Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
後頭蓋窩動静脈奇形(以下AVM)といっても,小脳の各部から脳幹に至るまで種々の部位のAVMがあるが,このうち脳幹内部に主座を持つものは手術の対象とならない.個々の部位の手術のすべてを論ずることはできないので,代表的な3つの部位のAVMの平均的症例を取出し,簡単に手術手技の要点を述べることにする.
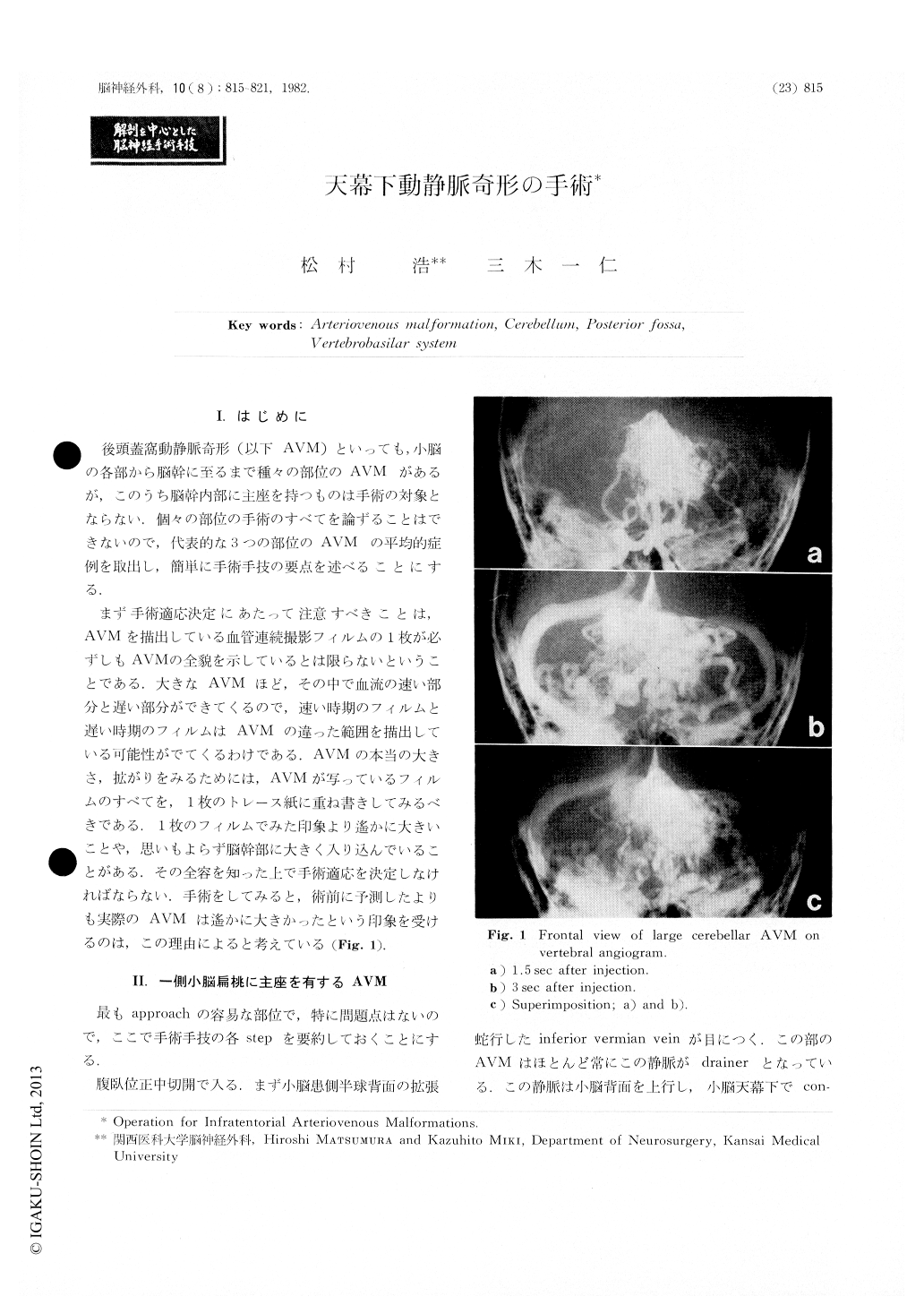
まず手術適応決定にあたって注意すべきことは,AVMを描出している血管連続撮影フィルムの1枚が必ずしもAVMの全貌を示しているとは限らないということである,大きなAVMほど,その中で血流の速い部分と遅い部分ができてくるので,速い時期のフィルムと遅い時期のフィルムはAVMの違った範囲を描出している可能性がでてくるわけである.AVMの本当の大きさ,拡がりをみるためには,AVMが写っているフィルムのすべてを,1枚のトレース紙に重ね書きしてみるべきである.1枚のフィルムでみた印象より遙かに大きいことや,思いもよらず脳幹部に大きく入り込んでいることがある.その全容を知った上で手術適応を決定しなければならない.手術をしてみると,術前に予測したよりも実際のAVMは遙かに大きかったという印象を受けるのは,この理由によると考えている(Fig.1).
Concerning infratentorial AVMs in three representativelocalizations, their surgical approaches, technical standardsand technical difficulties were described and discussed.
At the beginning, our opinion emphasized that feedingarteries should be divided into parent feeders and properfeeders. Parent arteries are anatomically normal ones evenif dilated by the presence of peripheral shunt. Properfeeders, however, supply only AVMs without perfusingany normal brain tissues. Draining veins were also dividedinto two, parent drainers and proper drainers.
Copyright © 1982, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.