Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
近年の新生児医療の発展のなかでもとりわけ呼吸窮追症候群(以下RDS)に対する治療成績の向上は目覚しく,低出生体重児の生存率が飛躍的に上昇した.従来,救命不可能とされた低出生体重児のうちでも最近では1000g以下の超未熟児が後遺症なく生存可能となっている12).これに伴い超未熟児水頭症にも,その中枢神経系機能障害を改善するために神経外科医が対応せざるをえない現況となってきた.私たちは従来より新生児水頭症患児に出生直後の暫定的な頭蓋内圧のコントロール法として,miniature Ommaya's reservoir(富士システムズKK,Fig.1A)を設置し髄液排除を行ってきた9,10).本法を超未熟児水頭症に試み,現在まで出生体重996g,966gの胎児水頭症患児2例と,802g,926g,963gの脳室内出血後水頭症患児3例の合計5症例を経験した.
Abstract
Use of the miniature Ommaya's reservoir in the treatment of extremely low birth-infant (under 1,000mg) with hydrocephalus was studied in a series of five patients. The reservoir has a small-caliber with a 3cm ventricular catheter. For these infants, this minia-ture Ommaya's reservoir is extremely useful for protec-tion of the cortical mantle until a definitive procedure can be carried out after increase of body weight. The clinical course in five cases are summarized.
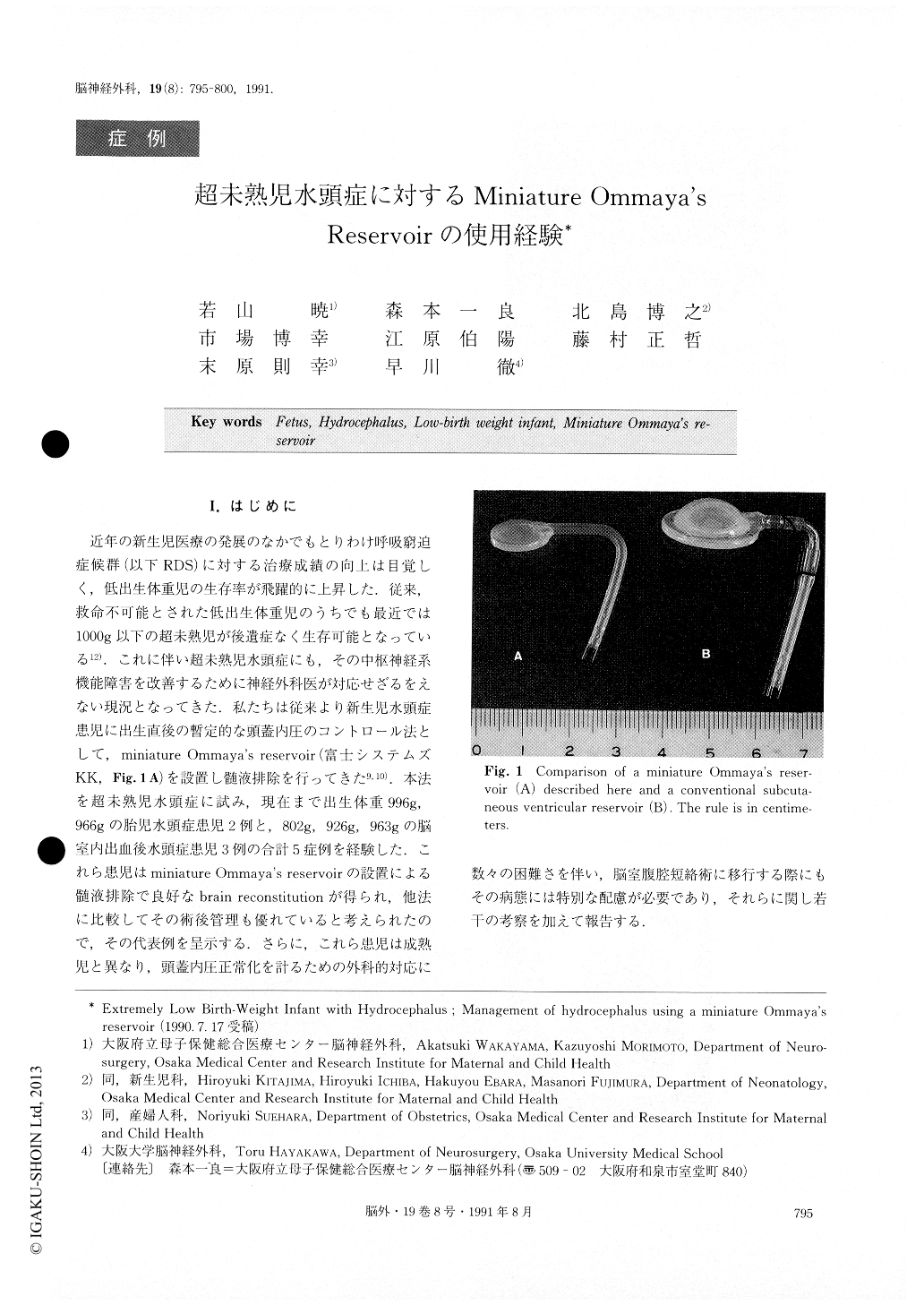
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


