Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
この症候群は,1869年にその臨床像を詳しく報告したスイスの眼科医Johann Friedrich Hornerの名をとってHorner症候群とよばれているが,彼以前にもいくつかの報告がみられる。最初に報告をしたのはフランスの外科医Pourfour du Petitであるといわれている。彼は錐体交叉を実際上明らかにした最初の人としても知られているが,1727年に肋間神経に関する論文の中で,今日Horner症候群として知られている症候群を初めて記載した。現在Pourfour du Petit症候群というと逆Horner症候群を指すが,実際にはHorner症候群こそが彼の名を冠してよばれるべきであったのである。1838年にHareは腕神経叢への癌浸潤により本症候群を呈した1例を報告し,また1863年にWeir-Mitchell,MorehouseならびにKeenは頸部の弾創による頸部交感神経損傷により,一側の眼瞼下垂,縮瞳,同側顔面の無汗症を呈した一兵士例を報告した。実験的にはこれより先の1852年にBcrnardがウサギを使った実験で交感神経損傷により本症候群が起こることを証明した。Horncr6)が"Ubereine Form von Ptosis"という論文でこの症状を詳しく記載したのはその後であるが,それ以後この症候群はよく知られるようになり,一般にHorner症候群とよばれるようになった。
Horner's syndrome is one of the most famous physical sign due to damage to the cervical sympathetic pathway. The cardinal features are miosis, narrowing of the palpebral fissure and enophthalmos, often associated with anhidrosis, ocular hypotonicity, hyperemia of the conjunctiva and others.
This syndrome bears the name of Johann Friedrich Horner, the Swiss ophthalmologist, who described it in detail in 1869. But the first clinical description of this syndrome was made by French surgeon Pourfour du Petit as early as in 1727. In 1852, this syndrome was described in experimental animals by Claude Bernard.
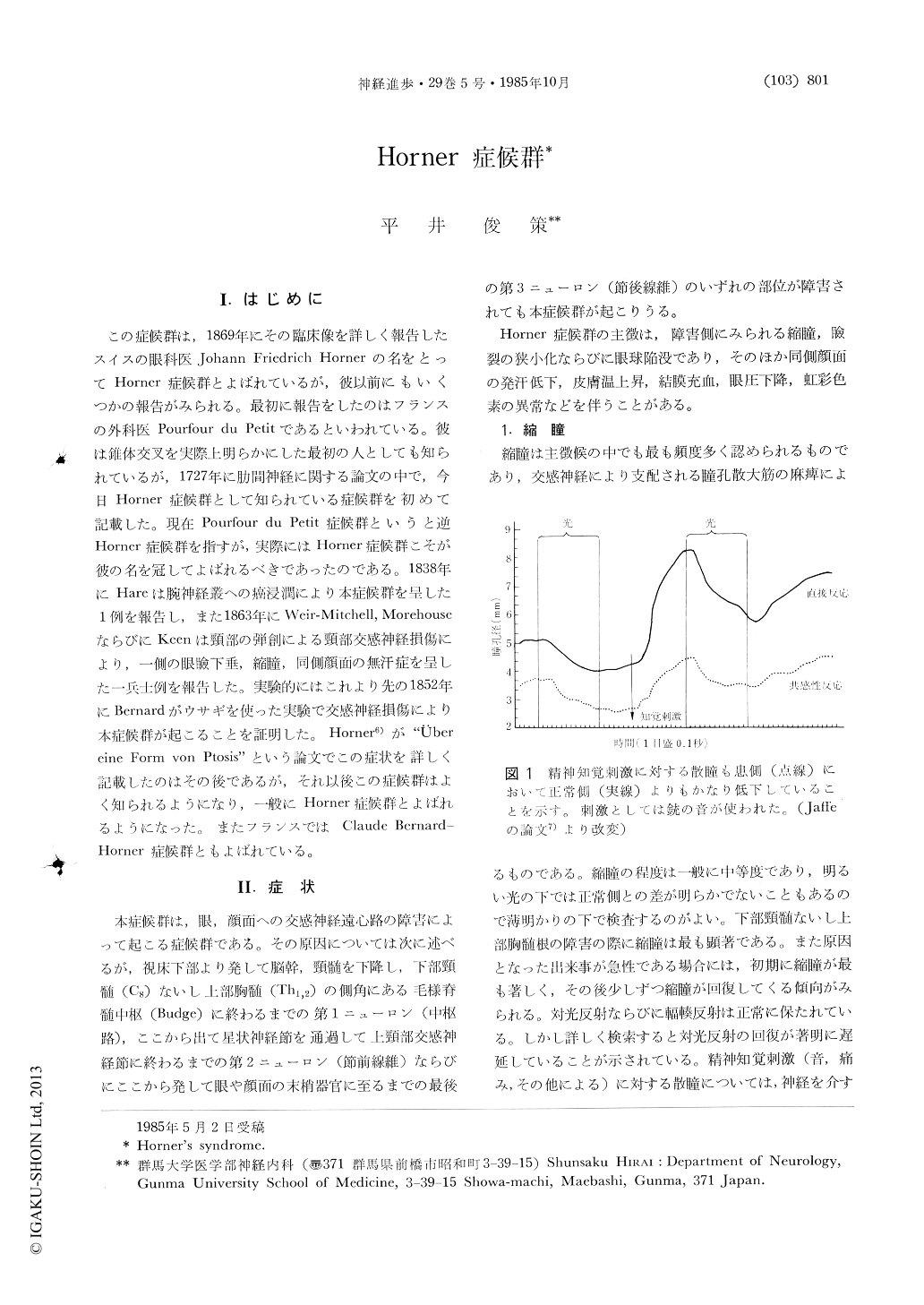
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


