Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
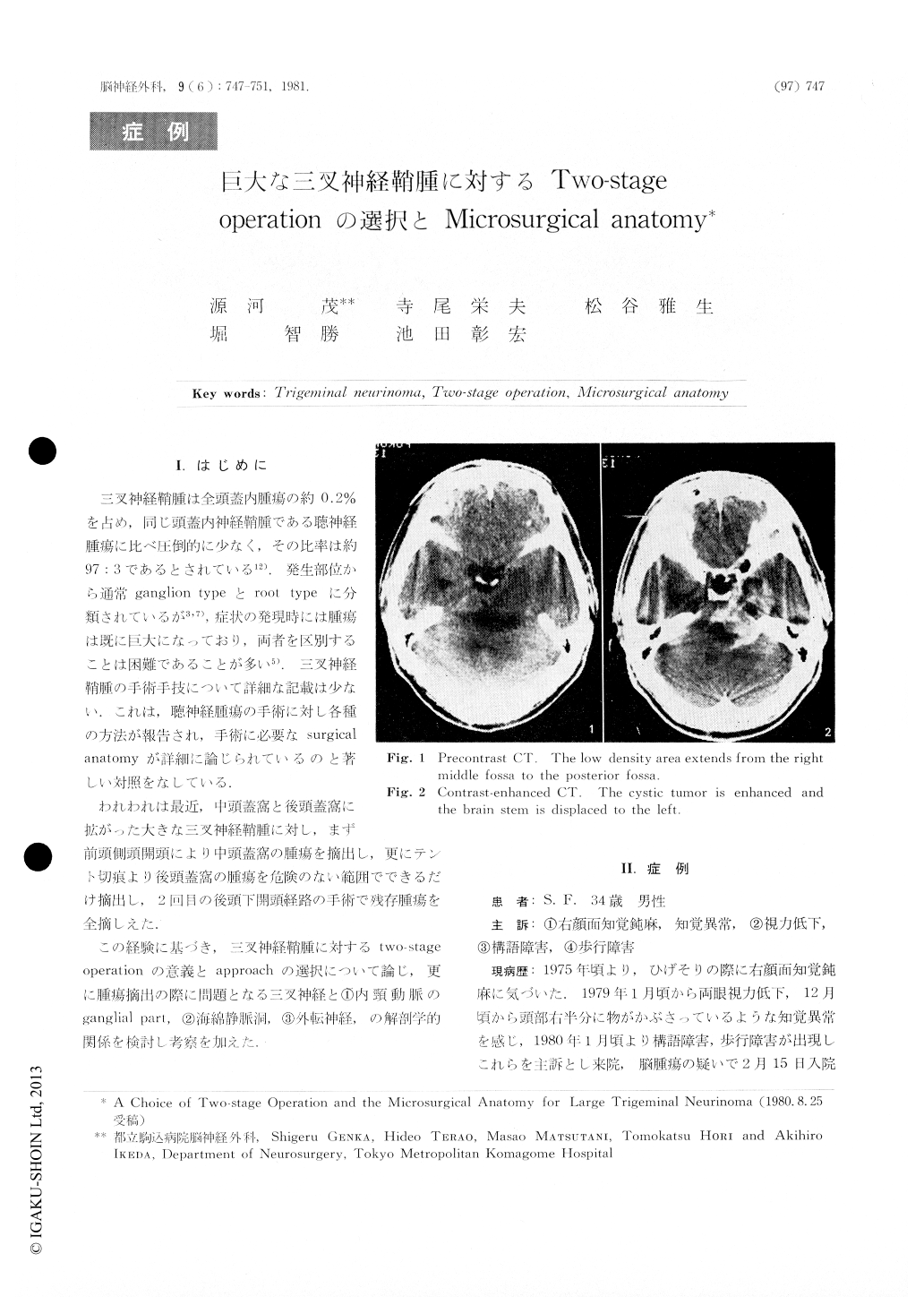
三叉神経鞘腫は全頭蓋内腫瘍の約0.2%を占め,同じ頭蓋内神経鞘腫である聴神経腫瘍に比べ圧倒的に少なく,その比率は約97:3であるとされている12).発生部位から通常ganglion typeとroot typeに分類されているが福,症状の発現時には腫瘍は既に巨大になっており,両者を区別することは困難であることが多い5).三叉神経鞘腫の手術手技について詳細な記載は少ない.これは,聴神経腫瘍の手術に対し各税の方法が報告され,手術に必要なsurgical anatomyが詳細に論じられているのと著しい対照をなしている.
われわれは最近,中頭蓋窩と後頭蓋窩に拡がった大きな三叉神経鞘腫に対し,まず前頭側頭開頭により中頭蓋窟の腫瘍を摘出し,更にテント切痕より後頭蓋窩の腫瘍を危険のない範囲でできるだけ摘出し,21回目の後頭下開頭経.路の手術で残存腫瘍を全摘しえた.
この経験に基づき,三叉神経鞘腫に対するtwo-stageoperationの意義とapproachの選択について論じ,更に腫瘍摘出の際に問題となる三叉神経と①内頸動脈のganglial part,②海綿静脈洞,③外転神経,の解剖学的関係を検討し考察を加えた.
A large trigeminal neurinoma extending from the middle fossa to the posterior fossa was successfully removed by a twostage operation. The benefit of twostage operation for this type of trigeminal neurinoma is discussed and microsurgical anatomy useful for this operation is described.
Case report. A 34-year-old man was admitted because of right facial numbness, unstable gait and visual disturbance. Neurological examination revealed right trigeminal palsy, horizontal nystagmus, left pyramidal tract signs and choked discs.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


