Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
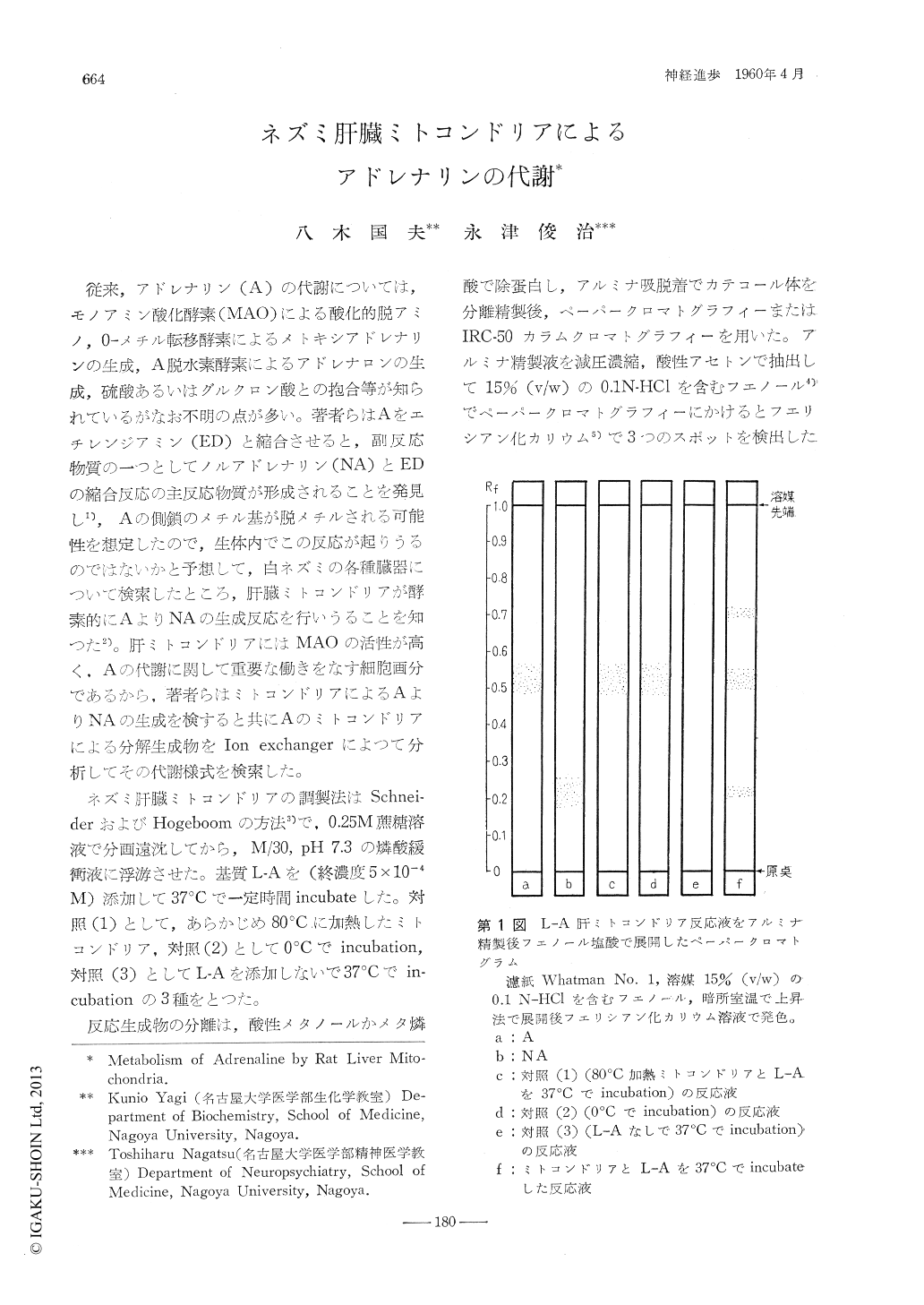
従来,アドレナリン(A)の代謝については,モノアミン酸化酵素(MAO)による酸化的脱アミノ,0-メチル転移酵素によるメトギシアドレナリンの生成,A脱水素酵素によるアドレナロンの生成,硫酸あるいはグルクロン酸との抱合等が知られているがなお不明の点が多い。著者らはAをエチレンジアミン(ED)と縮合させると,副反応物質の一つとしてノルアドレナリン(NA)とEDの縮合反応の主反応物質が形成されることを発見し1),Aの側鎖のメチル基が脱メチルされる可能性を想定したので,生体内でこの反応が起りうるのではないかと予想して,白ネズミの各種臓器について検索したところ,肝臓ミトコンドリアが酵素的にAよりNAの生成反応を行いうることを知つた2)。肝ミトコンドリアにはMAOの活性が高く,Aの代謝に関して重要な働きをなす細胞画分であるから,著者らはミトコンドリアによるAよりNAの生成を検すると共にAのミトコンドリアによる分解生成物をIon exchangerによつて分析してその代謝様式を検索した。
ネズミ肝臓ミトコンドリアの調製法はSchneiderおよびHogeboomの方法3)で,0.25M蔗糖溶液で分画遠沈してから,M/30,pH 7.3の燐酸緩衝液に浮游させた。
The metabolism of L-adrenaline by rat livermitochondria has been studied. L-Adrenaline wasincubated with rat liver mitochondria in M/30, PH 7.3 phosphate buffer at 37℃ for 60min. Afterextraction with acid methanol, the catechol derivatives were purified by alumina adsorption, andthe eluate was analyzed by the following threemethods: (1) IRC-50 column chromatography, (2) paper chromatography, and (3) paper chromatography after condensation with ethylenediamine. The following three control experimentswere carried out in the same way: (1) heatedmitochondria, (2) incubation at 0℃, and (3)without the addition of adrenaline.
When the alumina eluate was analyzed by IRC-50 column chromatography, 8 peaks were Observedby the estimation of absorbance at 279 mμ. Among 4 peaks in acid and neutral fractions, thefirst peak was identified with 3,4-dihydroxymandelic acid (formed by aldehyde oxidase from 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl glycolic aldehyde), and thesecond peak was supposed to be 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl glycolic aldehyde (formed by monoamineoxidase from adrenaline). Among 4 peaks in basicfraction, the first peak was adrenaline (addedsubstrate), and the second peak existed at theposition of noradrenaline. A portion of the secondpeak was condensed with ethylenediamine, andthe condensate was the same as that of noradrenaline, when tested by paper chromatography orpaper electrophoresis. Another portion of thesecond peak was tested with trihydroxyindolereaction after oxidation at pH 6.0, and it producedstrong fluorescent substance. By these examinations, this substance was identified with noradrenaline.
The paper chromatography of the alumina eluateusing phenol containing 15% (v/w) 0.1 N-HCl assolvent showed 3 spots when the paper strips werecolored with K3Fe (CN)6 The spot at Rf 0.52was adrenaline. The spot at Rf 0.70 was determined to be 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl glycolic aldehyde. The spot at Rf 0.21 had the same Rf valueas that of noradrenaline, and it produced fluorescent substance when treated with ethylenediaminemethod or trihydroxyindole reaction.
The paper chromatography of the ethylenediamine condensates of the alumina eluate using 5%Na2HPO4・12H2O as solvent showed the same results. Yellow fluorescent spot at Rf 0.37 was themain condensate of adrenaline. Bluish greenfluorescent spot at Rf 0.09 was found to be derivedfrom 3 substrances : (1) side condensate of adrenaline formed during condensation reaction, (2)main condensate of noradrenaline which was enzymatically formed from adrenaline, (3) maincondensate of 3,4-dihydroxymandelic acid whichwas also formed enzymatically.
These results showed the formation of noradrenaline from adrenaline by rat liver mitochondria, besides the formation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycolic aldehyde, 3,4-dihydroxymandelic acid andothers.
Copyright © 1960, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


