われわれの外来を受診するめまい患者が老齢化するとともに,これらのめまいの多くは,高血圧,低血圧などを含め循環障害が主たる原因と考えられる。特に椎骨脳底動脈系の循環障害によるめまい症が注目されるところである。この椎骨脳底動脈循環不全症を確実に診断することはめまいとともに脳神経症状を伴い,血管造影,神経科学的諸検査が行なえれば容易であるが,明らかな脳神経症状を伴わない場合にはその診断はしばしば困難である。しかしながらその症状の発現にはめまいを初期症状とし,ほとんどの症例にめまいを伴う点を考えれば,われわれ耳鼻科医にとつて,神経耳科学的諸検査を駆使し,脳神経症状を伴う前に椎骨脳底動脈循環不全症によるめまいと的確に診断することができれば,不幸な転帰を迎える患者を減少せしめることが期待される。それ故,われわれは従来よりDoppler法による超音波血流計で非観血的に椎骨動脈,総頸動脈など,脳内注入動脈の血流動態を測定し,その診断の一補助手段としての可能性を検討している。
The velocity of the blood flow in the common carotid and vertebral arteries was measured in 29 healthy persons and 38 vertiginous patients by means of ultrasonic doppler method. The blood flow waves averaged 15 times with medical computer (ATAC-201 NIHONKODEN), using the spike of QRS as a trigger. In healthy individuals the maximum velocity in the common carotid artery was 60.9±15.5 cm/sec on the right side and 58.9± 12.8 cm/sec on the left; the diastolic velocity was 14.4±5.9 cm/sec and 13.1±4.3 cm/sec. In the vertebral artery the maximum systolic velocity was 13.6±5.9 cm/sec on the right side and 13.8±6.0 cm/sec on the left. The diastolic velocity was 7.1 ± 3.1 cm/sec and 7.2±3.1 cm/sec.
From the measurement of the velocity of the blood flow in the vertebral arteries there were no difference in the control group and of the vertiginous.
Copyright © 1976, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


