Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
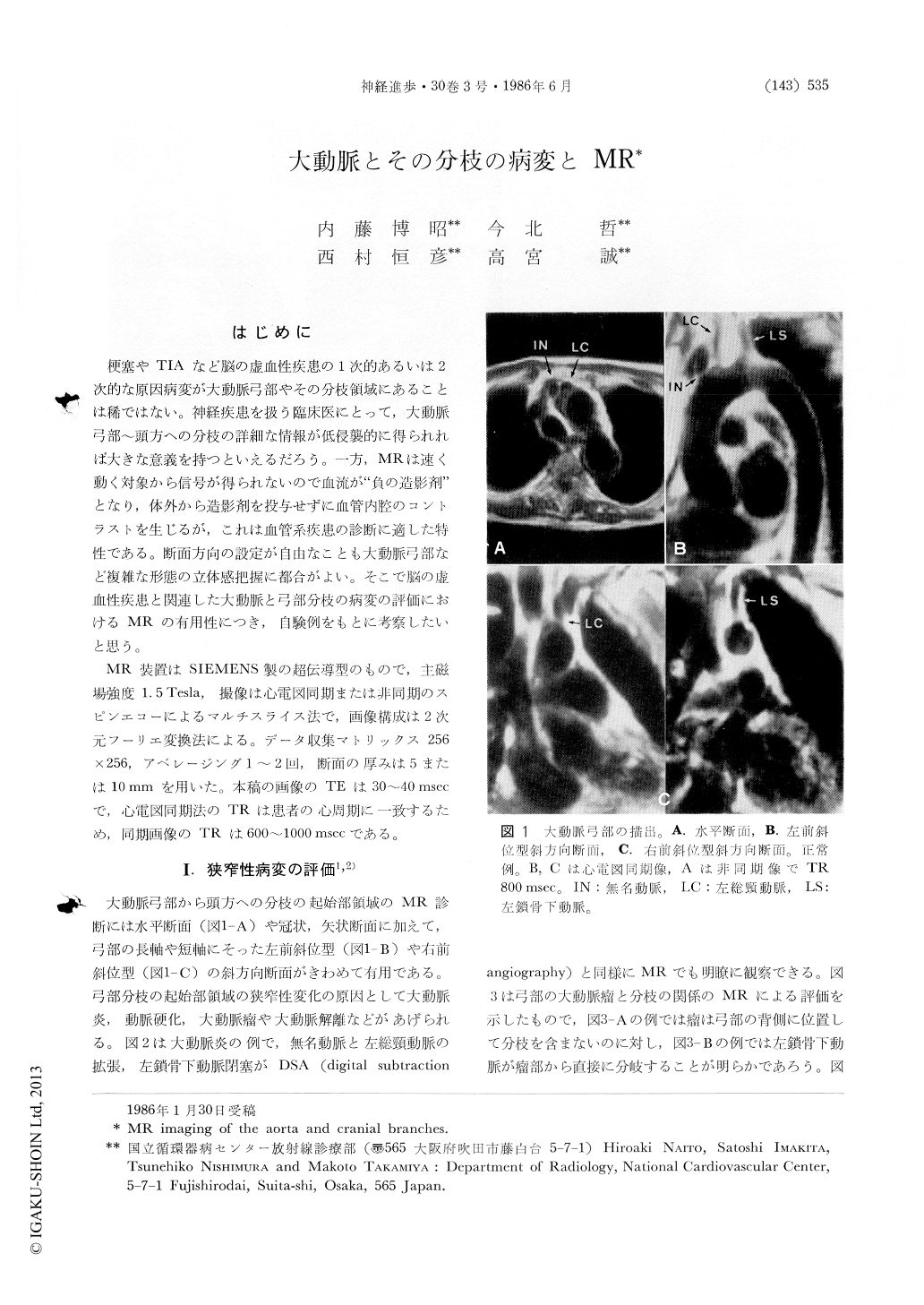
はじめに
梗塞やTIAなど脳の虚血性疾患の1次的あるいは2次的な原因病変が大動脈弓部やその分枝領域にあることは稀ではない。神経疾患を扱う臨床医にとって,大動脈弓部〜頭方への分枝の詳細な情報が低侵襲的に得られれば大きな意義を持つといえるだろう。一方,MRは速く動く対象から信号が得られないので血流が"負の造影剤"となり,体外から造影剤を投与せずに血管内腔のコントラストを生じるが,これは血管系疾患の診断に適した特性である。断面方向の設定が自由なことも大動脈弓部など複雑な形態の立体感把握に都合がよい。そこで脳の虚血性疾患と関連した大動脈と弓部分枝の病変の評価におけるMRの有用性につき,自験例をもとに考察したいと思う。
MR装置はSIEMENS製の超伝導型のもので,主磁場強度1.5Tesla,撮像は心電図同期または非同期のスピンエコーによるマルチスライス法で,画像構成は2次元フーリエ変換法による。データ収集マトリックス256×256,アベレージング1〜2回,断面の厚みは5または10mmを用いた。本稿の画像のTEは30〜40 msecで,心電図同期法のTRは患者の心周期に一致するため,同期画像のTRは600〜1000 msecである。
Usefulness of MR is discussed in this article regarding the evaluation of pathoanatomy or pathophysiology of the aorta and cranial branches related to ischemic cerebrovascular diseases. MR imaging studies were performed utilizing 1.5 Tesla superconductive system. Spin-echo mutislice technique was employed with or without ECG-gated data acquisition.
1) Assessment of obstructive change in cranial branches
MR accurately demonstrated anatomy of the aortic arch. Obstruction of cranial branches owing to the diseases of aortic arch such as aortitis, aneurysm and dissection was clearly delineated, especially in right anterior or left anterior oblique imaging planes. Cervical vessels were also well visualized. Stenotic change of carotid and vertebral arteries could be detectable with MR.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


