Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
Ⅰ.緒言
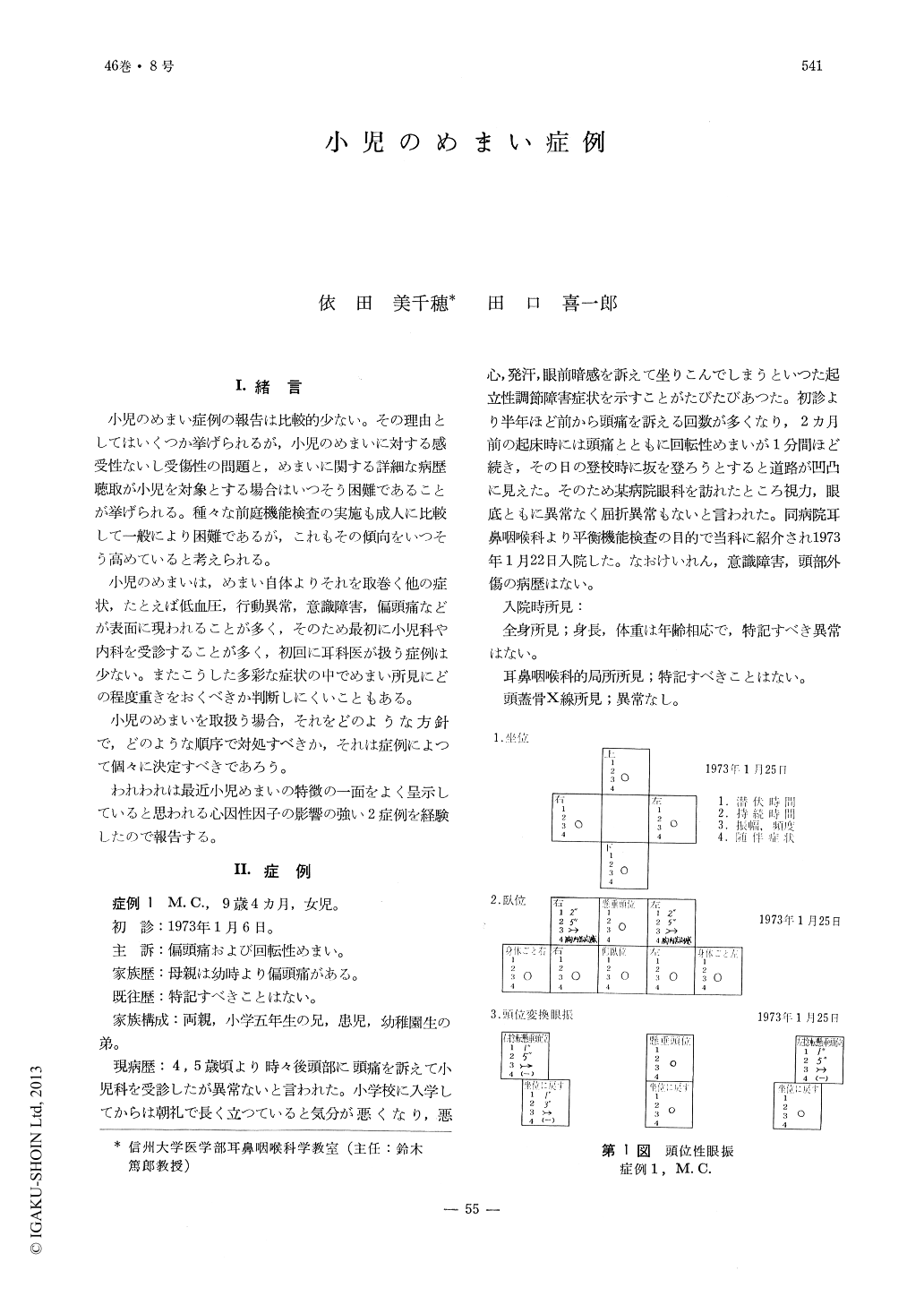
小児のめまい症例の報告は比較的少ない。その理由としてはいくつか挙げられるが,小児のめまいに対する感受性ないし受傷性の問題と,めまいに関する詳細な病歴聴取が小児を対象とする場合はいつそう困難であることが挙げられる。種々な前庭機能検査の実施も成人に比較して一般により困難であるが,これもその傾向をいつそう高めていると考えられる。
小児のめまいは,めまい自体よりそれを取巻く他の症状,たとえば低血圧,行動異常,意識障害,偏頭痛などが表面に現われることが多く,そのため最初に小児科や内科を受診することが多く,初回に耳科医が扱う症例は少ない。またこうした多彩な症状の中でめまい所見にどの程度重きをおくべきか判断しにくいこともある。
小児のめまいを取扱う場合,それをどのような方針で,どのような順序で対処すべきか,それは症例によつて個々に決定すべきであろう。
われわれは最近小児めまいの特徴の一面をよく呈示していると思われる心因性因子の影響の強い2症例を経験したので報告する。
Two cases of vertigo due to psychogenic origin in young children are reported.
In the first case, aged 9, who had frequent attacks of migraine headache was suddenly affected with vertigo. The EEG taken during the patient's light sleep showed high voltage with slow waves which pointed to epilepsy. Psychiatric study of the patient disclosed that her affections were due to disturbed emotion caused by absence of the parents from the home during theday. Shortening of the mother's working hours brought recovery of the patient's health.
The second case a girl, aged 9, had transient vertigo and blackout on several occasions. The attacks were considered as of psychogenic inorigin because they had occurred since the parents were divorced from each other.
Both cases were considered as manifest dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Copyright © 1974, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


