Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
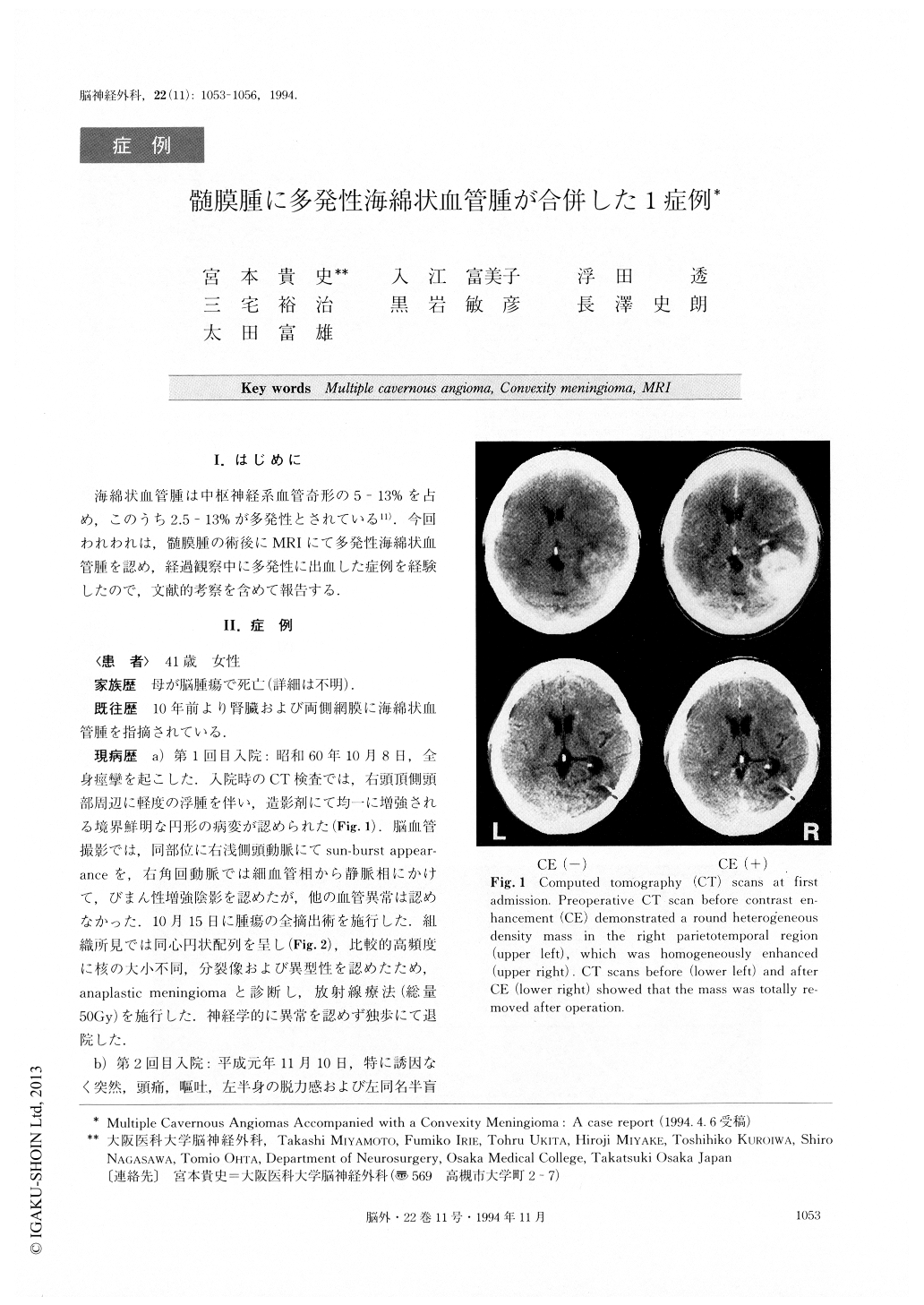
海綿状血管腫は中枢神経系血管奇形の5-13%を占め,このうち2.5-13%が多発性とされている11).今回われわれは,髄膜腫の術後にMRIにて多発性海綿状血管腫を認め,経過観察中に多発性に出血した症例を経験したので,文献的考察を含めて報告する.
We reported a rare case of multiple cavernous angioma accompanied with a convexity meningioma.
A 41-year-old female developed generalized convul-sion on October 8, 1985. Plain computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a round heterogeneous density mass in the right parietotemporal region, which was homogeneously enhanced. Angiography demonstrated a tumor stain fed by the right angular artery and the posterior branch of the right middle meningeal artery. Total removal of the tumor was performed. Since histo-logical examination disclosed meningothelial cells, whorl formation, polymorphism and necrotic tissue, she received radiation therapy (total 50Gy) under the di-agnosis of anaplastic meningioma.
On November 10, 1988, she suddenly developed headache, nausea, motor weakness and homonymous hemianopia on the left side. CT scan revealed in-tracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) near the region where the meningioma used to be. Magnetic resonance image (MRI) demonstrated a high intensity mass at T1-weighted image and mixed intensity mass at T2-weighted image. Furthermore, there were multiple low intensity spotty lesions at the cerebral and cerebellar hemisphere in T1 and T2-weighted image. A few parts of these lesions showed central high intensity cores and perifocal low intensity areas, which were called ring formations or reticulated cores with black rims. The multiple lesions could not be detected by CT scan. ICH was evacuated. Histological examination revealed no specific pathology except necrotic tissue around the hematoma wall. Diagnosis of radiation necrosis was made.
On October 25, 1992 she suddenly complained of left hemihypesthesia. CT scan demonstrated two high den-sity spotty areas at the left caudate head and right thalamus. MRI showed these two lesions as reticulated cores with black rims. Stereotaxic biopsy was perform-ed at right frontal lobe, and cavernous angioma was confirmed histologically.
We followed this case with multiple cavernous angio-mas for 7 years. Two cavernous angiomas yielded minor hemorrhages although the sizes of the non-hemorrhagic cavernomas changed little. MRI is much more sensitive and useful than CT scan in order to de-tect and observe the change of cavernous angioma.
Copyright © 1994, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


