Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
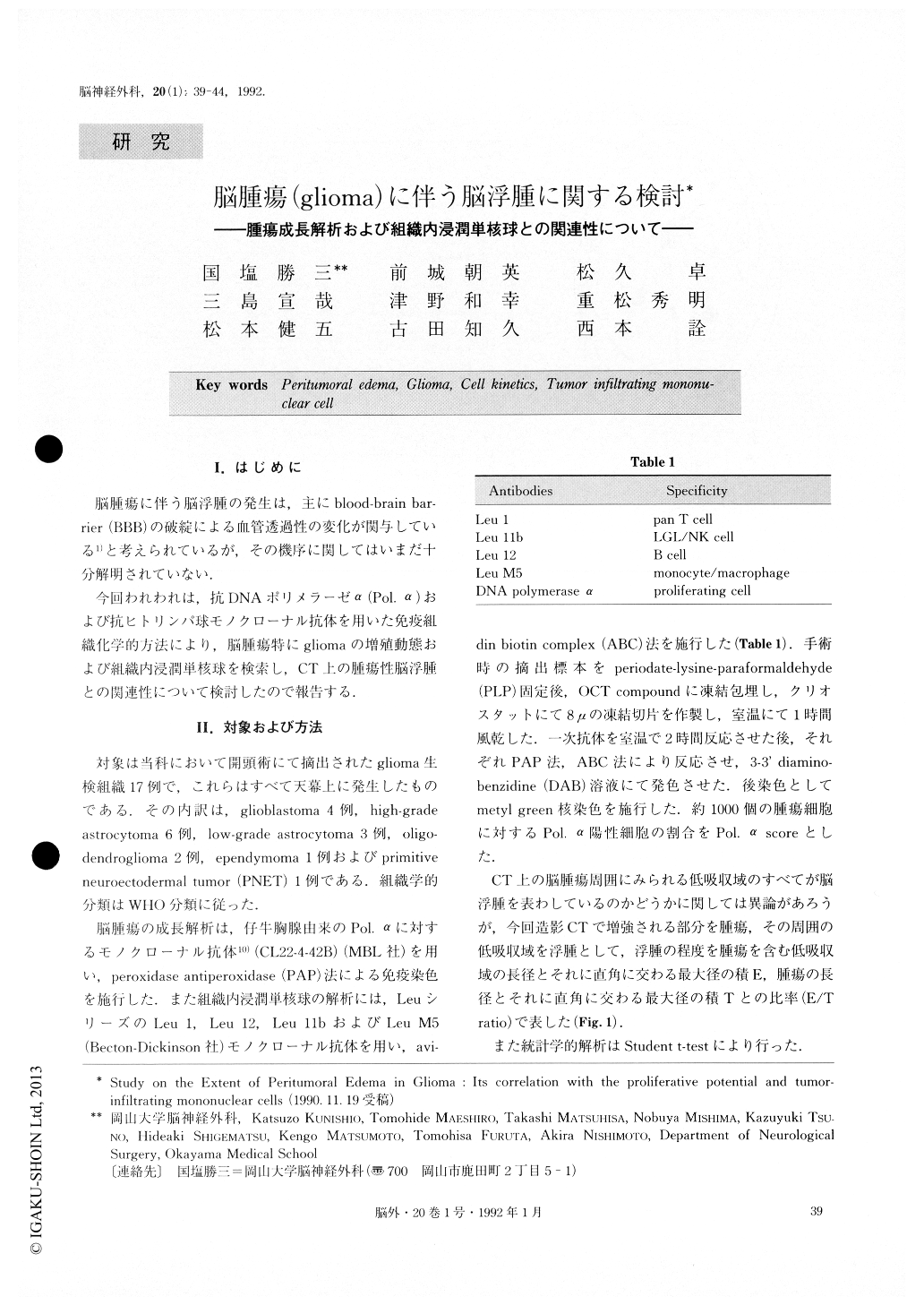
I.はじめに
脳腫瘍に伴う脳浮腫の発生は,主にblood-brain bar—rier(BBB)の破綻による血管透過性の変化が関与している1)と考えられているが,その機序に関してはいまだ十分解明されていない.
今回われわれは,抗DNAポリメラーゼα(Pol.α)および抗ヒトリンパ球モノクローナル抗体を用いた免疫組織化学的方法により,脳腫瘍特にgliomaの増殖動態および組織内浸潤単核球を検索し,CT上の腫瘍性脳浮腫との関連性について検討したので報告する.
The correlation between the extent of peritumoral edema and the proliferative potential or the infiltration of mononuclear cells was studied in 17 gliomas. The peritumoral edema was evaluated on contrast enhanced CT scan as the ratio of the low density area around the tumor to the enhanced high density area. The prolifera-tive potential and the infiltration of mononuclear cellsinto the tumor were investigated immunohistochemical-ly using monoclonal antibody (MAb) against DNA polymerase a and anti-Leu MAb's respectively.
There was a significant correlation between the ex-tent of the peritumoral edema and the percentage of DNA polymerase a positive cells. The degree of the in-filtration of mononuclear cells into the tumor tissue also correlated with the extent of peritumoral edema. In gliomas with high poliferative potential and/or se-vere infiltration of mononuclear cells, the peritumoral edema may be aggravated by disruption of the blood-brain-barrier and increased vascular permeability.
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


