Japanese
English
研究
脳組織に対する放射線化学療法の影響—Positron Emission Tomography(PET)による経時的評価
Radiochemotherapy-relatecl Changes in the Brain Parenchyma of Glioma Patients Evaluated Repeatedly by C15O2, C15O, 15O2, and18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET
峯浦 一喜
1
,
須田 良孝
1
,
笹嶋 寿郎
1
,
古和田 正悦
1
,
小川 敏英
2
,
宍戸 文男
3
,
上村 和夫
3
Katsuyoshi MINEURA
1
,
Yoshitaka SUDA
1
,
Toshio SASAJIMA
1
,
Masayoshi KOWADA
1
,
Toshihide OGAWA
2
,
Fumio SHISHIDO
3
,
Kazuo UEMURA
3
1秋田大学脳神経外科
2秋田大学放射線科
3秋田県立脳血管研究センター放射線科
1Neurosurgical Service, Akita University Hospital
2Department of Radiology Akita University Hospital
3Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Research Institute for Brain and Blood Vessels-Akita
キーワード:
Gliomas
,
Brain parenchyma
,
Positron emission tomography(PET)
,
Radiochemotheraby
,
Metabolism
Keyword:
Gliomas
,
Brain parenchyma
,
Positron emission tomography(PET)
,
Radiochemotheraby
,
Metabolism
pp.945-952
発行日 1989年10月10日
Published Date 1989/10/10
DOI https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1436202898
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
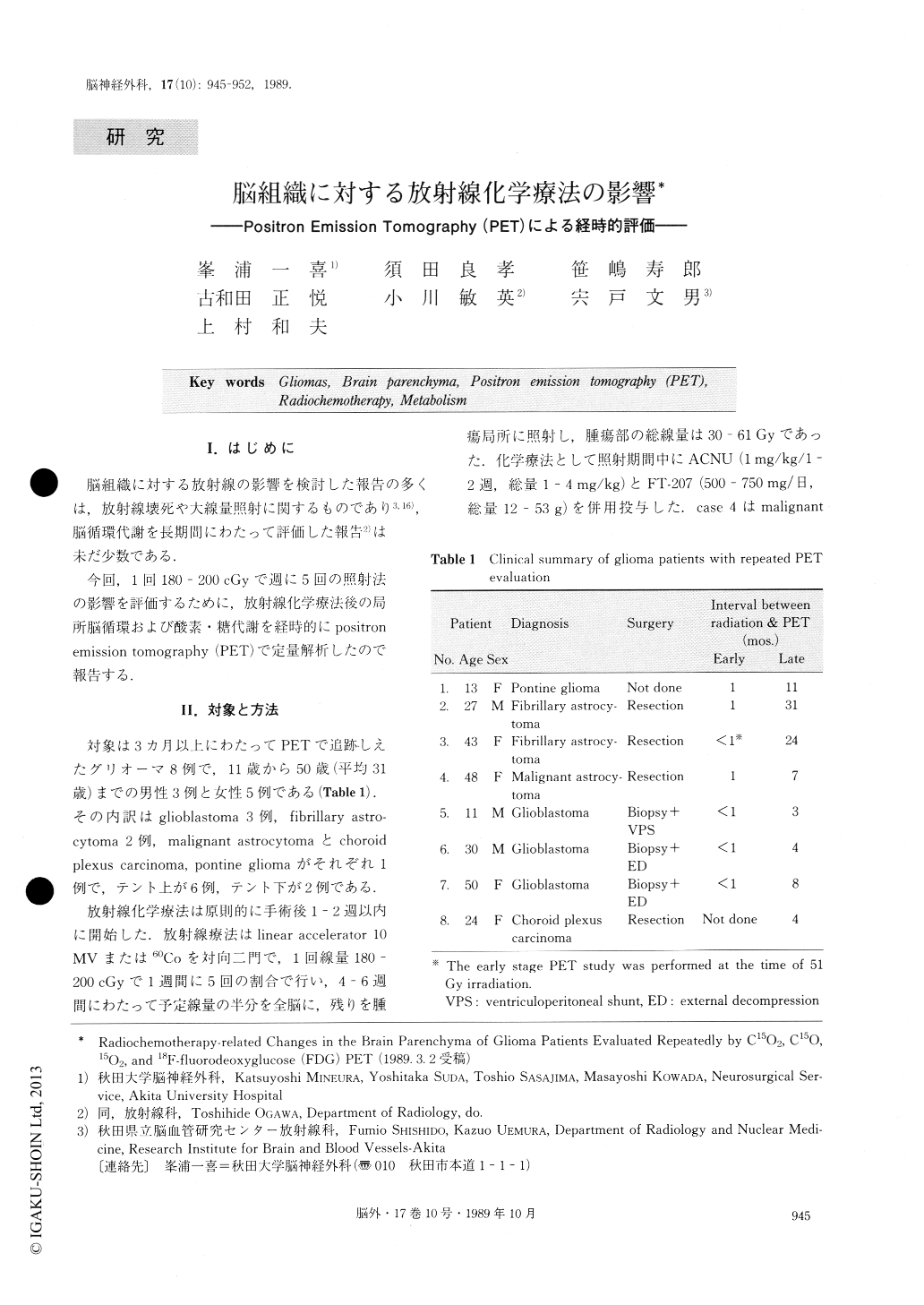
脳組織に対する放射線の影響を検討した報告の多くは,放射線壊死や大線量照射に関するものであり3,16),脳循環代謝を長期間にわたって評価した報告2)は未だ少数である.
今回,1回180-200cGyで週に5回の照射法の影響を評価するために,放射線化学療法後の局所脳循環および酸素・糖代謝を経時的にpositronemission tomography(PET)で定量解析したので報告する.
The aim of this study was to evaluate effects of radiochemotherapy on blood flow and metabolism using C15O2, C15O, 15O2 and and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET).
Conventional, external radiotherapy (180-200 cGy/5 fractions/week) using 60Co or a 10MV linear accelerator was given in conjunction with chemotherapy of nimustine hydrochloride (ACNU) and tegafur (FT-207) in eight patients with gliomas.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


