Japanese
English
特集 瞳孔のすべて
交代性Horner症候群
Alternating Horner syndrome
古川 哲雄
1
Tetsuo FURUKAWA
1
1東京医科歯科大学医学部神経内科
1Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Tokyo Medical and Dental University
pp.811-816
発行日 1985年10月10日
Published Date 1985/10/10
DOI https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1431905736
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
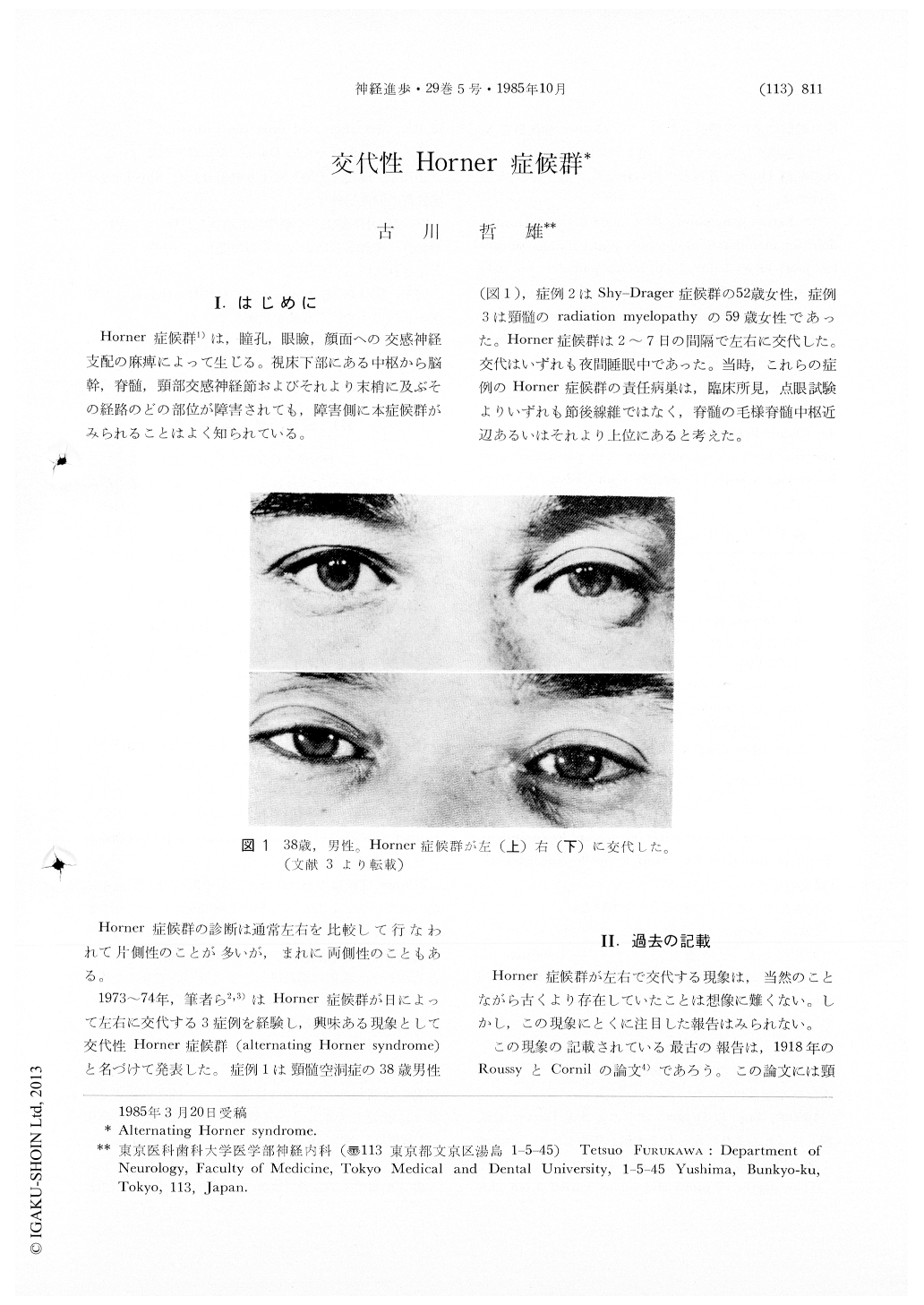
Horner症候群1)は,瞳孔,限瞼,顔面への交感神経支配の麻痺によって生じる。視床下部にある中枢から脳幹,脊髄,頸部交感神経節およびそれより末梢に及ぶその経路のどの部位が障害されても,障害側に本症候群がみられることはよく知られている。
Horner症候群の診断は通常左右を比較して行なわれて片側性のことが多いが,まれに両側性のこともある。
Abstract
Horner syndrome is due to ipsilateral sympathetic nerve interruption to the eye and face. Although it is usually unilaterally, and rarely bilaterally, observed, Horner syndrome may alternate from one side to the other. This phenomenon is called alternating Horner syndrome.
Reported cases of alternating Horner syndrome in the literature were reviewed and the pathogenesis and the mechanism of the phenomenon were discussed.
Thirtyone cases were recorded in the literature.
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


