Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
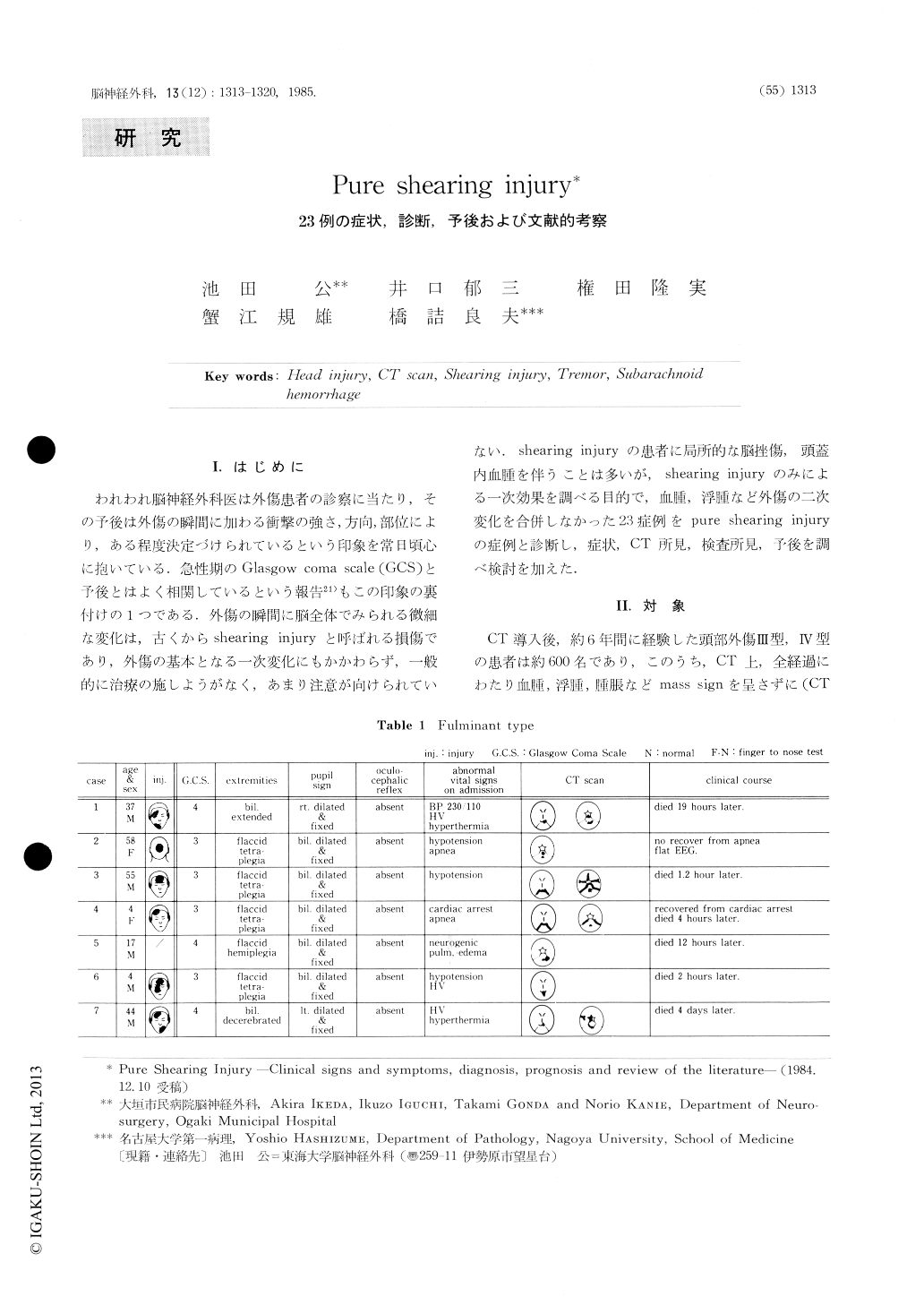
われわれ脳神経外科医は外傷患者の診察に当たり,その予後は外傷の瞬間に加わる衝撃の強さ,方向,部位により,ある程度決定づけられているという印象を常日頃心に抱いている.急性期のGlasgow coma scale(GCS)と予後とはよく相関しているという報告21)もこの印象の裏付けの1つである.外傷の瞬間に脳全体でみられる微細な変化は,古くからshearing injuryと呼ばれる損傷であり,外傷の基本となる一次変化にもかかわらず,一般的に治療の施しようがなく,あまり注意が向けられていない.shearing injuryの患者に局所的な脳挫傷,頭蓋内血腫を伴うことは多いが,shearing injuryのみによる一次効果を調べる目的で,血腫,浮腫など外傷の二次変化を合併しなかった23症例をpure shearing injuryの症例と診断し,症状,CT所見,検査所見,予後を調べ検討を加えた.
In some of the brains of head injury, shearing of axons and vessels caused by direct impact is seen widely in the white matter. This type of injury is designated by neuropathologists as shear injury or diffuse damage of impact type. Macroscopic lesions adjacent to the superior cerebeller peduncle and le-sions of the corpus callosum are commonly seen in the brains with severe shearing injuries and the former is detected by CT scan as a high density at the quadrigeminal cistern, and this indicates occur-rence of a severe shearing injury. Among 600 patients with head injuries, we managed 23 cases with pure shearing injury.
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


