Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
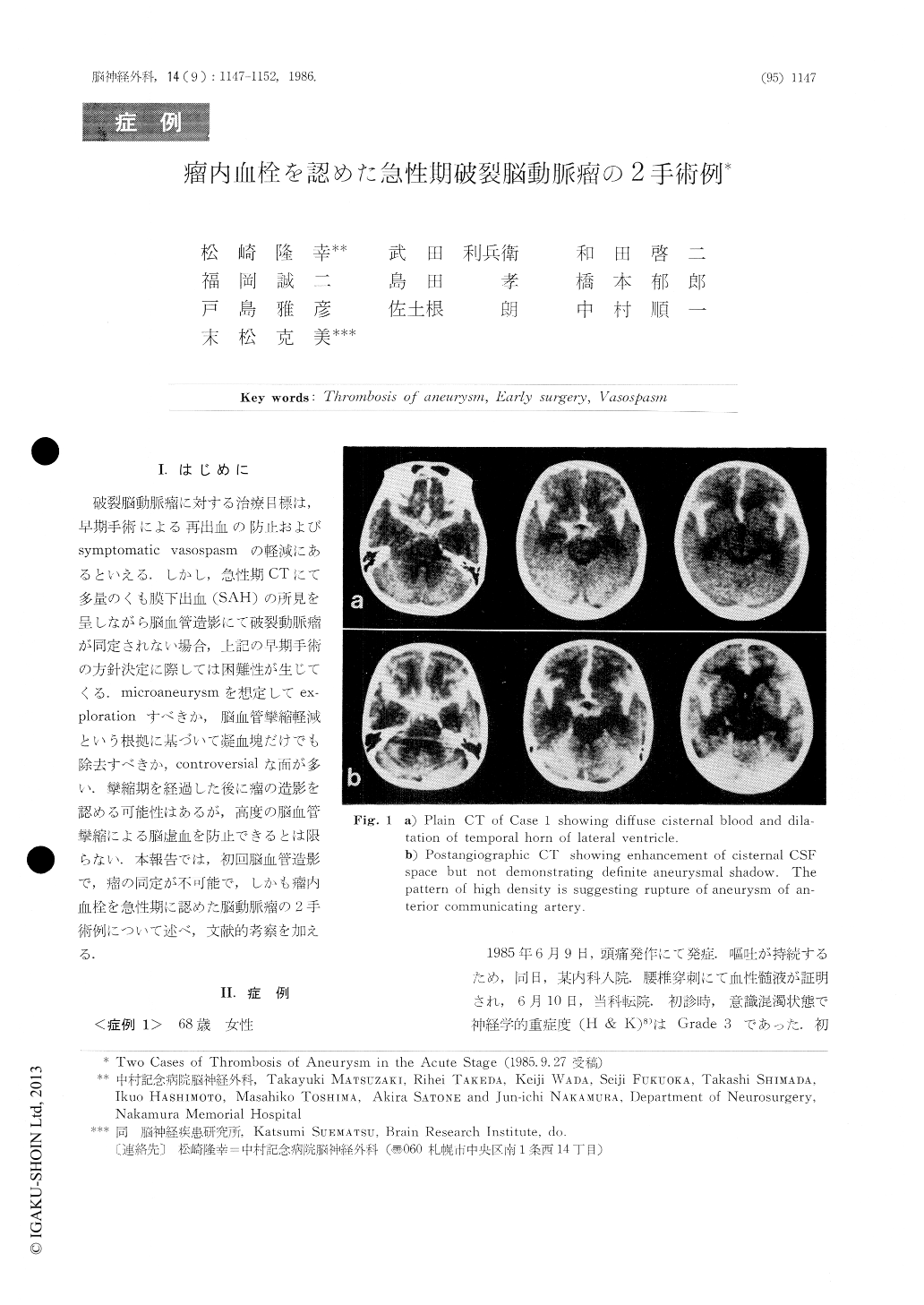
破裂脳動脈瘤に対する治療目標は,早期手術による再出血の防止およびsymptomatic vasospasmの軽減にあるといえる.しかし,急性期CTにて多量のくも膜下出血(SAH)の所見を呈しながら脳血管造影にて破裂動脈瘤が同定されない場合,上記の早期手術の方針決定に際しては困難性が生じてくる.microaneurysmを想定してex—plorationすべきか,脳血管攣縮軽減という根拠に基づいて凝血塊だけでも除去すべきか,controversialな面が多い.攣縮期を経過した後に瘤の造影を認める可能性はあるが,高度の脳血管攣縮による脳虚血を防止できるとは限らない.本報告では,初回脳血管造影で,瘤の同定が不可能で,しかも瘤内血栓を急性期に認めた脳動脈瘤の2手術例について述べ,文献的考察を加える.
Thrombus formation within aneurysm is common and has generally been proved to be a slowly pro-gressive phenomenon.
We report two cases of acute completely throm-bosis of aneurysms. The initial angiogram failed to reveal aneurysm and other etiology of suharachnoid hemorrhage. CT revealed diffuse cisternal blood and acute hydrocephalus. We decided to operate on these patients in the acute stage because of the generally-known strict correlation between the amount of cisternal high density on CT and the subsequentdevelopment of vasospasm and ischemic event.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


