Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
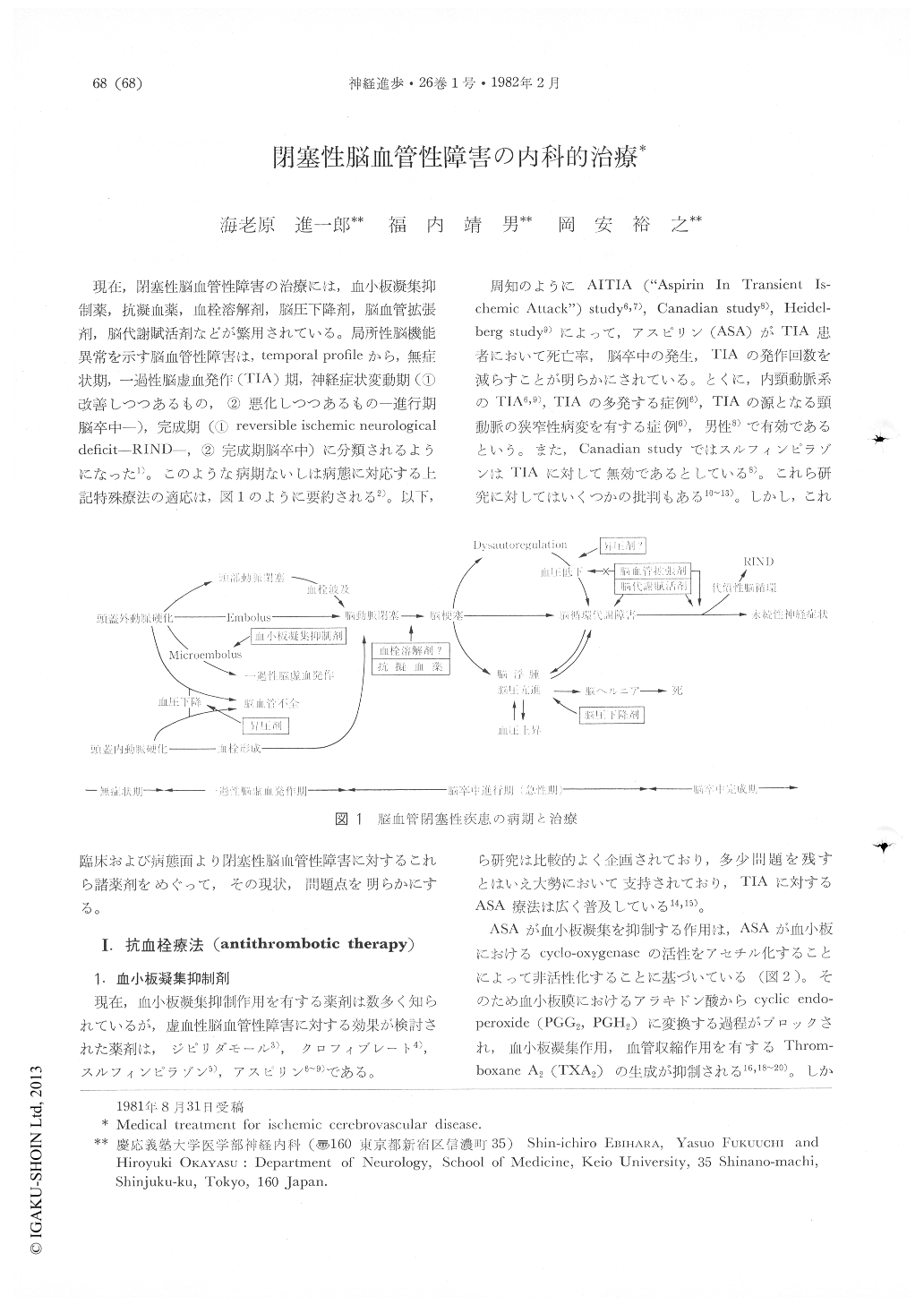
現在,閉塞性脳血管性障害の治療には,血小板凝集抑制薬,抗凝血薬,血栓溶解剤,脳圧下降剤,脳血管拡張剤,脳代謝賦活剤などが繁用されている。局所性脳機能異常を示す脳血管性障害は,temporal profileから,無症状期,一過性脳虚血発作(TIA)期,神経症状変動期(①改善しつつあるもの,②悪化しつつあるもの—進行期脳卒中—),完成期(①reversible ischemic neurologicaldeficit-RIND-,②完成期脳卒中)に分類されるようになった1)。このような病期ないしは病態に対応する上記特殊療法の適応は,図1のように要約される2)。以下,臨床および病態面より閉塞性脳血管性障害に対するこれら諸薬剤をめぐって,その現状,問題点を明らかにする。
The clinical stage (temporal profil) of ischemic stroke contain a number of categories, including transient ischemic attack (TIA), progressing stroke (stroke in evolution), reversible ischemic neurological deficit (RIND), and completed stroke. The pathogenesis of TIA falls into two major categories, microembolic and hemodynamic. Microemboli have been to consist mainly of agglutinated thrombocytes at autopsy examination. The emboli most commonly originate from the extracranial neck vessels. Aspirin is the first choice for the treatment of TIA.
Copyright © 1982, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


