Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
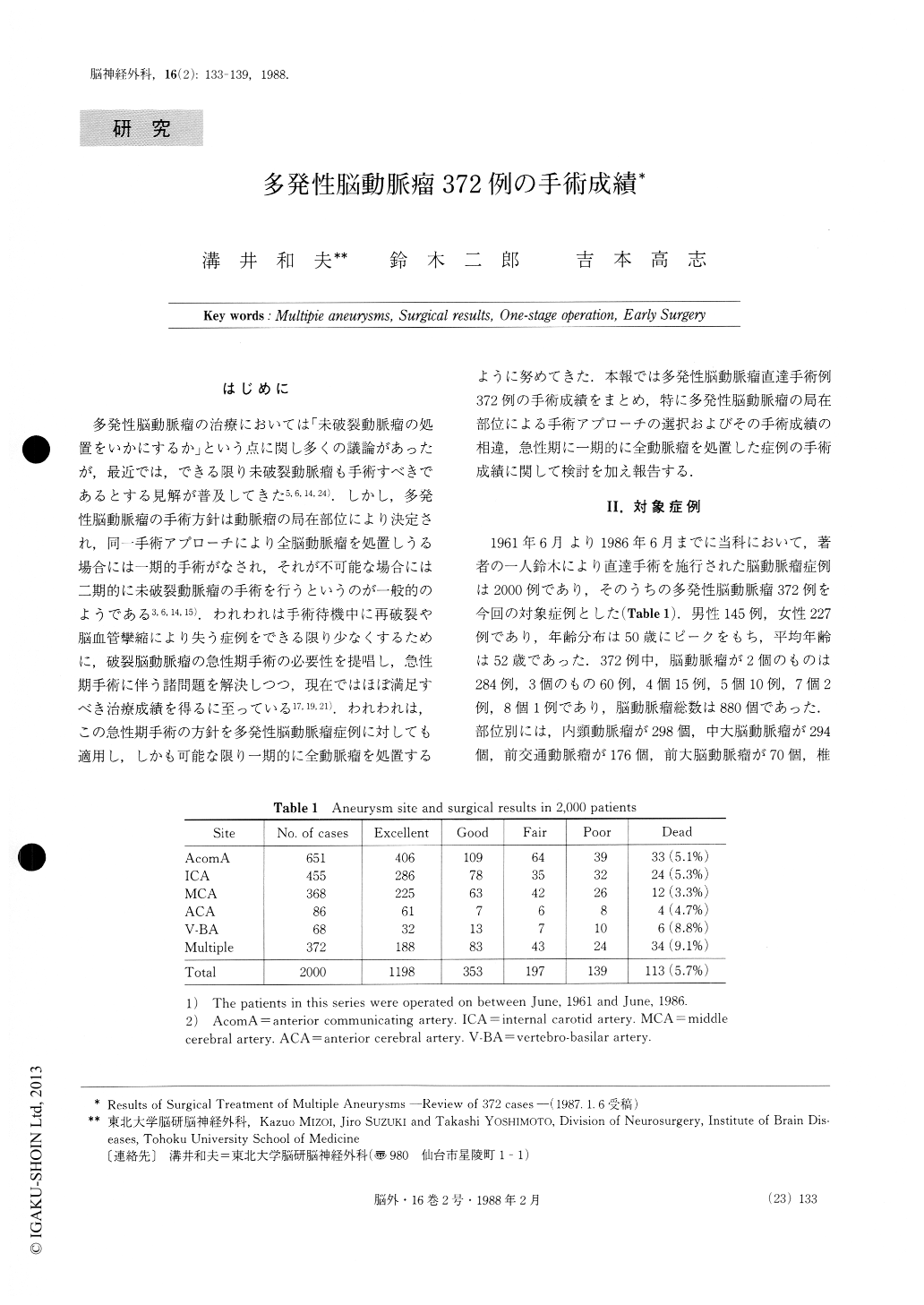
多発性脳動脈瘤の治療においては「未破裂動脈瘤の処置をいかにするか」という点に関し多くの議論があったが,最近では,できる限り未破裂動脈瘤も手術すべきであるとする見解が普及してきた5,6,14,24).しかし,多発性脳動脈瘤の手術方針は動脈瘤の局在部位により決定され,同一手術アプローチにより全脳動脈瘤を処置しうる場合には一期的手術がなされ,それが不可能な場合には二期的に未破裂動脈瘤の手術を行うというのが一般的のようである3,6,14,15).われわれは手術待機中に再破裂や脳血管攣縮により失う症例をできる限り少なくするために,破裂脳動脈瘤の急性期手術の必要性を提唱し,急性期手術に伴う諸問題を解決しつつ,現在ではほぼ満足すべき治療成績を得るに至っている17,19,21).われわれは,この急性期手術の方針を多発性脳動脈瘤症例に対しても適用し,しかも可能な限り一期的に全動脈瘤を処置するように努めてきた.本報では多発性脳動脈瘤直達手術例372例の手術成績をまとめ,特に多発性脳動脈瘤の局在部位による手術アプローチの選択およびその手術成績の相違,急性期に一期的に全動脈瘤を処置した症例の手術成績に関して検討を加え報告する.
The authors review the surgical results in 372 cases of multiple intracranial aneurysms during this 25-year period in which one of the authors (JS) performed 2.000 direct operations for aneurysms. All patients were classified into four groups according to the location of aneurysms as follows : Group 1 : multiple aneurysms including anterior communicating artery aneurysm (157 cases) ; Group 2 : multiple aneurysms of unilateral anterior circulation (72 cases) ; Group 3 : multiple aneurysms of bilateral anterior circulation (110 cases) ; Group 4 : multiple aneurysms including vertebrobasilar artery aneurysms ( 33 cases).
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


